Tilting-pad bearing used for rotors
A rotor and bearing technology, applied in the field of bearings, can solve the problems of easy formation of negative pressure, weakened pad stability, and increased gap between pads and rotors, preventing irregular swings, preventing oil film instability, and increasing stability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
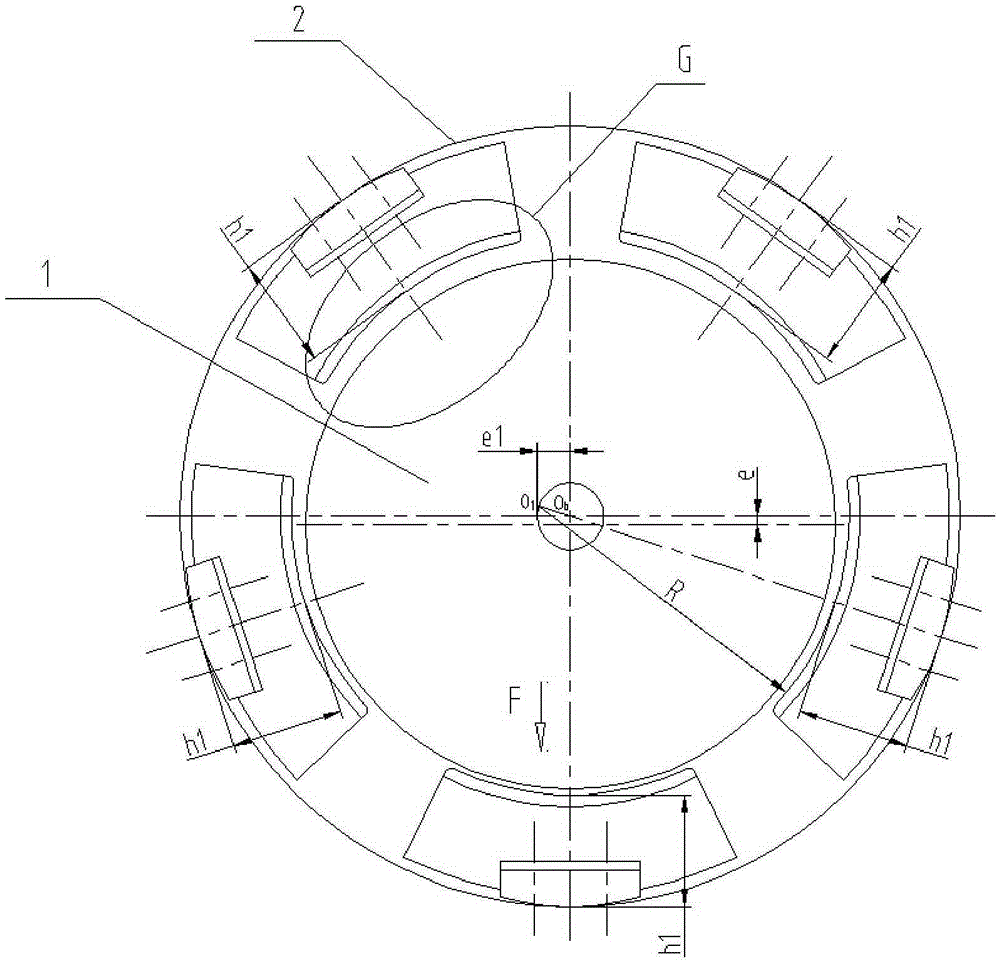
[0026] Such as Image 6 Shown: a tilting pad bearing for a rotor, including a housing 2, several load-bearing pads 3 and several non-load-bearing pads 4, the non-load-bearing pads 4 are provided with a device for connecting the rotor 1 to the corresponding The non-bearing tiles 4 maintain balance and stability and are used to adjust the first gasket 5 of the preload value of the non-bearing tiles 4; the bearing tiles 3 are provided with a balance and For a stable second gasket 6 , the thickness of the first gasket 5 is greater than that of the second gasket 6 .
[0027] When there are five radial pad bearings and the load acts on the pads, the number of bearing pads 3 is 3, and the number of non-loading pads 4 is 2;
[0028] A second gasket 6 is designed on the bearing pad 3 to maintain balance and stability between the rotor 1 and the corresponding bearing pad 3, and a first gasket 5 is designed on the non-bearing pad 4 for both It is used to keep the rotor 1 and the corres...
Embodiment 2
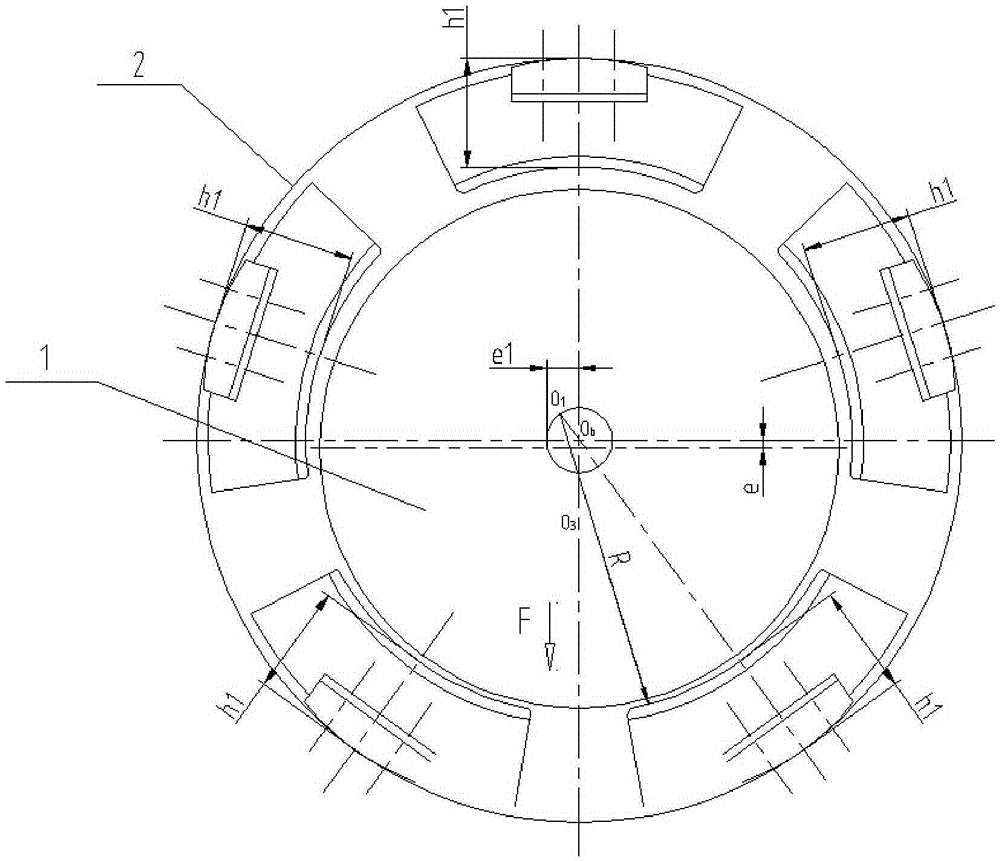
[0034] Such as Figure 7 Shown: This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the only difference is that when there are five radial pad bearings and the load acts between the pads, the number of bearing pads 3 is 2, The number of non-bearing tiles 4 is 3, for the convenience of observation, the Figure 7 The load-bearing tile 3 is marked A, and the three non-bearing tiles are respectively marked B1, B2 and B1 in turn.
[0035] Such as Figure 7 Shown: According to the principle of force distribution, the gap between the non-load bearing pad 4 marked with B1 and the rotor 1 is smaller than the gap between the non-load bearing pad 4 marked with B2 and the rotor 1, then the gap between the non-load bearing pad 4 marked with B2 and the rotor 1 is smaller. Adding the thickness &2 of the first gasket 5 on 4 is larger than adding the thickness &1 of the first gasket 5 on the non-bearing tile 4 marked with B1, and the traditional tile eccentricity is e1 (such as figure 2 s...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Such as Figure 8 Shown: This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the only difference is that when there are 4 pads with radial tilting pad bearings and the load acts between the pads, the number of bearing pads 3 is 2, The number of non-bearing tiles 4 is 2, for the convenience of observation, the attached Figure 8 The bearing tiles 3 and non-bearing tiles 4 are marked accordingly, wherein the bearing tile 3 is marked with A, and the non-bearing tile 4 is marked with B.
[0039] The traditional tile eccentricity is e1 (such as Figure 4 shown), and after adding the first gasket 5 and the second gasket 6, the eccentric distance of the non-bearing pad 4 is e2=e1+&, where & is the thickness of the first gasket 5 minus the second gasket 6 Thickness values (eg Image 6 As shown), after adding the first gasket 5 and the second gasket 6, the eccentricity of the non-load bearing pad 4 increases, so the oil film stiffness and oil film damping between the non...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com