A high-temperature oxidation-resistant readout circuit lead-out electrode and its preparation method
A technology that resists high temperature oxidation and reads out circuits, and is used in circuits, electrical components, and final product manufacturing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
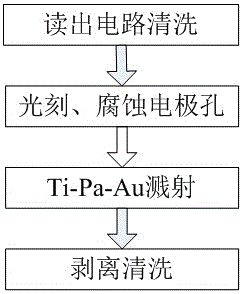
[0030] like figure 1 As shown, a preparation method of a high-temperature oxidation-resistant readout circuit lead-out electrode comprises the following steps:
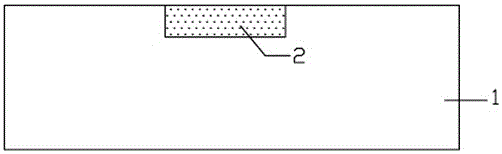
[0031] Step a, readout circuit cleaning: if figure 2 As shown, after the readout circuit 1 is taped out from a silicon factory, the lead-out electrode is an Al metal layer 2 . The readout circuit 1 is used as the substrate, and it is firstly cleaned: each is washed three times with toluene, acetone, and ethanol in sequence, and the residual solution is blown dry with a nitrogen gun.
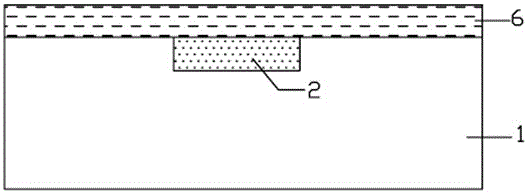
[0032] Step b, photolithography and etching electrode holes: on the readout circuit 1, apply photoresist AZ6130 at a speed of 3500 rpm for 30 seconds, the thickness of the coating is 2 μm, and the coating time is 30 seconds, and then at 80 ° C Pre-bake for 2 minutes to form a photoresist layer 6, such as image 3 shown. Use a photolithography machine to expose, use AZ300MIF developer to develop, and control the development time, so...
Embodiment 2
[0037] like figure 1 As shown, a preparation method of a high-temperature oxidation-resistant readout circuit lead-out electrode comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step a, readout circuit cleaning: if figure 2 As shown, after the readout circuit 1 is taped out from a silicon factory, the lead-out electrode is an Al metal layer 2 . The readout circuit 1 is used as the substrate, and it is firstly cleaned: each is washed three times with toluene, acetone, and ethanol in sequence, and the residual solution is blown dry with a nitrogen gun.
[0039] Step b, photolithography and etching electrode holes: on the readout circuit 1, apply photoresist AZ6130 for 30 seconds at a speed of 2500 rpm, with a coating thickness of 3 μm, and then pre-bake at 80°C for 3 minutes to form photoresist layer 6, such as image 3 shown. Use a photolithography machine to expose, use AZ300MIF developer to develop, and control the development time, so that the photoresist in the electrode hole ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] like figure 1 As shown, a preparation method of a high-temperature oxidation-resistant readout circuit lead-out electrode comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step a, readout circuit cleaning: if figure 2 As shown, after the readout circuit 1 is taped out from a silicon factory, the lead-out electrode is an Al metal layer 2 . The readout circuit 1 is used as the substrate, and it is firstly cleaned: each is washed three times with toluene, acetone, and ethanol in sequence, and the residual solution is blown dry with a nitrogen gun.
[0046] Step b, photolithography and etching electrode holes: on the readout circuit 1, apply photoresist AZ6130 at a speed of 2800 rpm for 30 seconds, with a coating thickness of 2.5 μm, and then pre-bake at 80°C for 2.5 minutes, Form a photoresist layer 6, such as image 3 shown. Use a photolithography machine to expose, use AZ300MIF developer to develop, and control the development time, so that the photoresist in the electrode h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com