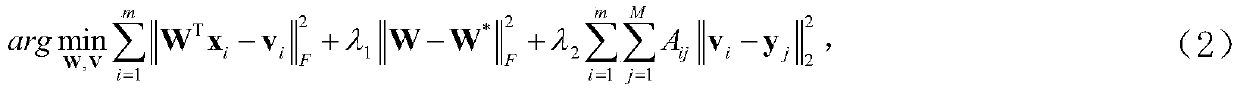Domain Adaptive Learning Method
A learning method and domain self-adaptation technology, applied in the field of domain self-adaptation, can solve problems such as domain shift, achieve low complexity, solve domain shift problems, and improve performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
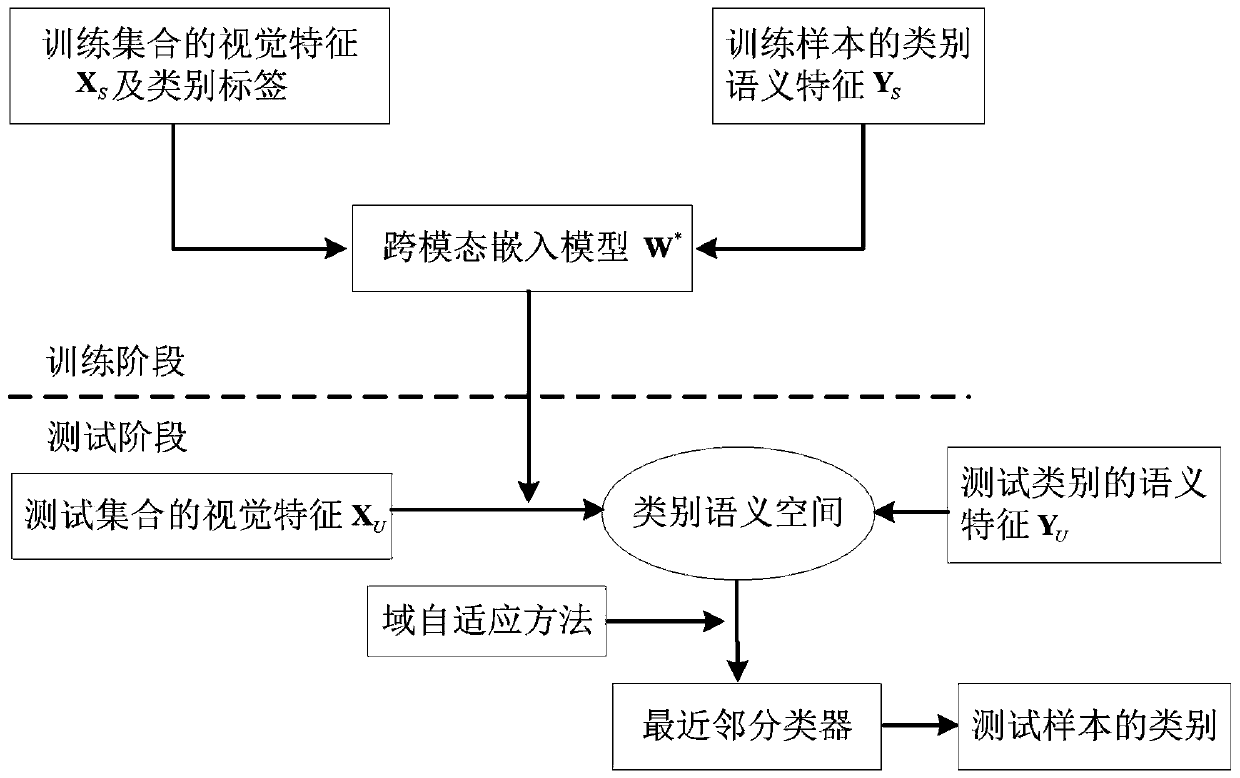
[0033] The invention relates to a domain adaptive technology oriented to the field of computer vision. Aiming at the problem that the distribution of training categories and test categories is different in some scenarios, directly applying the model learned from training categories to test categories is prone to domain shift, and a new domain adaptive learning technology is proposed. To achieve the purpose of improving the classification effect. The invention also provides a zero-sample classification system realized by the method.
[0034] Taking the specific application of zero-sample classification as an example, the specific principle of the present invention will be introduced below.
[0035] use Represents a training data set containing n samples, where represents the visual feature space, Contains N categories. use Represents m test samples from M categories, and the training categories and test categories are disjoint, that is: Each category utilizes an emb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com