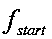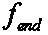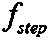Network boundary equivalence method for electromagnetic transient calculation of power grid
An electromagnetic transient calculation and network boundary technology, applied in the value field, can solve problems such as the inability to accurately describe the impedance spectrum characteristics of the external network, the error of electromagnetic transient calculation results, and the electrical connection of split boundary nodes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0068] A network boundary equivalent method for grid electromagnetic transient calculation, comprising the following steps:
[0069] S1. Steps for preset harmonic impedance observation bus: specify the working directory and power flow mode number of the power grid data, and set the starting frequency of frequency scanning f start =50Hz, stop frequency f end =2000Hz, scan step f step =10Hz. Set the harmonic impedance observation bus, such as Figure 8 The buses YUL, LANCJ and BANGD shown are harmonic impedance observation buses.
[0070] S2. The step of presetting the equivalence boundary: setting the initial equivalence boundary, such as Figure 8 Line LANCJ-BAT shown.
[0071] S3. The step of obtaining the basic parameters of the harmonic admittance matrix: sequentially read the busbar, line, transformer, generator, reactive power compensation, load input situation and power frequency parameters corresponding to the specified power flow mode number in the PSASP progra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com