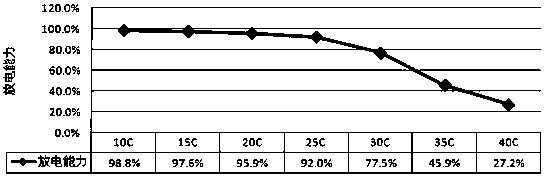
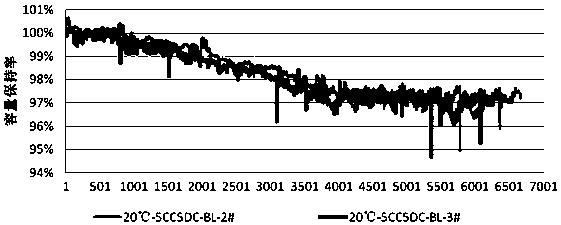
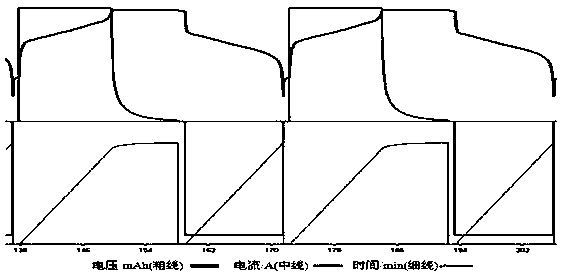
A method for solving the gas failure of lithium titanate battery
A lithium titanate battery, flatulence technology, applied in electrical components, secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of fast charging capability, low probability of defective products, and improved battery discharge power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] A method for solving the flatulence failure of a lithium titanate battery, which sequentially includes a chemical conversion process, an aging process, and a vacuum packaging process. The chemical conversion process uses lithium nickel cobalt manganate / lithium manganate as the positive electrode material, and industrial lithium titanate as the negative electrode Material, the semi-finished battery cell to be formed into the object obtained by compounding, coating, assembling, and adding electrolyte includes the following steps in sequence:
[0052] Step 1: Charge with a constant current of 0.01C for 20 hours, where the cut-off voltage is 1.8V;
[0053] Step 2: Charge with a constant current of 0.1C for 7 hours, where the cut-off voltage is 2.8V;
[0054] Step 3: Charge with 0.2C current constant current for 1h and then sleep for 5min, where the cut-off voltage is 2.8V;
[0055] Step 4: Discharge at a constant current of 0.5C for 3 hours and then sleep for 5 minutes, where the c...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The steps are the same as in Example 1, the difference is:
[0066] In the formation process,
[0067] Step 1: Charge with 0.05C constant current for 4h;
[0068] Step 2: Charge with a constant current of 0.1C for 2h;
[0069] Step 3: Charge at a constant current of 0.3C for 1 hour and then sleep for 5 minutes;
[0070] Step 7: Repeat steps 5 to 6 4 times and then sleep for 5 minutes;
[0071] Step 10: Repeat steps 8 to 9 4 times in a loop;
[0072] In the aging process, the aging temperature is 60°C, and the aging time is 50h.
[0073] In the vacuum packaging process, the vacuum degree inside the battery is -0.09MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0075] The steps are the same as in Example 1, the difference is:
[0076] In the formation process,
[0077] Step 1: Charge with a constant current of 0.1C for 2h;
[0078] Step 2: Charge with 0.2C constant current for 1h;
[0079] Step 3: Charge at a constant current of 0.5C for 1 hour and then sleep for 5 minutes;
[0080] Step 7: Repeat steps 5 to 6 5 times and then sleep for 5 minutes;
[0081] Step 10: Repeat steps 8 to 9 5 times in a loop;
[0082] In the aging process, the aging temperature is 65°C, and the aging time is 24h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com