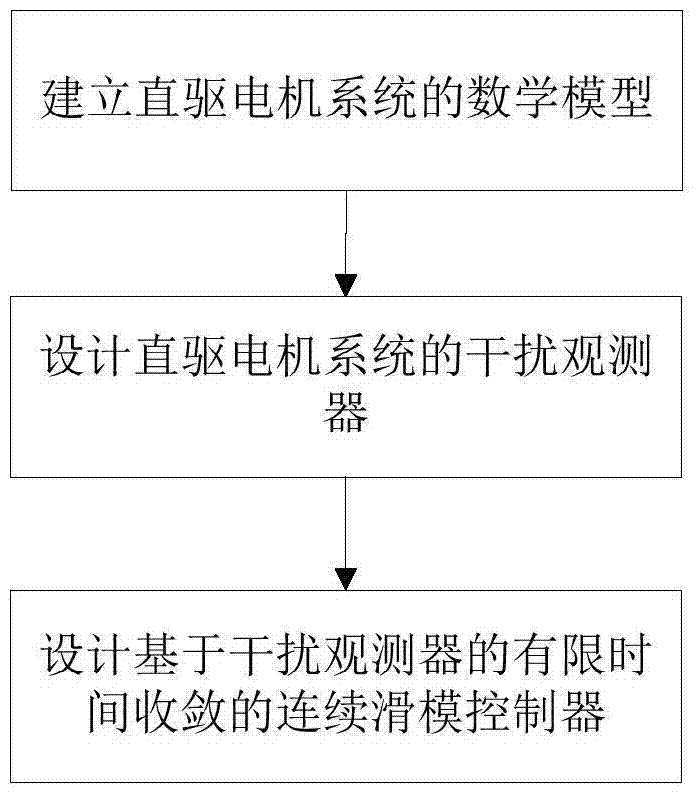
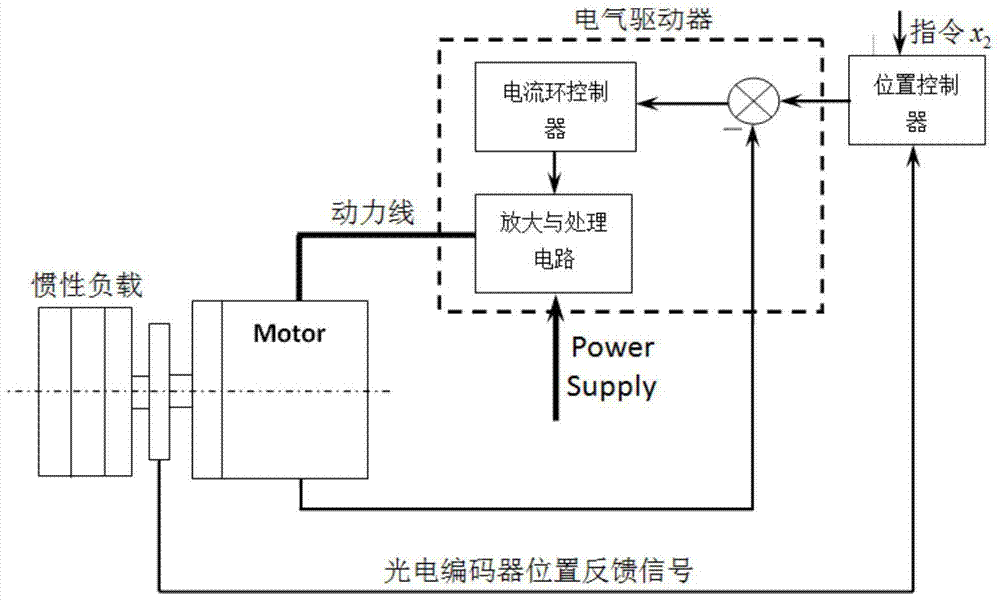
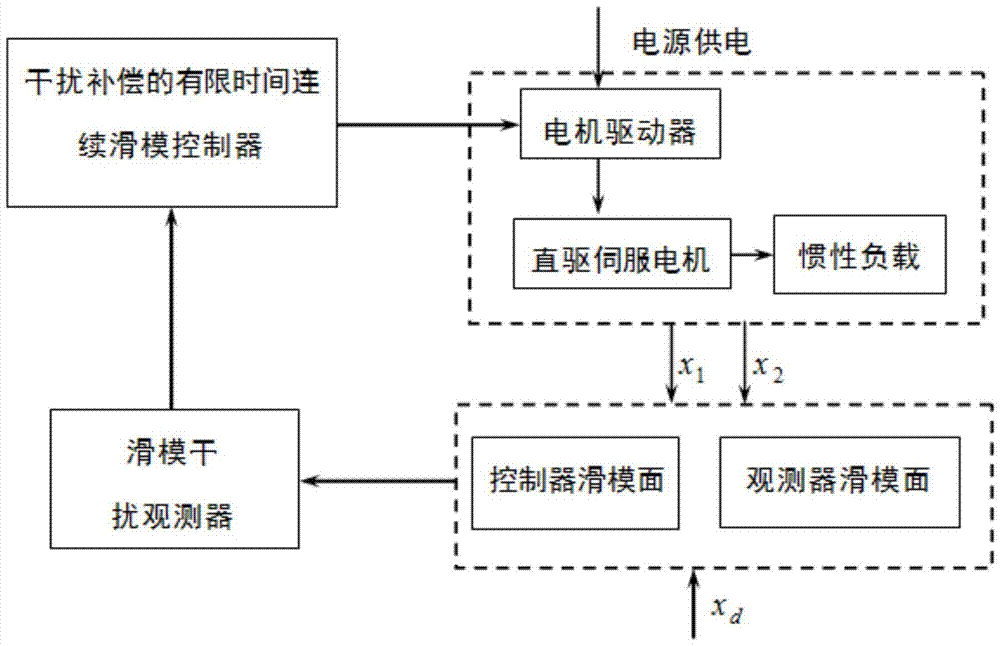
Finite-time continuous sliding mode control method for disturbance compensation of direct drive motor system
A direct-drive motor, limited-time technology, applied in adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., to eliminate observation errors, ensure robustness, and ensure transient control performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0092] In order to assess the performance of the designed controller, the following parameters are taken in the simulation to model the direct drive motor system:
[0093] Inertia load parameter m=0.00026kg m 2 ; Viscous friction coefficient B = 0.00143 m s / rad; Moment amplification factor k u =1.11N·m / V;
[0094] The desired instruction for a given system is: x d =20sin(t)[1-exp(-0.01t 3 )]o;
[0095] Interference level: d(x,t)=(0.1 / 0.00026)sin(0.5πt)[1-exp(-0.01t 3 )] N m.
[0096] Take the following controller for comparison:
[0097] Finite-time stable continuous sliding-mode control (UCFT-SMC) controller for disturbance compensation: taking the disturbance observer parameter k 1 =5000, β 1 =500,ε 1 =0.05,p 1 = 3 and q 1 =5; controller parameter λ 0 =32,λ 1 =36,α 1 =0.25, α 2 =0.4, λ 2 =56,λ 3 =60,α 0 = 0.3.
[0098] Sliding mode controller (SMC): In order to force the system state to reach the sliding mode surface, the selected controller parameter is λ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com