A surgical device for ophthalmic surgery
A surgical device and ophthalmic surgery technology, applied in ophthalmic surgery and other directions, can solve the problems of limited development and popularization, difficult to guarantee the surgical effect, easy loosening of the top pressure material, etc., to prevent the implantation position from being skewed, and the surgical effect to be stable and reliable. , to avoid the effect of squeezing the optic nerve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
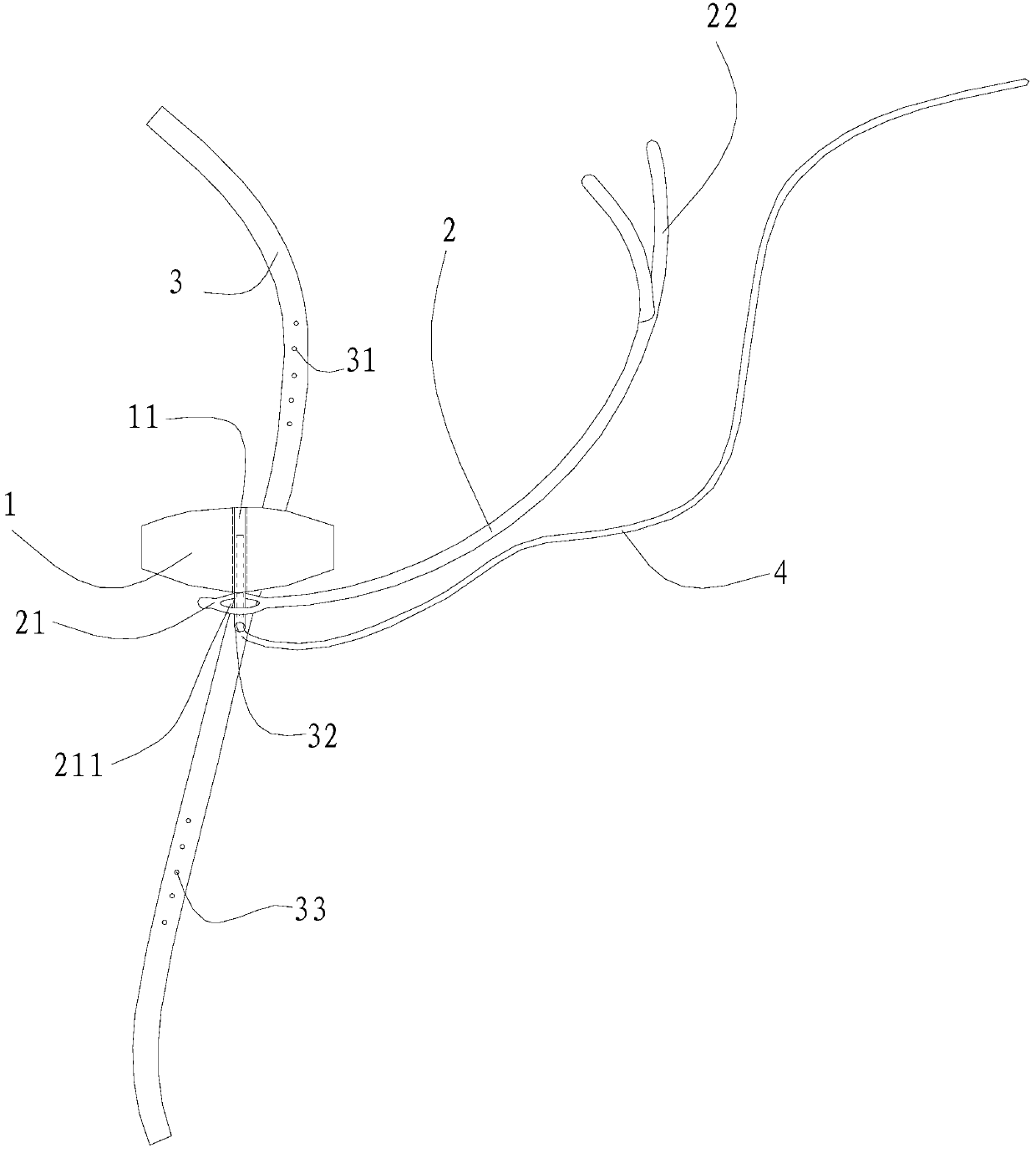
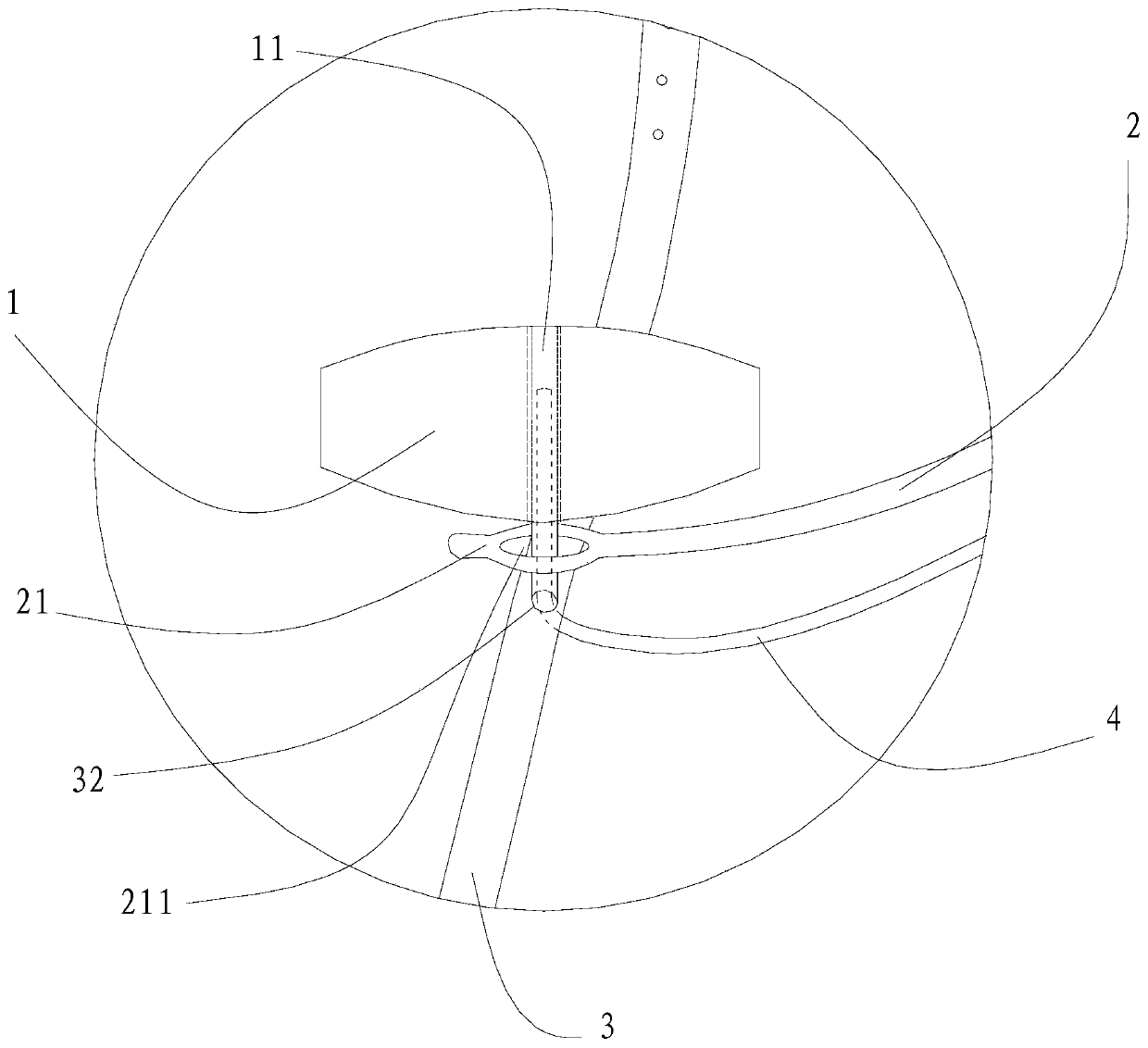
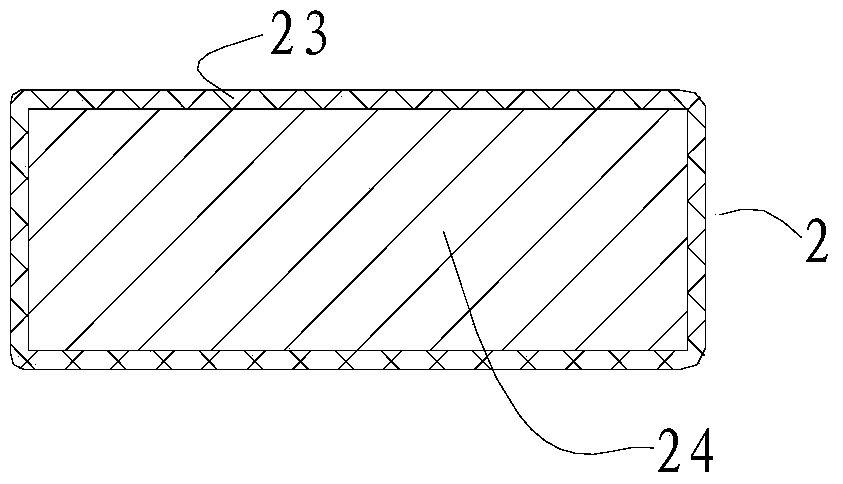
[0054] In the surgical device used in this embodiment, the pressing material 1 has a circular cross-section, an area of 28 square millimeters, and a height of 2 millimeters. The pressing material 1 is silica gel. The arc-shaped stent body 24 is titanium, and the coated biocompatible material layer 23 is silica gel. The length of the arc support 2 is 23 millimeters. The suture end 22 of the arc-shaped support 2 is a detachable segmental structure.
[0055] The use method of the surgical device for the above-mentioned ophthalmic surgery comprises the following steps: A. Put the surgical device under the temporal fascia sac of the eyeball, make the arc-shaped support 2 perpendicular to the limbus 54, and make the top pressure end 21 of the arc-shaped support 2 Place it on the posterior pole 55 of the eyeball, and make the suture end 22 of the arc-shaped support 2 parallel to the limbus 54; B. Cross one end of the traction strip 3 across the lateral rectus muscle and the infer...
Embodiment 2
[0062] As the surgical device described in Example 1, the cross-section of the pressing material 1 is petal-shaped (three petals), the maximum diameter is 11 mm, the cross-sectional area is 90 square mm, and the height is 3 mm. The pressing material 1 is silicon sponge. The arc-shaped stent body 24 is made of stainless steel, and the coated biocompatible material layer 23 is made of silica gel. The length of the arc support 2 is 21 millimeters. The suture end 22 of the arc-shaped support 2 is a detachable segmental structure. No light guide fiber 4 is attached to the top pressure end 21, and the position and height of the macular bulge are observed during the operation with the aid of an indirect ophthalmoscope. Other implementation steps are as embodiment 1.
[0063] Operation implementation: high myopia patient, male, 44 years old, left eye axis 27.5 mm, left eye macular splitting, macular retinal partial detachment, best corrected visual acuity 0.5 before operation, best...
Embodiment 3
[0065] As for the surgical device described in Example 1, the cross-section of the pressing material 1 is polygonal, the cross-sectional area is 52 square millimeters, and the height is 6.5 millimeters. The pressing material 1 is silicon sponge. The arc-shaped stent body 24 is titanium, and the coated biocompatible material layer 23 is silica gel. The length of the bracket 2 is 28 mm. The suture end 22 of the arc-shaped bracket 2 is Y-shaped, and is directly sutured on the corresponding part of the eyeball. Other implementation steps are as embodiment 1.
[0066] Operation implementation: high myopia patient, female, 46 years old, left eye axis 32.6 mm, left macular hole, best corrected visual acuity 0.05 before operation, best corrected visual acuity recovered to 0.3 6 months after operation, metamorphopsia The macular hole healed, and the degree of myopia decreased from -18.0Diopter before operation to -12.25Diopter after operation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com