Markov-model-based position prediction method
A technology of Markov model and forecasting method, applied in forecasting, character and pattern recognition, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as inability to construct frequent patterns, high error rate, and sparse data points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0070] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
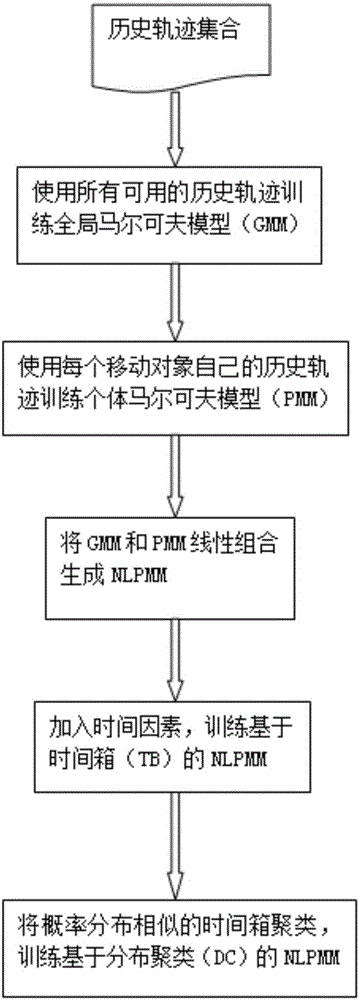
[0071] Such as figure 1 As shown, a Markov model-based next position prediction method includes the following steps:
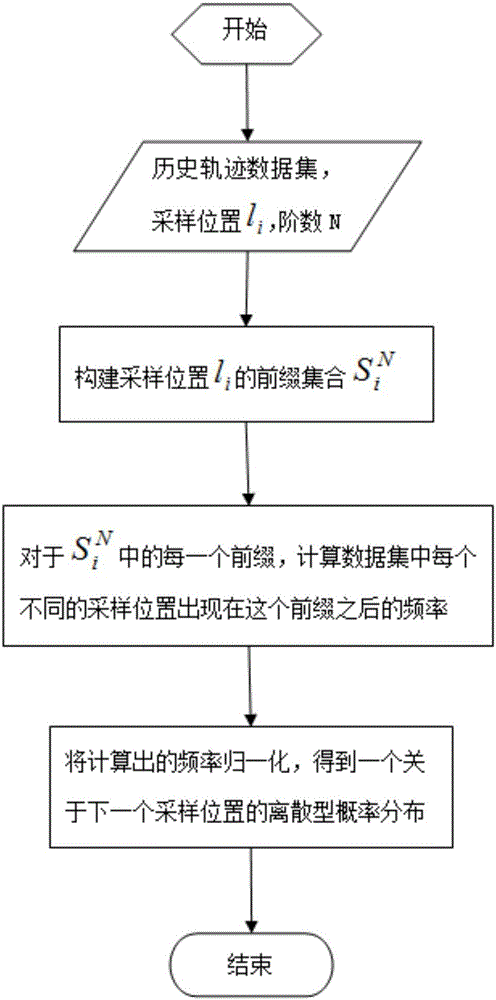
[0072] Step 1. Train a global Markov model (GMM) according to all available historical trajectories to predict the probability of the next sampling position of a moving object;
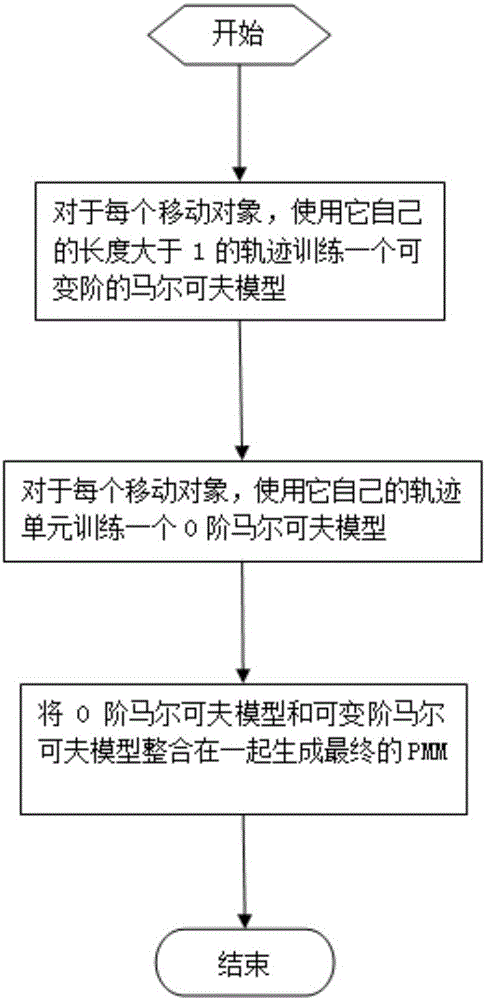
[0073] Step 2. Most people move on a regular basis (eg commuting to and from get off work), and they usually have their own personal mobility patterns. Therefore, we train an individual Markov model (PMM) for each moving object to predict the next sampling location;
[0074] Step 3. The two models (GMM and PMM) trained in Step 1 and Step 2 are combined using linear regression to produce more complete and accurate predictions;
[0075] Step 4. The movement of human beings shows the regularity of time to a large extent, and the prediction model should be time-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com