Method for monitoring absolute earth surface deformations of depression area by means of rising rail InSAR and falling rail InSAR without ground support
A surface deformation and subsidence area technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, measurement devices, etc. Reflect on land subsidence and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0040] In order to facilitate understanding of the present invention, at first the theoretical basis of the present invention is provided:
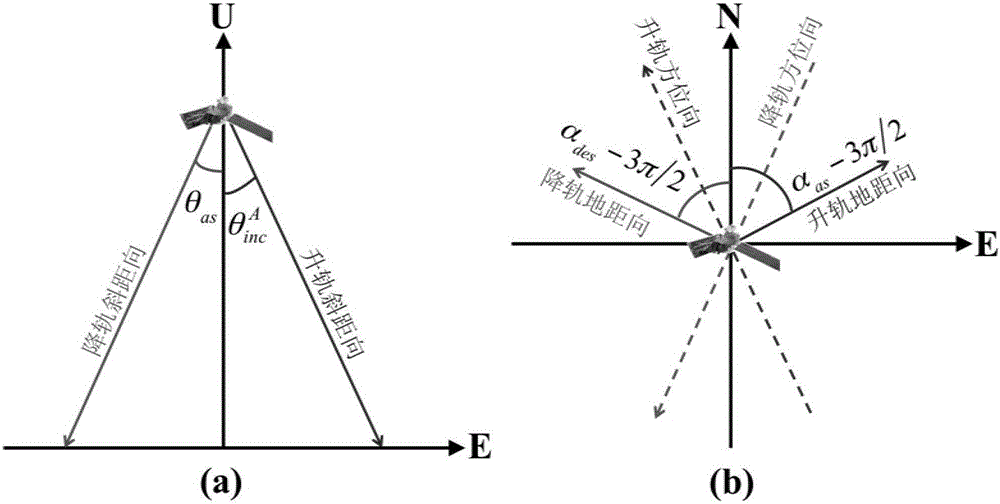
[0041] As we all know, the direct consequence of geological disasters is the deformation of the earth's surface. For InSAR technology, it can only monitor ground observation points x i The relative deformation relative to a reference point in the upward slope distance, namely
[0042] D. rat (x i ) = D real (x i )+K (1)
[0043] Among them, D rat (x i ) is the ground observation point x i InSAR slant-range relative deformation measurements on ; D real (x i ) is the ground observation point x i K is the constant difference between the InSAR slant distance relative deformation measurement and the slant distance absolute deformation, that is, the absolute offset.
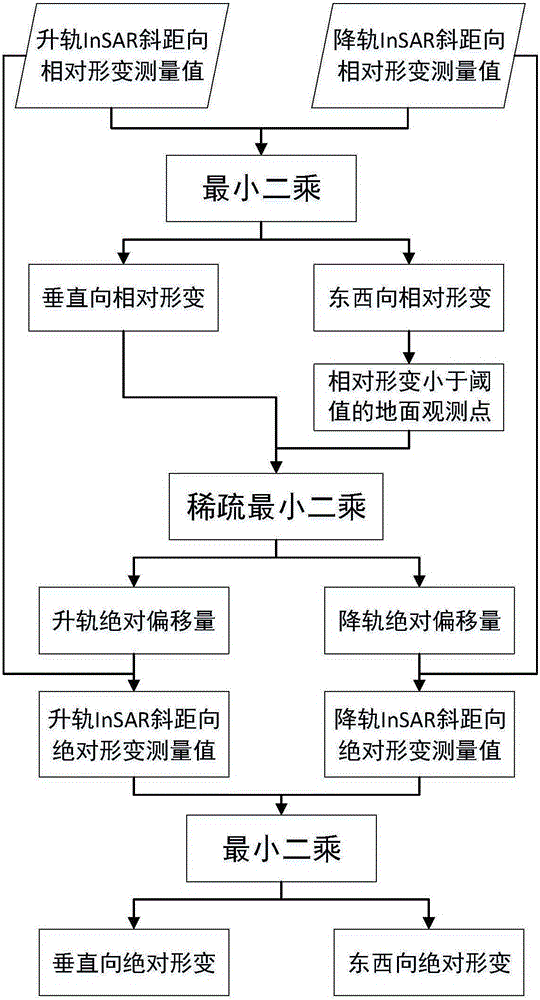
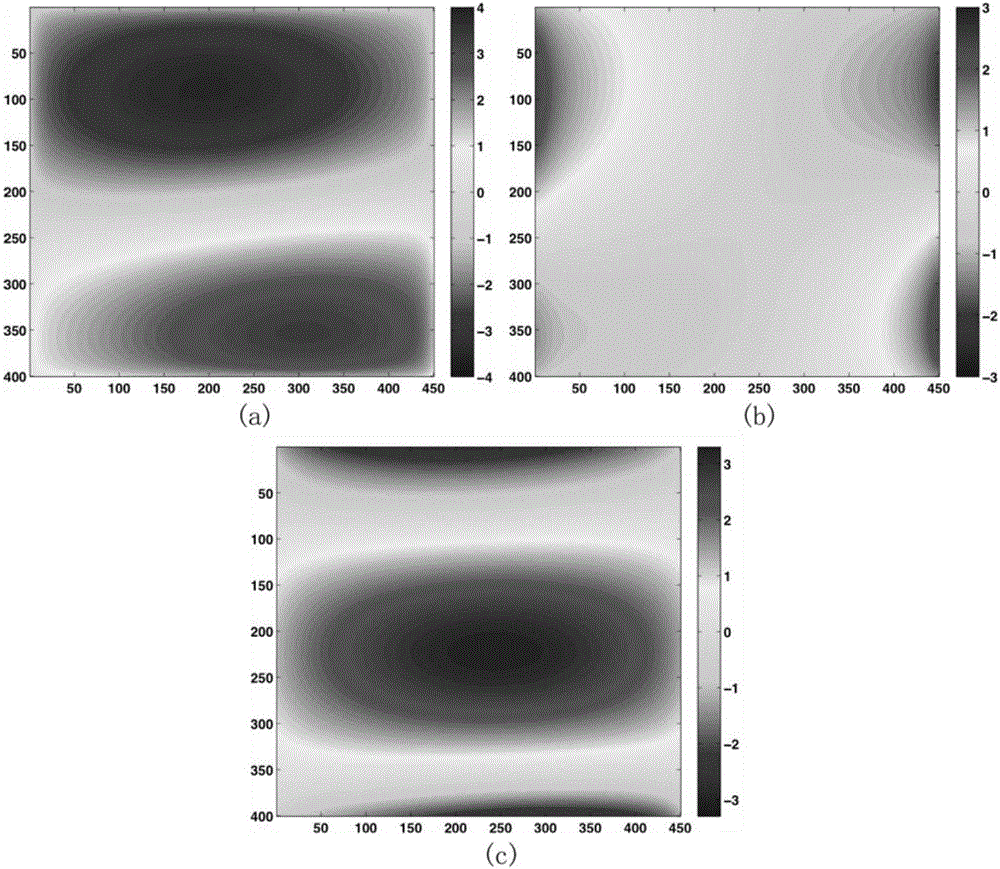
[0044] In practice, however, surface def...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com