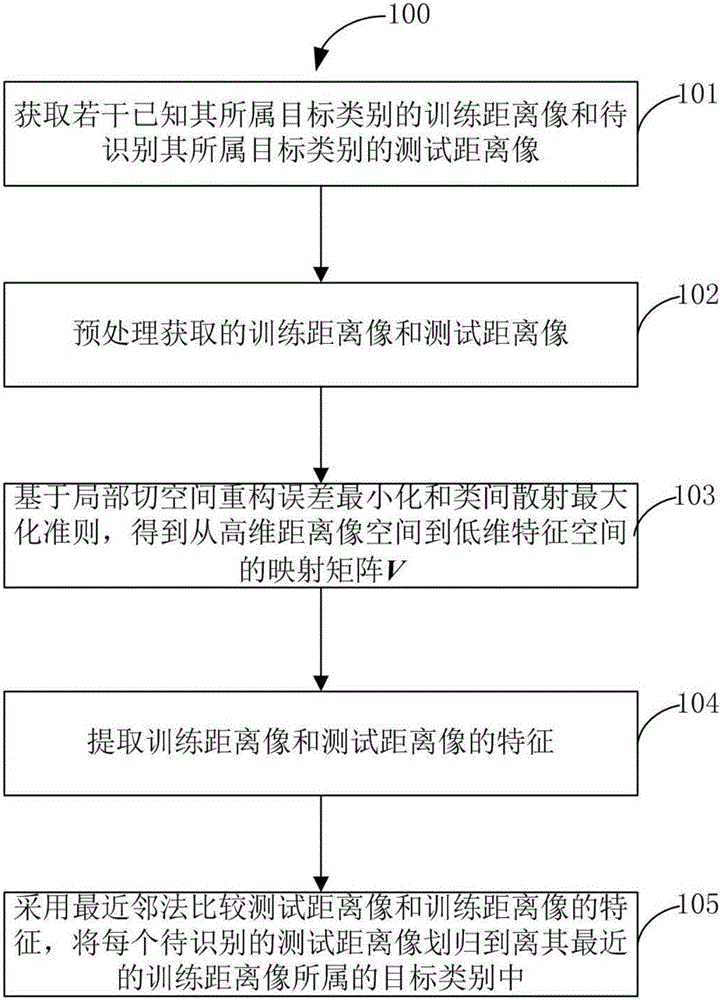
Radar object distance image recognition method based on kernel discrimination local tangent space arrangement
A radar target and spatial arrangement technology, applied in the direction of radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high-resolution range image attitude sensitivity problems such as limited solving ability, limited learning ability, and affecting recognition performance, so as to improve radar target Recognition Performance, Strong Learning and Representation Capabilities, Effects of Improving Recognition Performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
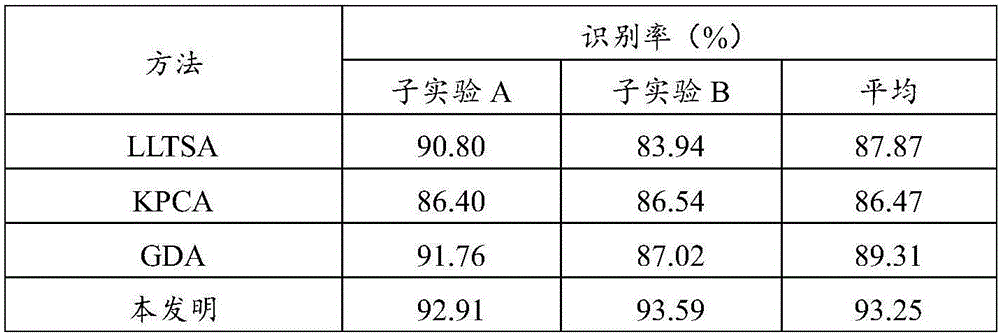
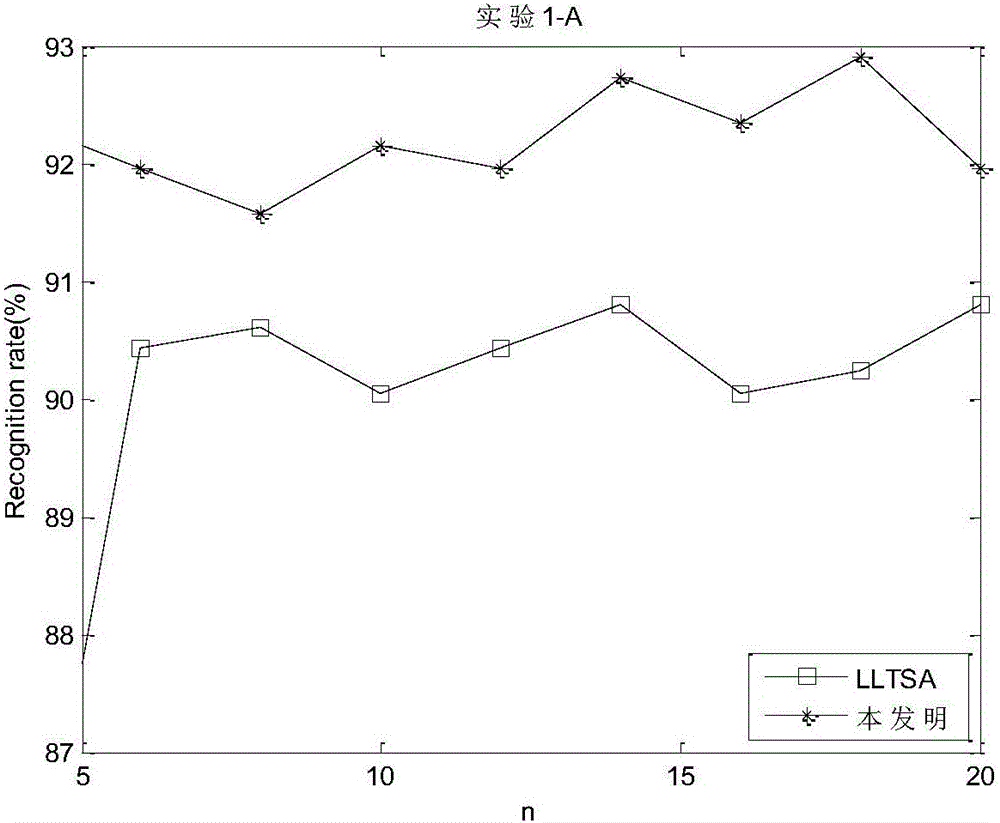
[0081] Use the first set of data to conduct two sub-experiments A and B respectively. In sub-experiment A, the first 1 / 3 range images of each aircraft were used as training range images, and the last 2 / 3 range images were used as test range images; in sub-experiment B, the first 1 / 5 range images of each aircraft were The last 4 / 5 range images are used as the test range images. The recognition rate obtained by the four methods in the two sub-experiments and the average recognition rate of the two experiments are as follows: figure 2 shown, from figure 2 The recognition results shown can be obtained:
[0082] (1) In sub-experiment A, except that the recognition rate of KPCA is relatively low, the recognition performance difference of other three methods is not too big; In sub-experiment B, the performance advantage of the recognition method provided by the present invention is more obvious, respectively high Pass LLTSA, GDA and KPCA about 10%, 6% and 7%.
[0083] (2) Combi...
experiment example 2
[0086] Use the first set of data and the second set of data to conduct two sub-experiments A and B respectively. In sub-experiment A, the first set of data is used as the training range image, and the second set of data is used as the test range image; in sub-experiment B, the second set of data is used as the training range image, and the first set of data is used as the test range image. The recognition rate obtained by the four methods in the two sub-experiments and the average recognition rate of the two experiments are as follows: Figure 4 shown, from Figure 4 The recognition results shown can be obtained:
[0087] (1) The recognition rate that two kinds of classic kernel methods KPCA and GDA obtain is the lowest, the recognition rate of LLTSA is higher than KPCA and GDA about 7~8%, the recognition rate of the present invention is the highest, higher than KPCA and GDA about 20%.
[0088] The reason is: in the experiment 2, the training range image and the test range i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com