Method for recognizing sweet spots in shale stratum
A shale and formation technology, applied in the field of identifying sweet spots in gas-bearing shale formations, can solve the problems of parameter description and definition of engineering sweet spots, undifferentiated geological sweet spots and engineering sweet spots, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
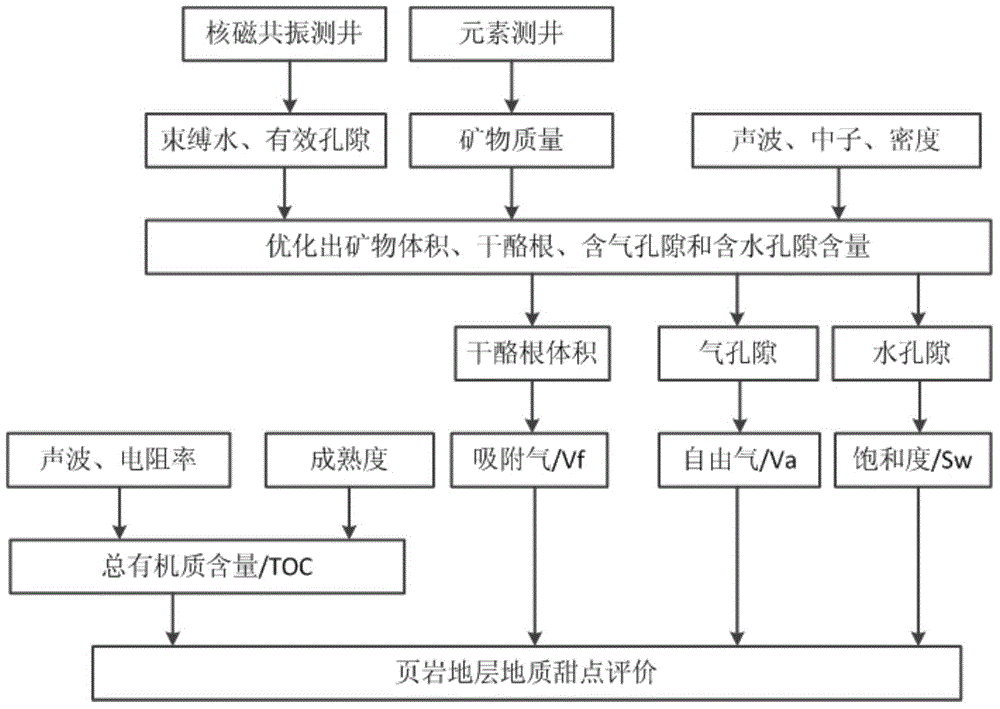
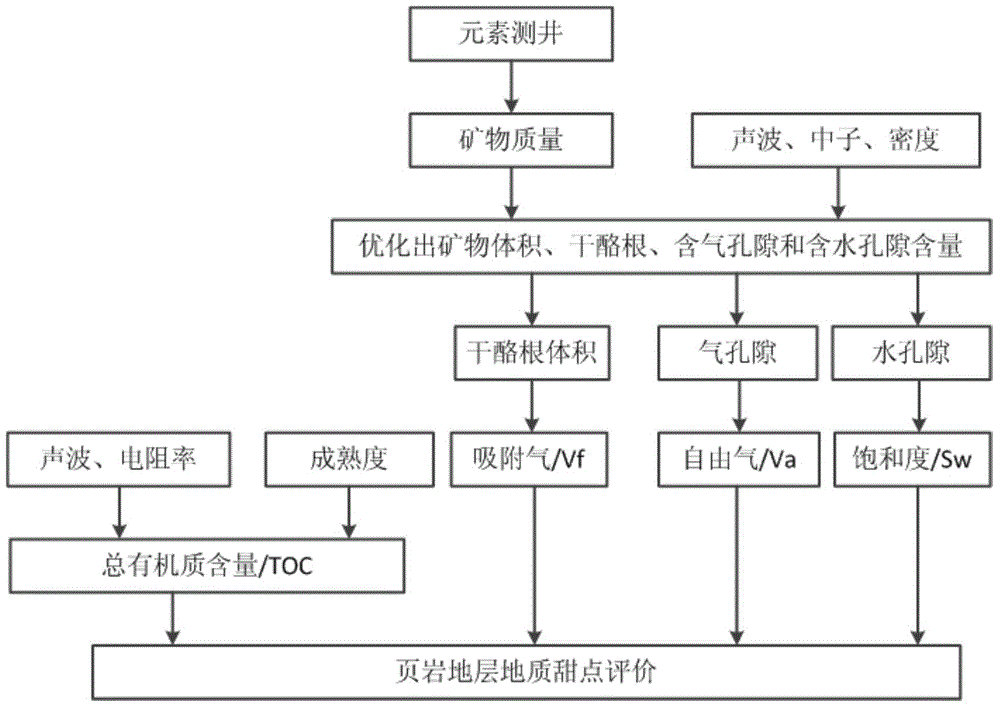
[0099] Firstly, the technical idea of identifying geological sweet spots is explained.
[0100] figure 1 A technical idea for identifying geological sweet spots in this embodiment is shown. The ideal identification method of geological sweet spot parameters requires accurate evaluation of each geological sweet spot parameter with existing logging methods. The porosity of shale formations is small, and conventional three-porosity logging methods (acoustic, neutron and density logging) are difficult to accurately evaluate the porosity of shale formations due to the influence of multi-mineral and organic matter instability , NMR logging methods are needed to accurately evaluate formation porosity and irreducible water content, wherein formation porosity includes movable gas porosity and movable water porosity. The element logging method can effectively judge the complex mineral types and contents of shale formations, and obtain other geological sweet spot parameters that are ...
Embodiment 2
[0191] In this embodiment, the logging data of a well in a shale formation in a block in southwest China is used as an example to illustrate the identification result of a shale formation sweet spot.
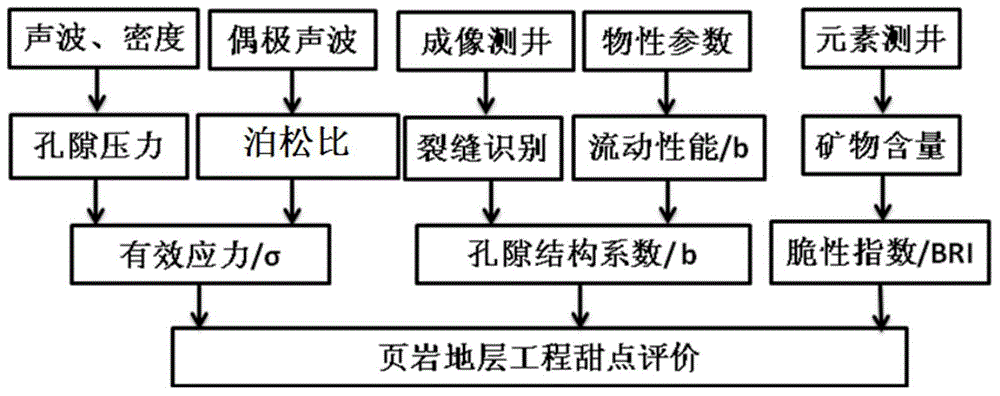
[0192] The lithology of high-quality shale in this block is mainly composed of yellow-gray shale and silty shale interbedded with thin lenticular limestone. Geological sweet spot parameters and engineering sweet spot parameters are shown in Table 1. In Table 1, TOC is total organic carbon content, Φg is gas-bearing pores; Vk is kerogen volume; Sg is gas saturation; BRI is brittleness index; σ is effective stress, and b is pore structure index.
[0193] Table 1 Statistical table of sweet spot coefficients in Jiaoshiba shale formation
[0194]
[0195] according to Figure 9 As shown in the radar map, the geological sweet spot coefficient can be determined to be 0.72, according to Figure 10 As shown in the radar chart, the engineering sweet spot coefficient can be determine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com