Multi-modal brain-image injured pathological tissue image segmentation method
A brain imaging, multimodal technology, applied in image analysis, image enhancement, image data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of uneven modal image quality, incomplete reproducibility of segmentation process and results, and high algorithm complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0080] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
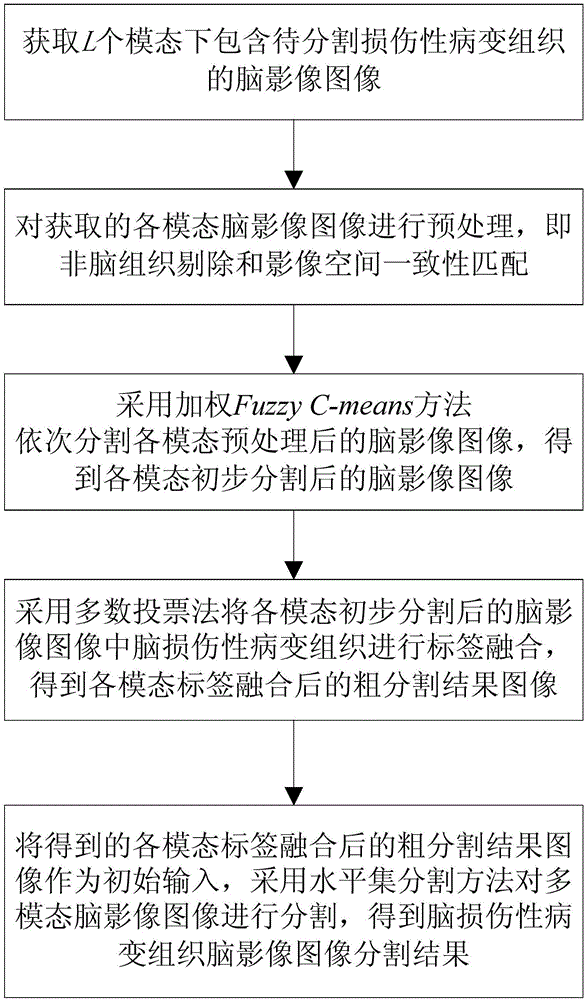
[0081] The present invention proposes a method for image segmentation of damaged lesion tissue in multimodal brain imaging, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0082] Step 1: Obtain brain imaging images containing damaged lesion tissue to be segmented under L modalities.
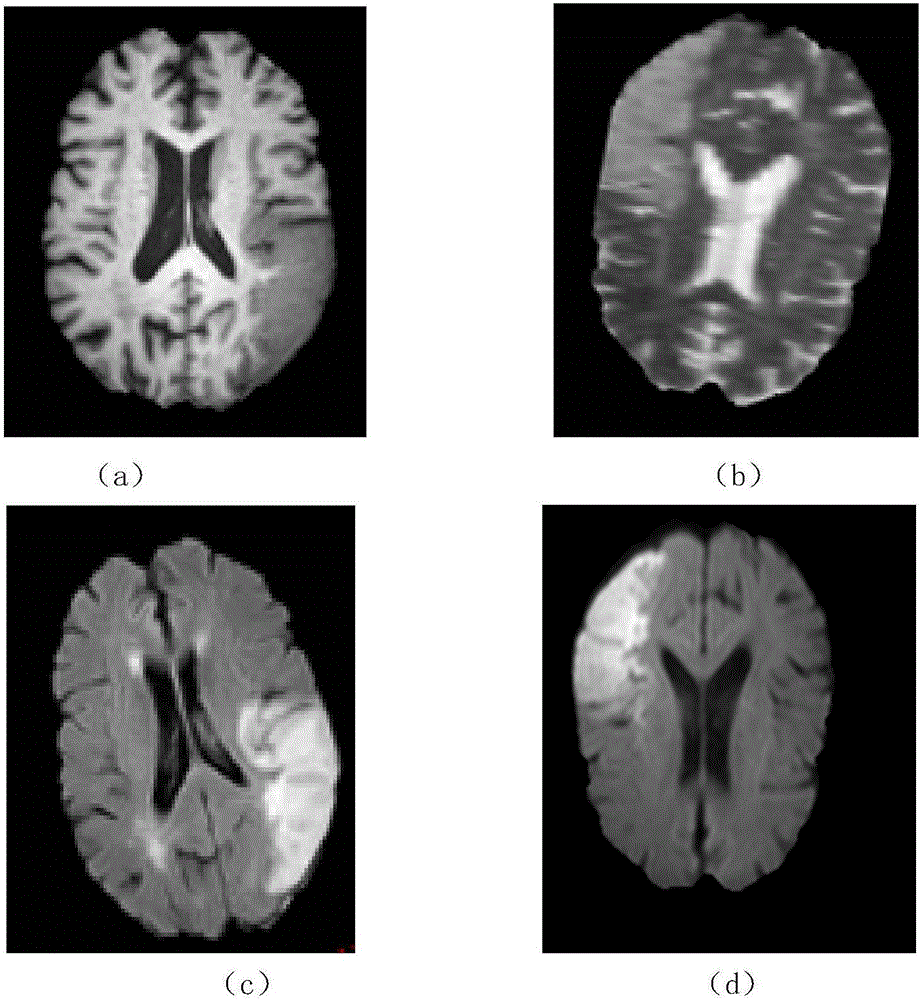
[0083] In this embodiment, brain imaging images containing damaged lesion tissue to be segmented under L=4 modalities are acquired, such as figure 1 shown.
[0084] Step 2: Perform preprocessing on the brain imaging images of each modality acquired in step 1, that is, non-brain tissue removal and image spatial consistency matching.
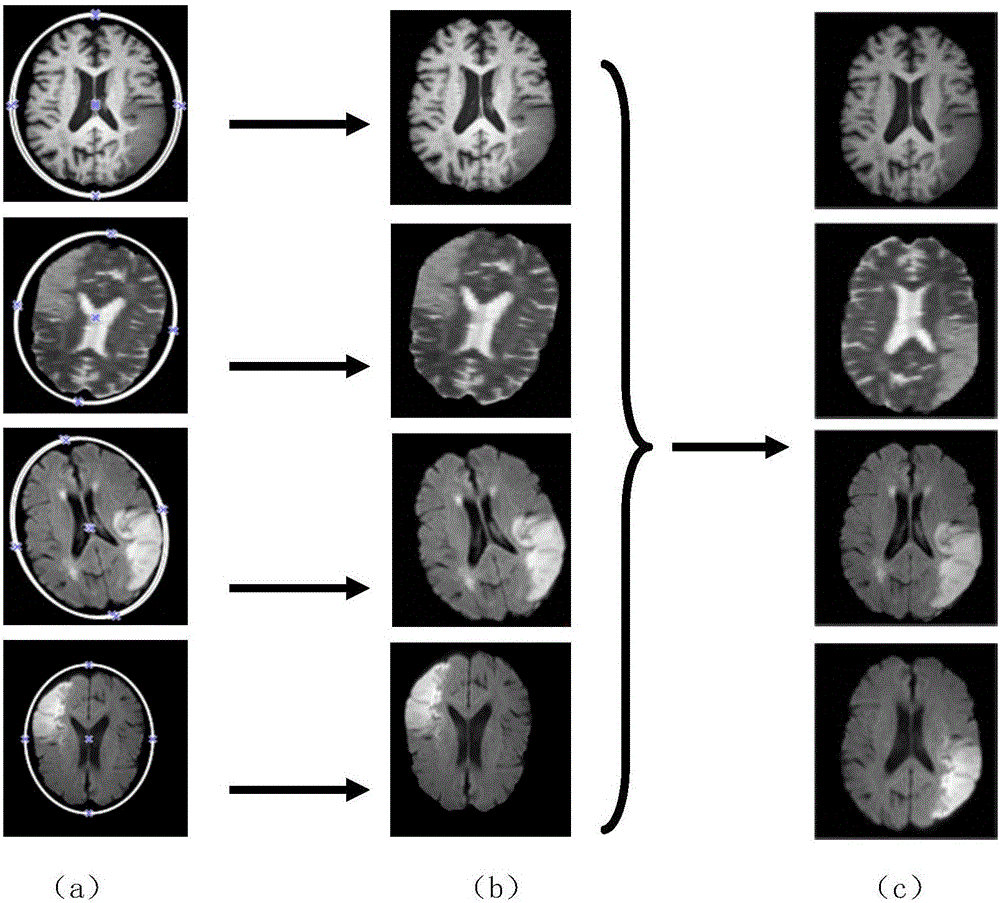
[0085] In this embodiment, there are two processing methods for preprocessing the brain imaging images of each modality acquired in step 1. The methods are as follows: image 3 shown, including the following steps: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com