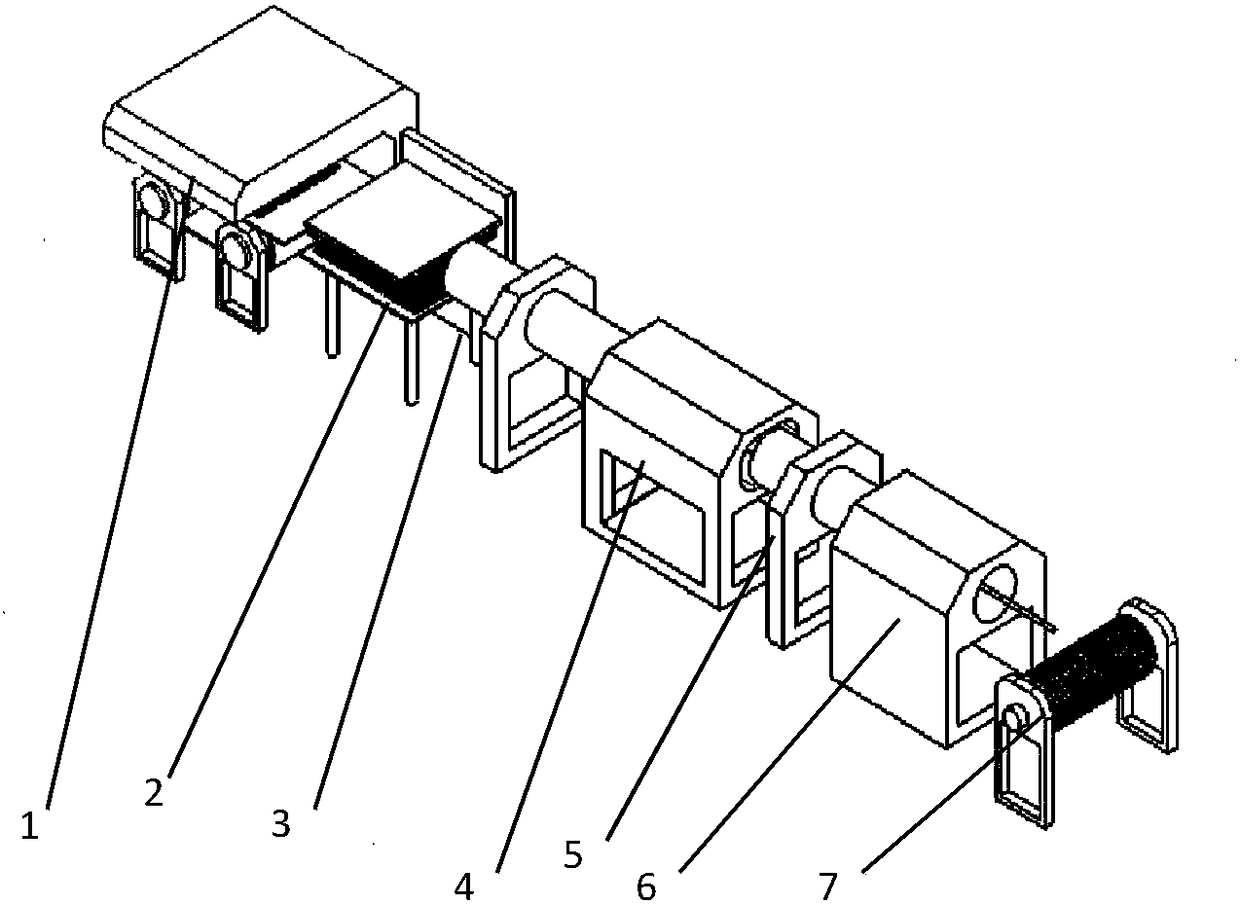
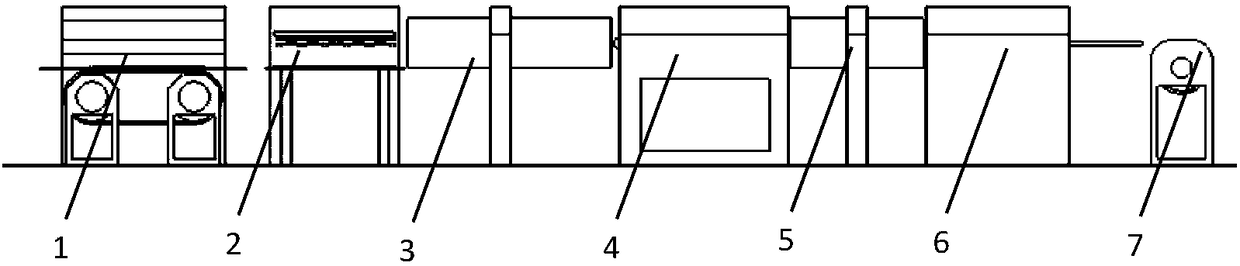
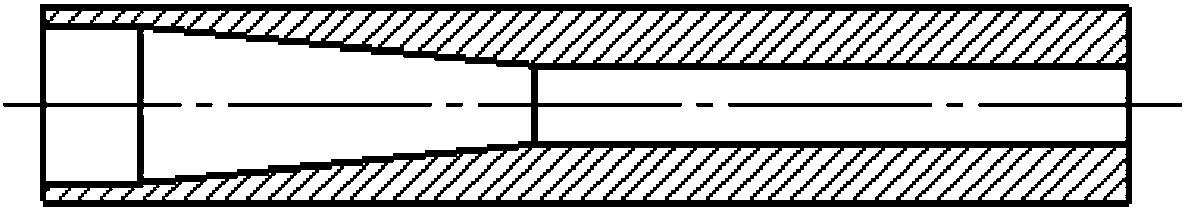
A kind of 3D printing filament reinforced by natural hemp fiber and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and fiber-reinforced technology, which is applied in the field of 3D printing materials, can solve problems such as unfavorable processing, application restrictions, hot end blockage, etc., and achieve the effects of good environmental performance, wide range of uses, and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The raw material formula in the present embodiment is as follows (according to mass percent, hereinafter are all the same as the present embodiment): 60% of low melting point polymer fiber; 35% of natural hemp fiber; 3% of silane coupling agent; Ethylene bis stearic acid amide 1% stearic acid 1%; low melting point fiber is PLA, natural hemp fiber is hemp.
[0029] 1. Mechanically degumming the hemp fiber and modifying the surface of the hemp fiber; spray coupling agent and corresponding additives to treat the hemp fiber to improve the polarity of the hemp fiber. The selected low-melting point fiber PLA is pretreated, and the PLA fiber is treated by spraying coupling agent and corresponding auxiliary agents.
[0030] 2. Blend low-melting polymer fibers and hemp fibers: Lay a layer of finely opened low-melting polymer fibers, then lay a layer of finely opened hemp fibers, and alternately lay multiple layers of low-melting polymer fibers And hemp fibers to form felt.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The raw material formula in the present embodiment is as follows: low melting point polymer fiber 55%; Natural hemp fiber 42%; Maleic anhydride 2%; Stearic acid 1%; Low melting point fiber is ABS, and natural hemp fiber is jute.
[0036] 1. The jute fiber is mechanically degummed, and the surface of the hemp fiber is modified. The jute fiber is treated by spraying the coupling agent and the corresponding auxiliary agent to improve the polarity of the jute fiber. The selected low-melting fiber ABS is pretreated, and the ABS fiber is treated by spraying coupling agent and corresponding auxiliary agents.
[0037] 2. Blending low-melting polymer fibers and jute fibers: laying a layer of finely opened low-melting polymer fibers, then laying a layer of finely opened jute fibers, and alternately laying multiple layers of low-melting polymer fibers and jute fibers, forming felt.
[0038] 3. Acupuncture the felt, then roll it up into strips.
[0039] 4. Pass the strip-shaped f...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The raw material formula in this embodiment is as follows: low-melting point polymer fiber 50%; natural hemp fiber 45%; silane coupling agent 2%; stearic acid 1%; low-melting point fiber is PP, natural hemp fiber is flax.
[0043] 1. The flax fiber is mechanically degummed, and the surface of the flax fiber is modified. The flax fiber is treated by spraying the coupling agent and the corresponding auxiliary agent to improve the polarity of the flax fiber. The selected low-melting point fiber PP is pretreated, and the PP fiber is treated by spraying coupling agent and corresponding auxiliary agents.
[0044] 2. Blend low-melting polymer fibers and flax fibers: Lay a layer of finely opened low-melting polymer fibers PP, then lay a layer of finely opened flax fibers, and alternately lay multiple layers of low-melting polymer fibers and Flax fibers, forming felt.
[0045] 3. Acupuncture the felt, then roll it up into strips.
[0046] 4. Heat the strip-shaped felt at 165°C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com