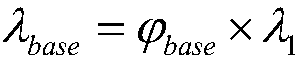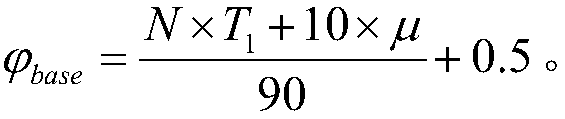An Anti-seismic Design Method for Improving the Collapse Resistance of Building Structures
A technology for building structure and seismic design, applied in the direction of buildings, building types, protective buildings/shelters, etc. The effect of improved seismic collapse capability, ease of acceptance and use, and safety assurance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0018] Specific embodiment one: a kind of anti-seismic design method that improves building structure anti-collapse ability comprises the following steps:
[0019] Step 1: Determine the number of floors N and site type of the building structure to be designed according to the design requirements and location; select the building structure system (such as reinforced concrete frame, steel frame, masonry structure, etc.), and design according to the conventional structure Method to preliminarily design the size of structural components and estimate the basic period T of the building structure 1 ;
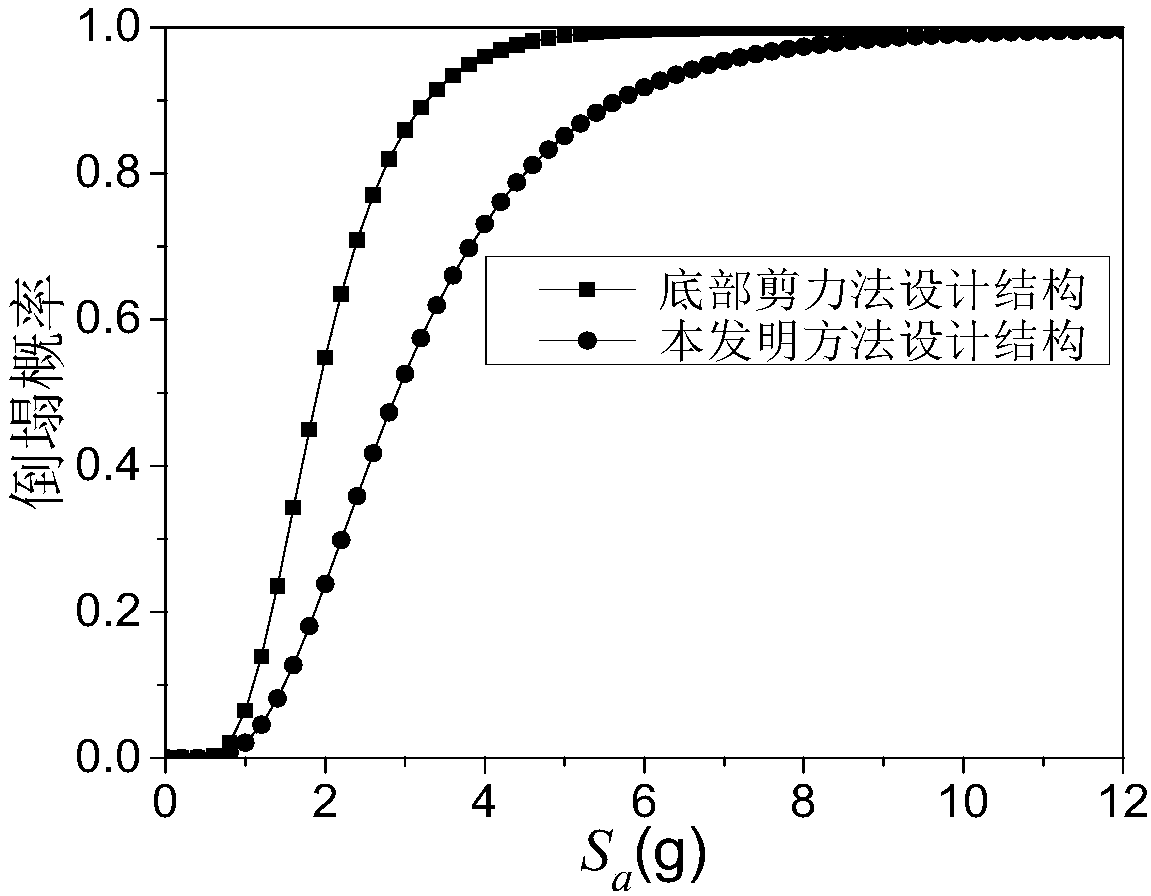
[0020] Step 2: Using the bottom shear force method given in the code for seismic design of buildings (such as the current "Code for Seismic Design of Buildings" GB50011-2010), calculate the seismic action on each floor of the structure and find The interstory shear force of each layer (its value is the same as the yield strength of each layer), calculate the bottom shear force V of th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: obtain new building structure bottom shear force V in the described step 4 base Specifically:
[0027] V base =λ base ×S 2
[0028] where the S 2 is the sum of the yield strength of each layer of the structure calculated using the bottom shear method considering the additional force on the top of the structure, λ base is the new shear coefficient at the bottom of the structure.
[0029] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and one of the specific implementation modes one to two is: the λ base Specifically:
[0031]
[0032] which stated Adjustment factor for bottom shear.
[0033] Other steps and parameters are the same as one of the specific implementation modes 1 to 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com