Large Format Scanners and Scanning Methods
A scanning method and scanner technology, applied in the direction of image communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor compatibility and scalability, large volume, low cost, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding design difficulty, avoiding scanning accuracy, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Reference Document 1 discloses a technical solution of an A4 format flatbed scanner, with a scanning range of about 210mm*297mm, a scanning viewfinder width of about 210mm, and a total optical path of about 270mm. Among them, CCD linear image sensors (such as Toshiba's TCD2712DG CCD Linear Image Sensors: effective pixel number 7500*3Line) can be used.
[0051] Take the flatbed / flatbed scanner of A1 format as an example, the scanning range is about 840mm*594mm, and the scanning accuracy is 800DPI. If you use the existing unidirectional scanning mode (scanning viewfinder width 594mm) and use a CCD line image sensor, you need to use a CCD line image sensor with a pixel number greater than 594 / 25.4*800=18710 points (such as Toshiba’s TCD2964BFG CCD Linear Image Sensors: the number of effective pixels is 21360*6Line); the total optical path is about 270mm*(594mm / 210mm)=764mm. Due to the large total optical path, the scanner is relatively large, and the required scanning ill...
Embodiment 2
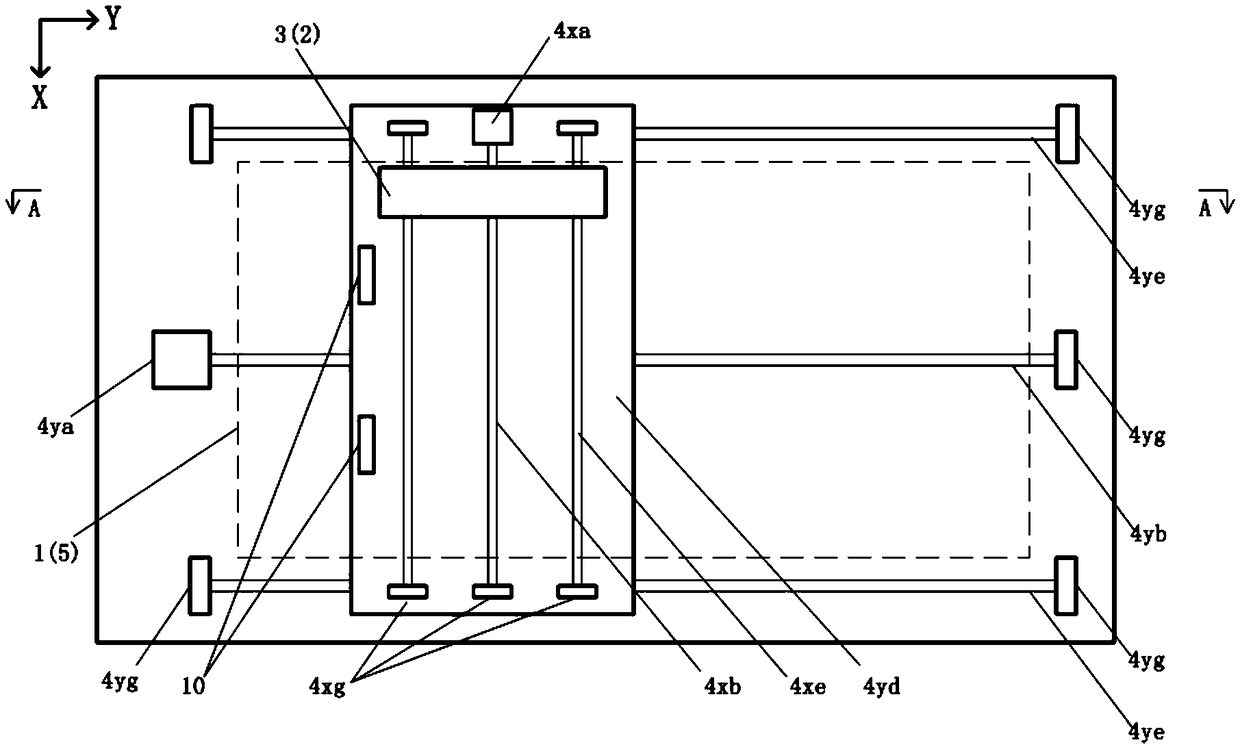
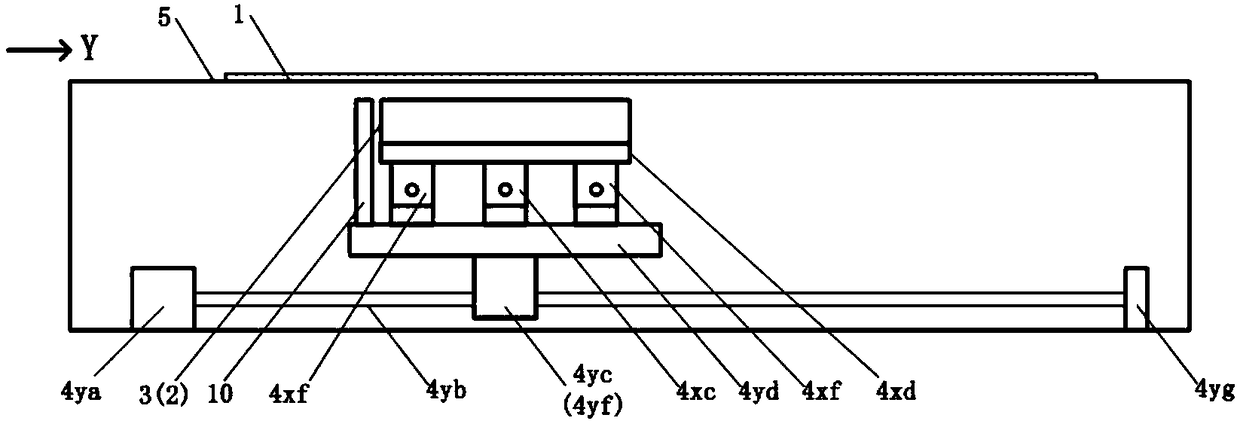
[0061] as attached image 3 , 4 As shown, for the paper-fed scanner, its specific structure is:
[0062] The section finder window 6 is located on one side of the original moving passage, and the paper feeding mechanism 7 includes several groups of rollers 8, which are respectively located on both sides of the original moving passage. At the front and rear ends, another part of the rollers 8b is set on the opposite side of the section viewfinder window, and the rollers 8 on both sides of the original moving passage cooperate with each other to transport the original 1 and flatten the original 1, so that the original 1 passes through the section sequentially viewfinder window 6, and the image sensor 2 sequentially scans in segments;
[0063] The transmission mechanism 4 is located on the same side of the section viewfinder window 6, including the X-axis stepping motor 4xa, the X-axis screw rod 4xb, the X-axis nut 4xc, the X-axis platform 4xd, the X-axis guide rail 4xe, the X-...
Embodiment 3
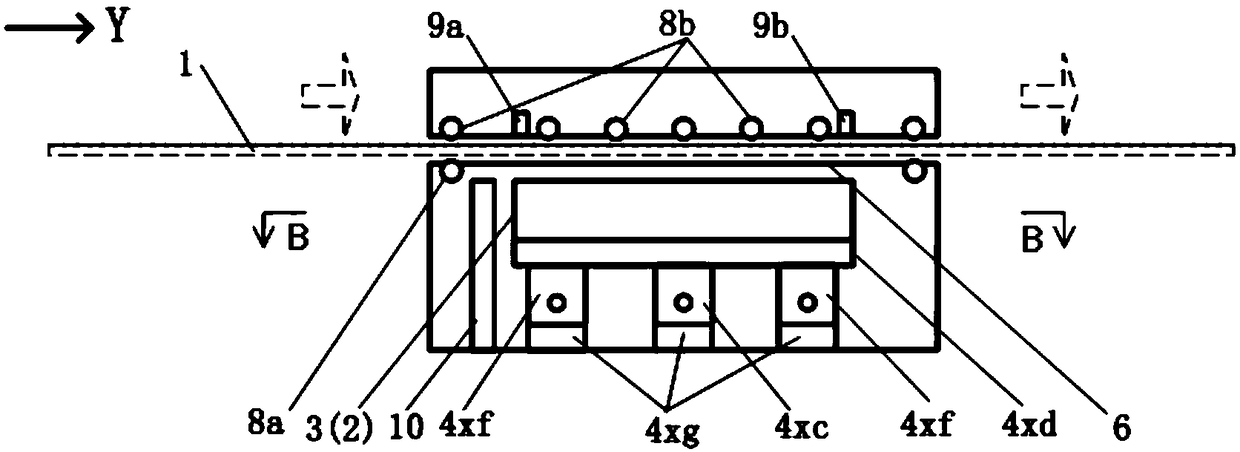
[0075] When the processing capacity of the image data processing system supporting the scanner is sufficient, a parallel scanning scheme of multiple scanning heads 3 can be adopted: that is, N scanning heads 3 are arranged side by side along the X-axis direction, and each scanning head 3 is arranged in parallel in the segmental scanning process. The section to be scanned is divided into N blocks along the X direction, and the moving range of each scanning head 3 can respectively cover the corresponding blocks; each scanning head 3 moves along the X-axis direction and is scanned by the image sensor 2 therein. The image of each block is then spliced into a complete scan section image through the image mosaic algorithm.
[0076] Such as Figure 8 , 9 As shown, taking three scanning heads 3a, 3b and 3c of the same specification arranged side by side at equal intervals on the X-axis platform 4xd as an example, the three scanning heads 3 move synchronously with the X-axis platfor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com