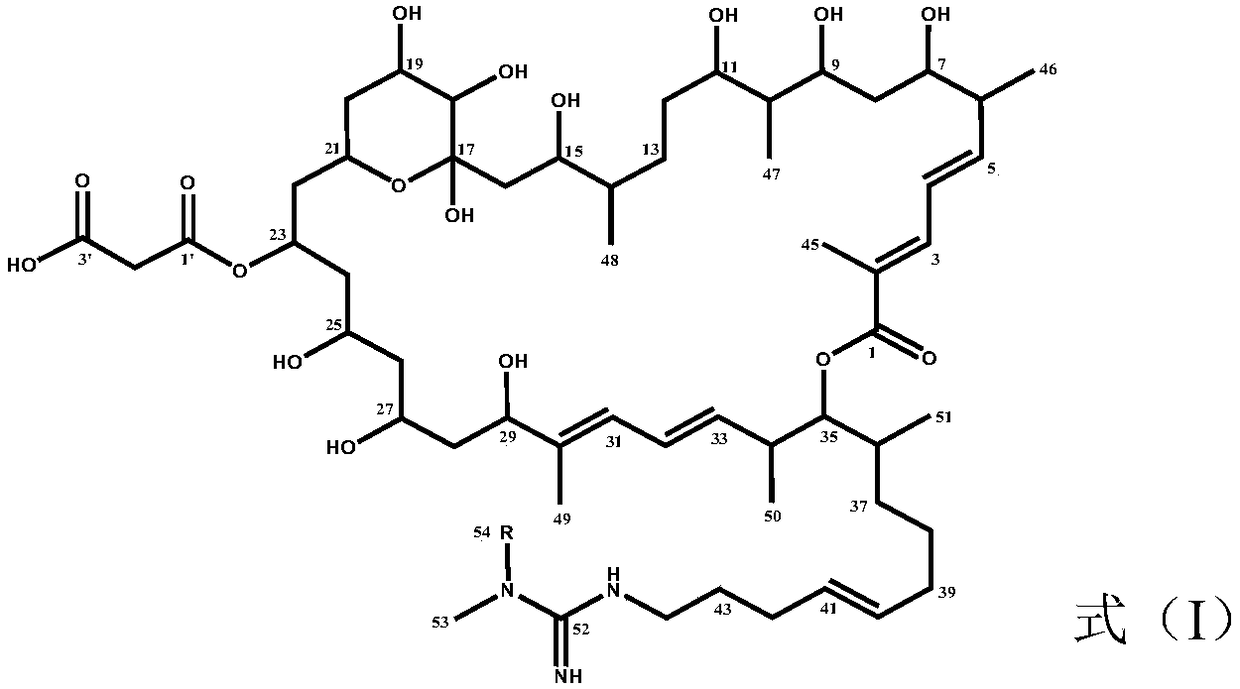
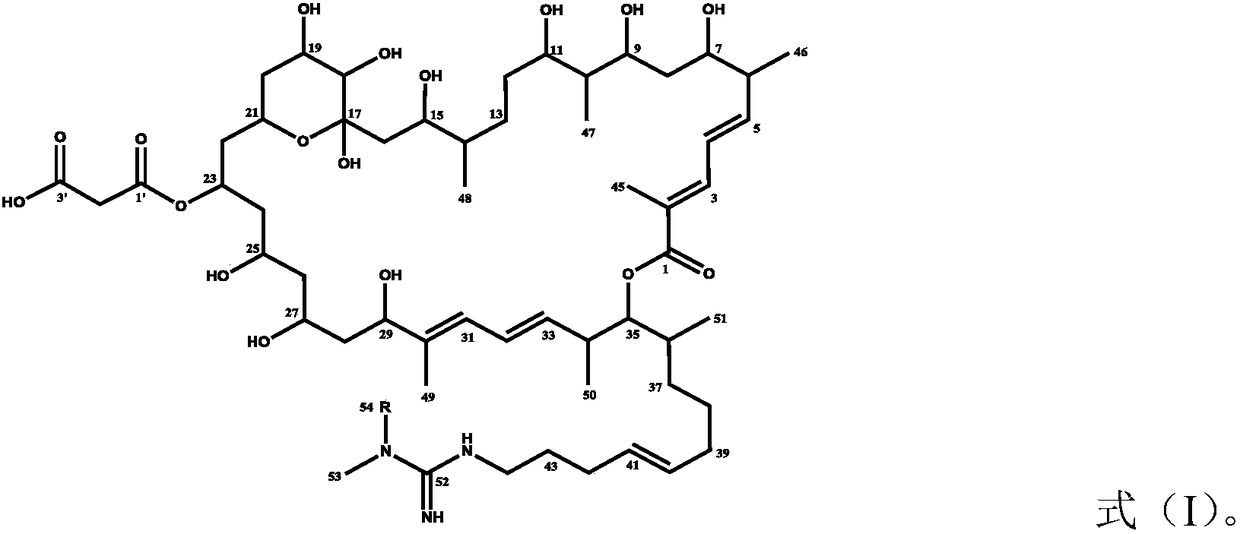
A method for inhibiting the growth of Plasmodium brassicae, a method for preventing and controlling clubroot of cruciferous crops, and the use of azamycin
A technology of cruciferous crops, Plasmodium brassicae, applied in the direction of biocides, plant growth regulators, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve growth and development disorders, nutrient absorption and water transport interruption, without ideal Measures and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] This example is used to illustrate the effect of using azamycin F3 to inhibit the growth of Plasmodium brassicae.
[0032] 1. Collection of Plasmodium brassicae
[0033] The diseased roots of cabbage, Chinese cabbage, cauliflower and rape that had clubroot were collected and planted in Jietou Town, Tengchong County, Yunnan Province, respectively, and the diseased root tissue sections were observed under a microscope. As a result, dormant sporangia and swimming sporangia were observed under the microscope. Resting spores were identified as Plasmodium brassicae.
[0034] Wash the collected fresh diseased roots and dry the surface moisture for later use. Squeeze 1g of the diseased root, try to avoid damaging the root tissue, release the spores and mix them with 50mL of sterile distilled water, filter through 15 layers of gauze, filter the filtrate through medium-speed filter paper again, put it in a 50mL centrifuge tube, and set it at 4500rpm Centrifuge for 10 min, disca...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This example is used to illustrate the effect of using azamycin F4 to inhibit the growth of Plasmodium brassicae.
[0043] 1. Collection of Plasmodium brassicae
[0044] With embodiment 1.
[0045] 2. The effect of azamycin F4 on the spores of Plasmodium brassicae
[0046] Follow the steps of Example 1, wherein the difference is that azamycin F4 is used instead of azamycin F3.
[0047] The results are shown in Table 2. The MIC values of azamycin F4 against Plasmodium brassicae were all less than or equal to 2.5 μg / mL, indicating that azamycin F4 had a strong inhibitory effect on Plasmodium brassicae.
[0048] Table 2
[0049] source of spores
[0050] Note: "—" means no inhibitory effect on the spores of Plasmodium brassicae was detected.
Embodiment 3
[0052] This example is used to illustrate the determination of the control effect of azamycin F3 on cabbage clubroot.
[0053] Choose healthy Chinese cabbage with consistent growth in the 8-9 leaf stage to measure the preventive and therapeutic effects.
[0054] 1. Preventive effect
[0055] Root irrigation with azamycin F3 (root irrigation at a concentration of 200 μg / mL), after 24 hours, the concentration of root irrigation inoculation was 1×10 5 Each / mL of the spore suspension of Plasmodium brassicae from Chinese cabbage prepared in Example 1, set sterile distilled water as the blank control, and the root irrigation volume of the three is 50mL / strain. After inoculation, they were placed in a 28°C incubator for moisturizing culture. Apply every 7 days.
[0056] 2. Therapeutic effect
[0057] The root irrigation inoculation concentration was 1×10 5 pcs / mL of the spore suspension of Plasmodium brassicae from cabbage prepared in Example 1, set sterile distilled water as a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com