A method for measuring the geometric parameters of spherical targets using a laser and a monocular camera
A technology of geometric parameters and lasers, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, photogrammetry/video metrology, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately measure the target position, inability to measure spherical targets at close range, etc., and achieve easy implementation on hardware , low cost and simple equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0036] The specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
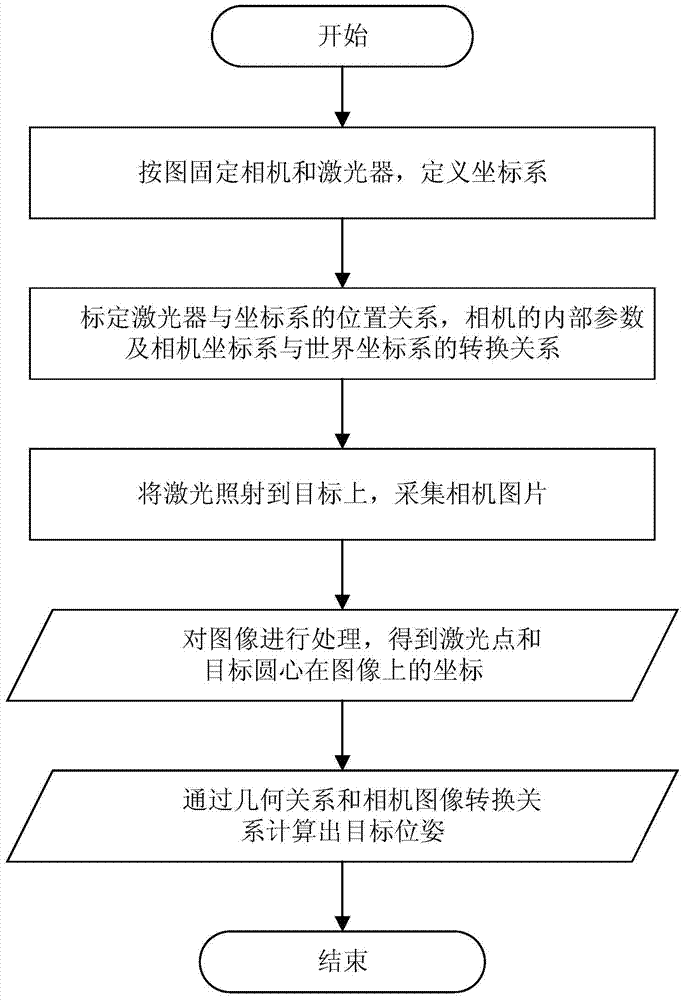
[0037] see figure 1 , the number of lasers used in this embodiment is four, and the implementation steps are as follows:
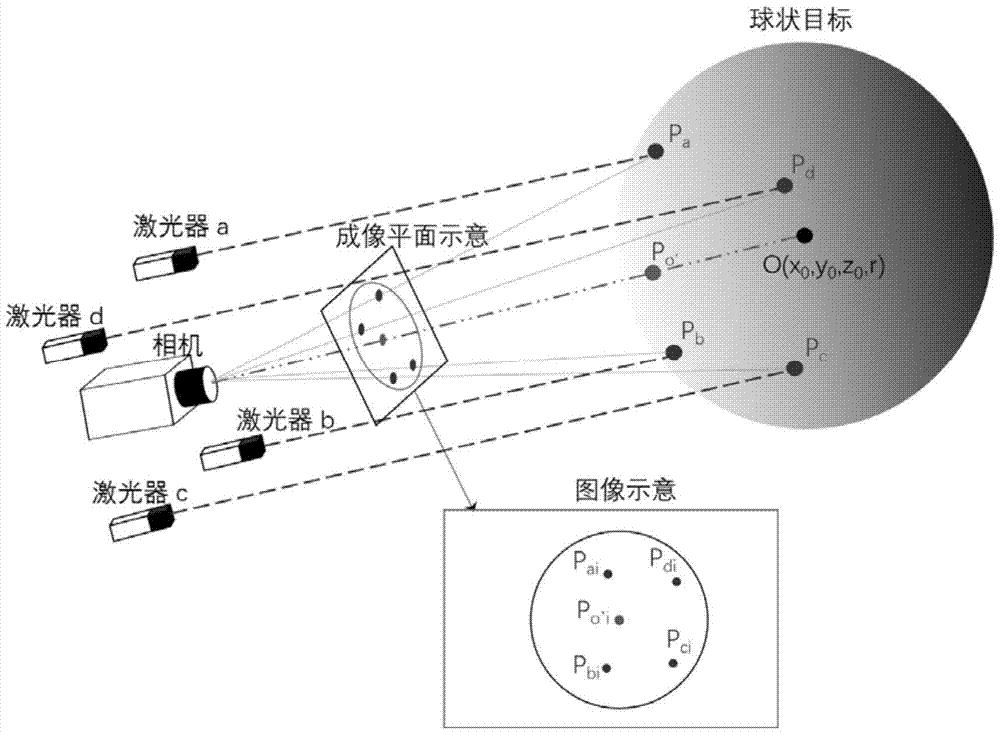
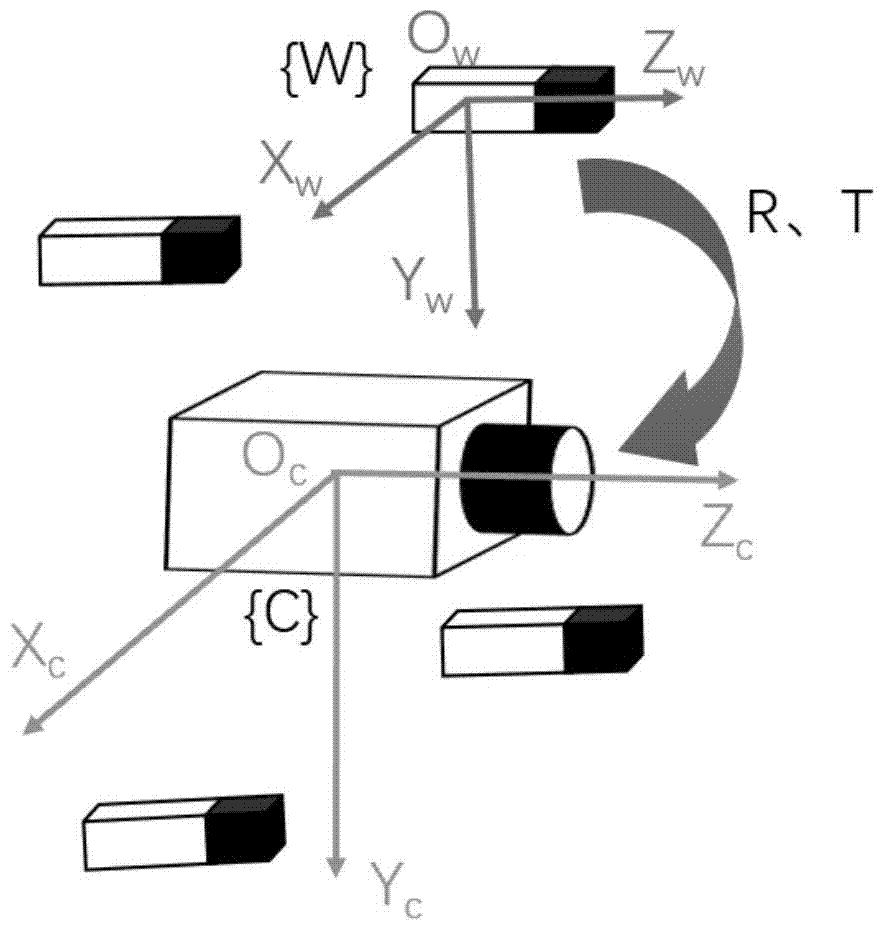
[0038] 1. If figure 2 As shown, the camera and the four lasers are fixed together, so that the direction of the laser beams emitted by the four lasers is roughly the same as that of the camera, and every three laser beams are not coplanar. The direction of the beam can be slightly convergent so that the beam can easily irradiate the target. As shown in Figure 3(a), the world coordinate system Ow is defined, and Ow is the right-handed coordinate system. The definition of Ow is determined by the actual application scenario, in order to determine the coordinates of the laser and the angle between the laser...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com