Cross angle of view gait recognition method based on two-dimensional coupling margin Fisher analysis
A two-dimensional coupling and gait recognition technology, applied in the field of pattern recognition and machine learning, can solve problems such as disaster of dimensionality, poor viewing angle, and destruction of gait energy map structure information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
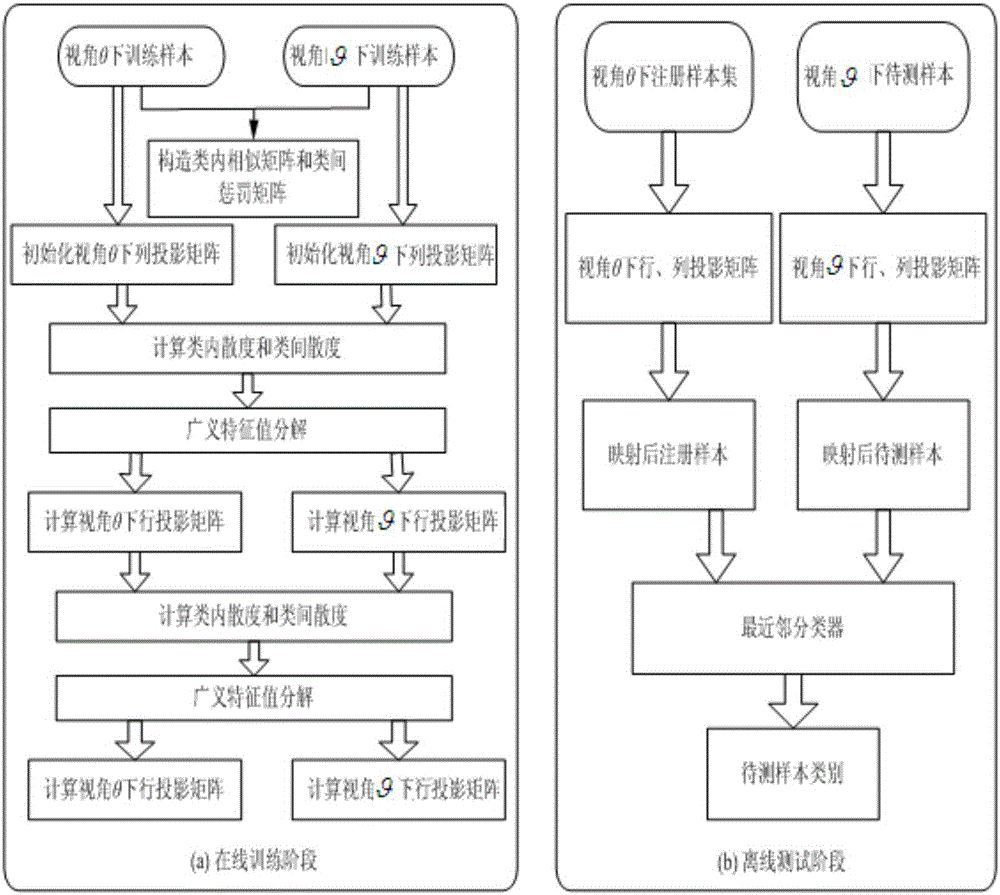
[0081] A cross-view gait recognition method based on two-dimensional coupled margin Fisher analysis, including: an online training phase and an offline testing phase;
[0082] The online training phase includes steps as follows:
[0083] 1) For two viewing angles θ and Under the gait energy map features, the intra-class similarity matrix and the inter-class penalty matrix are constructed;
[0084] 2) Initialize two viewing angles θ and The following column projection matrix, for a given column projection matrix, solve the between-class scatter matrix and the intra-class scatter matrix;
[0085] 3) Solve the generalized eigenvalue problem, and obtain the downlink projection matrix of two viewing angles;
[0086] 4) Solve the inter-class scatter and intra-class scatter matrices for a given row projection matrix;
[0087] 5) Solve the generalized eigenvalue problem, and obtain the following projection matrices for the two viewing angles;
[0088] Described off-line test st...
Embodiment 2
[0092] As described in Example 1, a cross-view gait recognition method based on two-dimensional coupling margin Fisher analysis, the difference is that in the online training phase, the two viewing angles θ and The training sample set composed of the following gait energy map features where X i Represents a collection of features The gait energy map features of the i-th sample in N θ Represents a collection of features The total number of samples in D xm ,D xn Respectively represent the set of features The length and width of the sample gait energy; Y j Represents a collection of features The gait energy map features of the jth sample in Represents a collection of features The total number of samples; D ym ,D yn Respectively represent the set of features The length and width of the sample gait energy;
[0093] Assume π i Represents the gait energy map feature X of the registered sample under the viewing angle θ i The class label for the view The gait en...
Embodiment 3
[0116] As described in Embodiment 2, a cross-view gait recognition method based on two-dimensional coupling margin Fisher analysis, the difference is that it also includes regularization to the formula (11), the method is as follows:
[0117] When learning projection matrices, overfitting problems are often avoided by adding a regularization factor,
[0118] arg m i n P J ( P ) = T r ( P T ZGZ T P ) T r ( P T Z ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com