Systems and methods for detecting malicious executable files
A technique for executing files and malicious intent, applied in the directions of instruments, program/content distribution protection, electronic digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
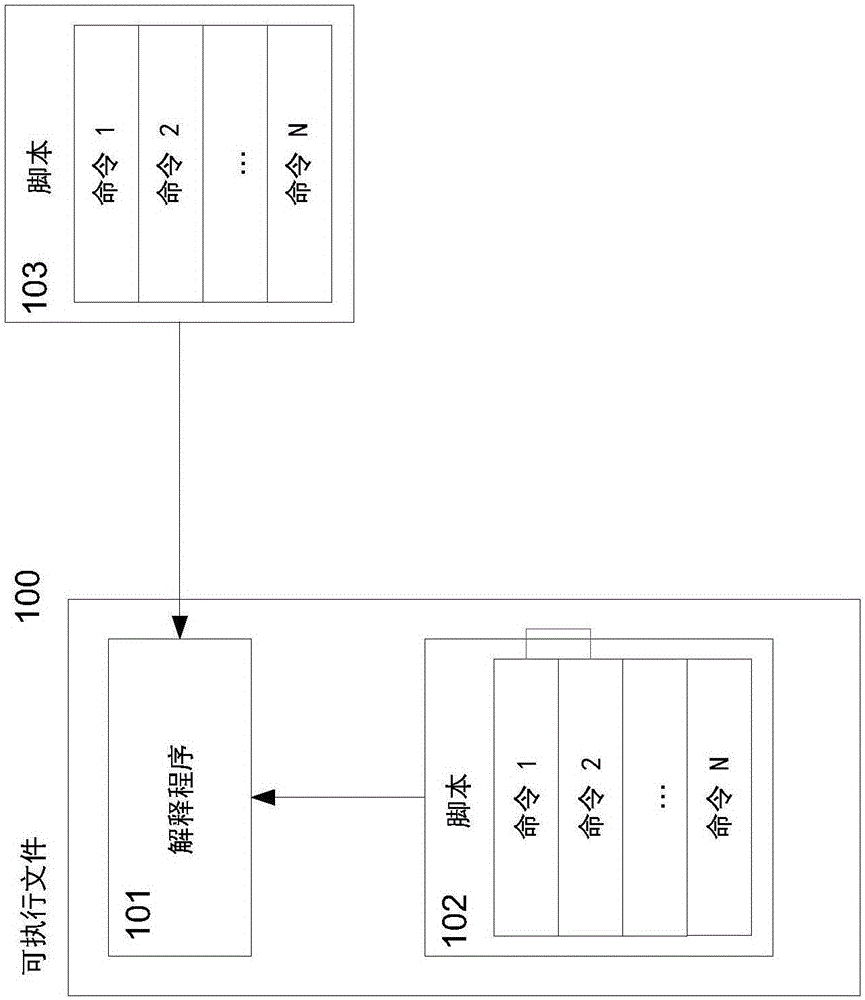
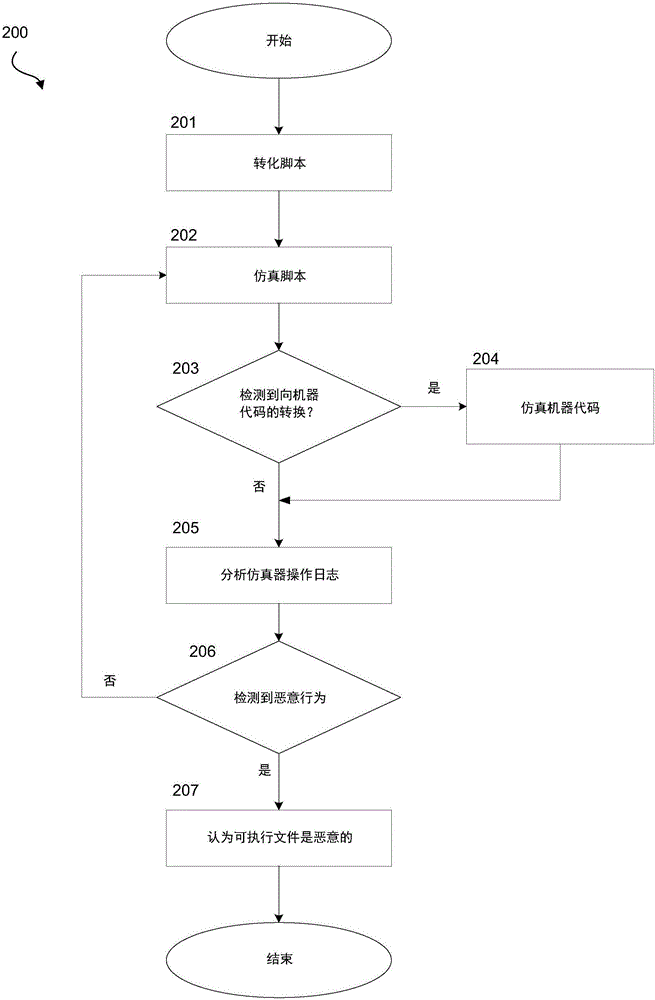
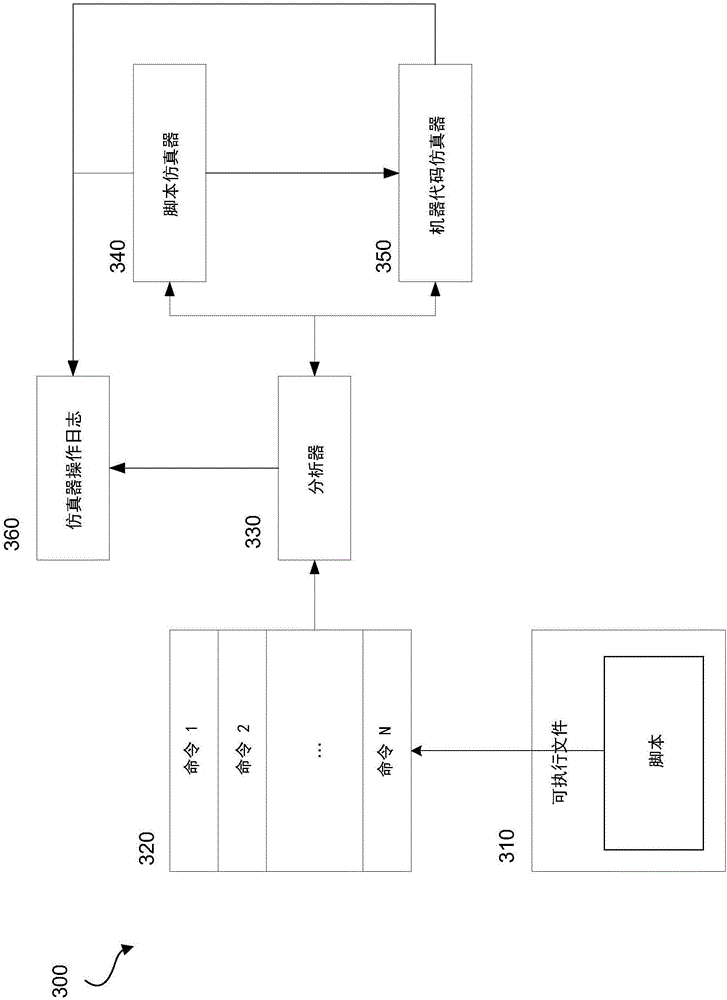
[0020] According to an embodiment, systems and methods are configured to perform analysis of executable files compiled from scripts written, for example, in the AutoIt language. Necessary features of such an executable include an interpreter. Therefore, hereinafter "executable file" refers to an executable file including an interpreter. In order to detect malicious executables, emulation of scripts contained in executables can be implemented. This emulation saves time, which is often not enough to emulate the executable itself. However, if the script is directly emulated, a smaller number of variables of the execution medium are monitored compared to classic emulation of machine code. Thus, if only script emulation is implemented, there is an opportunity for executables to be misinterpreted as trustworthy (or "clean" or non-malicious) due to the inability to thoroughly check the script's behavior. For this reason, embodiments of the present invention are configured to check...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com