Physical unclonable function circuit utilizing monostable timing offset
A timing deviation, function circuit technology, applied in the direction of internal/peripheral computer component protection, etc., can solve the problems of complex anti-tamper protection circuits, vulnerable to intrusive attacks, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
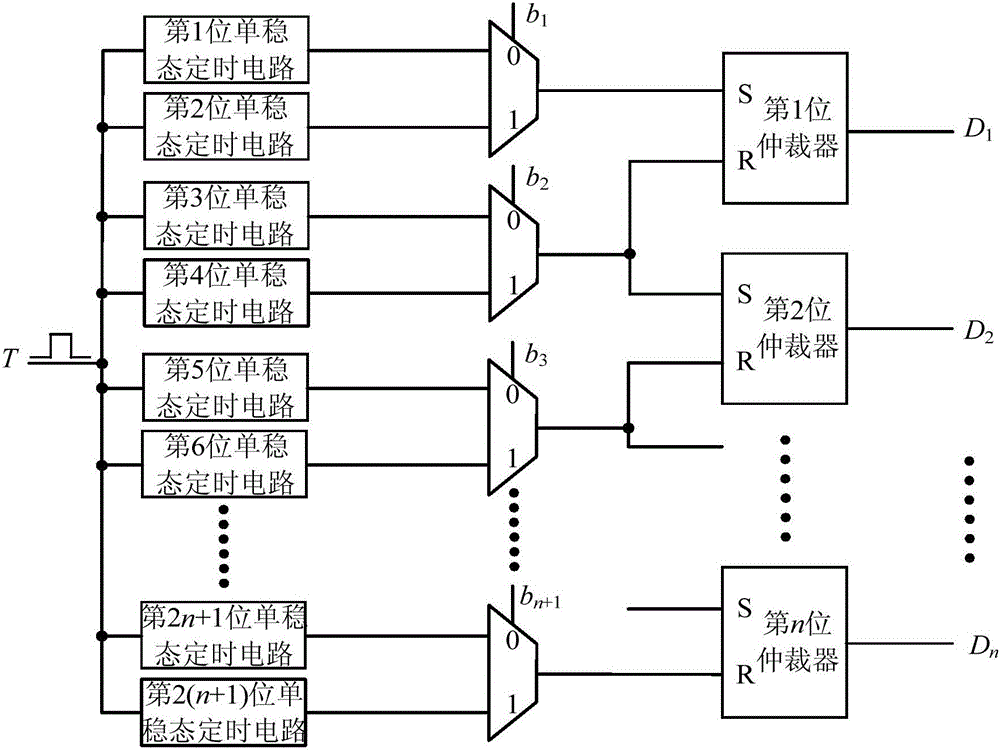
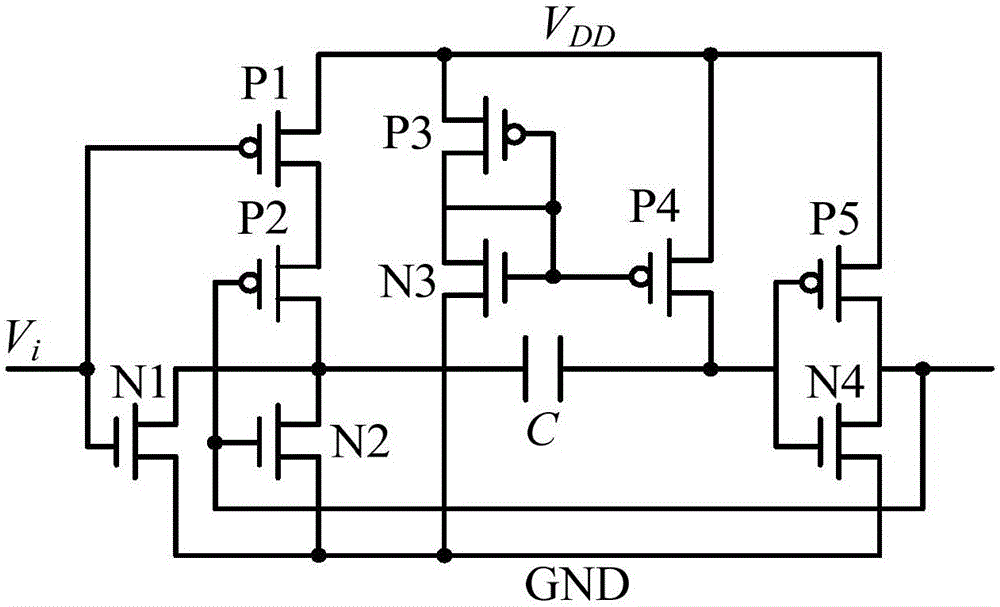
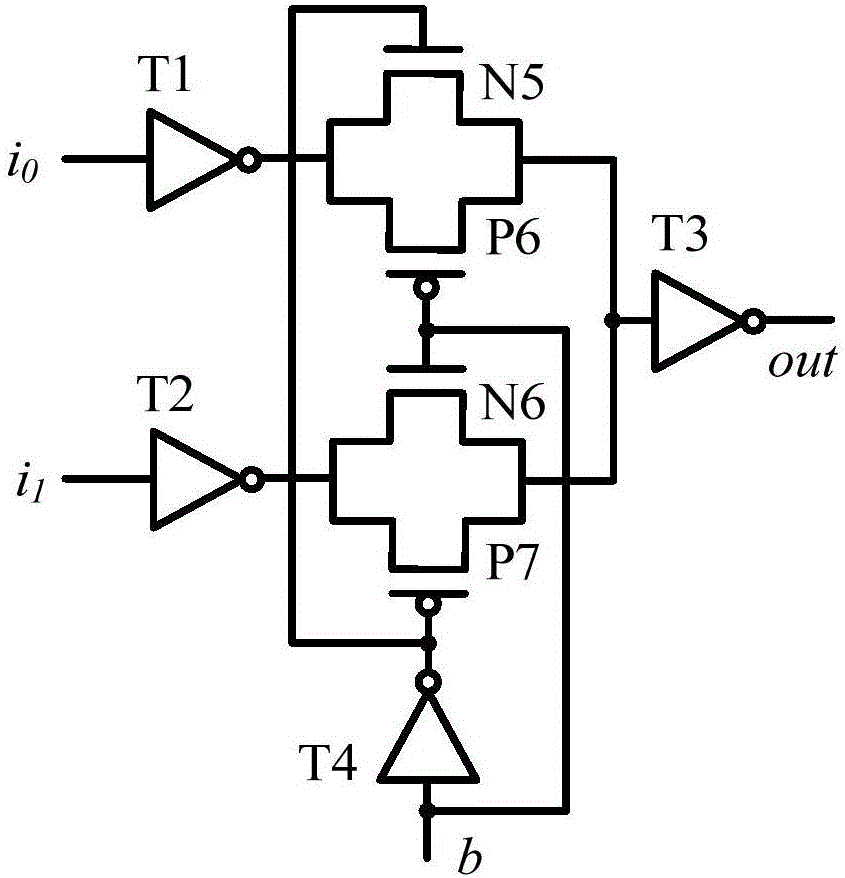
[0022] Example 1: as figure 1 A physical unclonable function circuit using monostable timing deviation is shown, including 2(n+1) monostable timing circuits, n+1 two-input selection circuits and n arbitrators, where n is greater than or equal to 1 integer, the two-input selection circuit has a first input terminal, a second input terminal, a control terminal and an output terminal, the control terminal of the two-input selection circuit is used to access an external excitation signal, and the arbiter has a first input terminal, a second input terminal end and output end; the output end of the 2j+1 bit monostable timing circuit is connected with the first input end of the j+1 bit two-input selection circuit, and the output of the 2nd (j+1) bit monostable timing circuit terminal is connected with the second input terminal of the j+1th two-input selection circuit, wherein, j=0, 1, 2,..., n; the output terminal of the first two-input selection circuit is connected with the first a...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 A physical unclonable function circuit using monostable timing deviation is shown, including 2(n+1) monostable timing circuits, n+1 two-input selection circuits and n arbitrators, where n is greater than or equal to 1 integer, the two-input selection circuit has a first input terminal, a second input terminal, a control terminal and an output terminal, the control terminal of the two-input selection circuit is used to access an external excitation signal, and the arbiter has a first input terminal, a second input terminal end and output end; the output end of the 2j+1 bit monostable timing circuit is connected with the first input end of the j+1 bit two-input selection circuit, and the output of the 2nd (j+1) bit monostable timing circuit terminal is connected with the second input terminal of the j+1th two-input selection circuit, wherein, j=0, 1, 2,..., n; the output terminal of the first two-input selection circuit is connected with the firs...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example three: as figure 1 A physical unclonable function circuit using monostable timing deviation is shown, including 2(n+1) monostable timing circuits, n+1 two-input selection circuits and n arbitrators, where n is greater than or equal to 1 integer, the two-input selection circuit has a first input terminal, a second input terminal, a control terminal and an output terminal, the control terminal of the two-input selection circuit is used to access an external excitation signal, and the arbiter has a first input terminal, a second input terminal end and output end; the output end of the 2j+1 bit monostable timing circuit is connected with the first input end of the j+1 bit two-input selection circuit, and the output of the 2nd (j+1) bit monostable timing circuit terminal is connected with the second input terminal of the j+1th two-input selection circuit, wherein, j=0, 1, 2,..., n; the output terminal of the first two-input selection circuit is connected with the fir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com