Monitoring device and monitoring method for steam dryness of laboratory and steam flooding experimental device
A monitoring device and laboratory technology, applied in measurement devices, humidity control, earthwork drilling, etc., can solve problems such as effect influence, large error, and inability to accurately measure steam dryness, and achieve automatic control and reduce personnel. The effect of workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
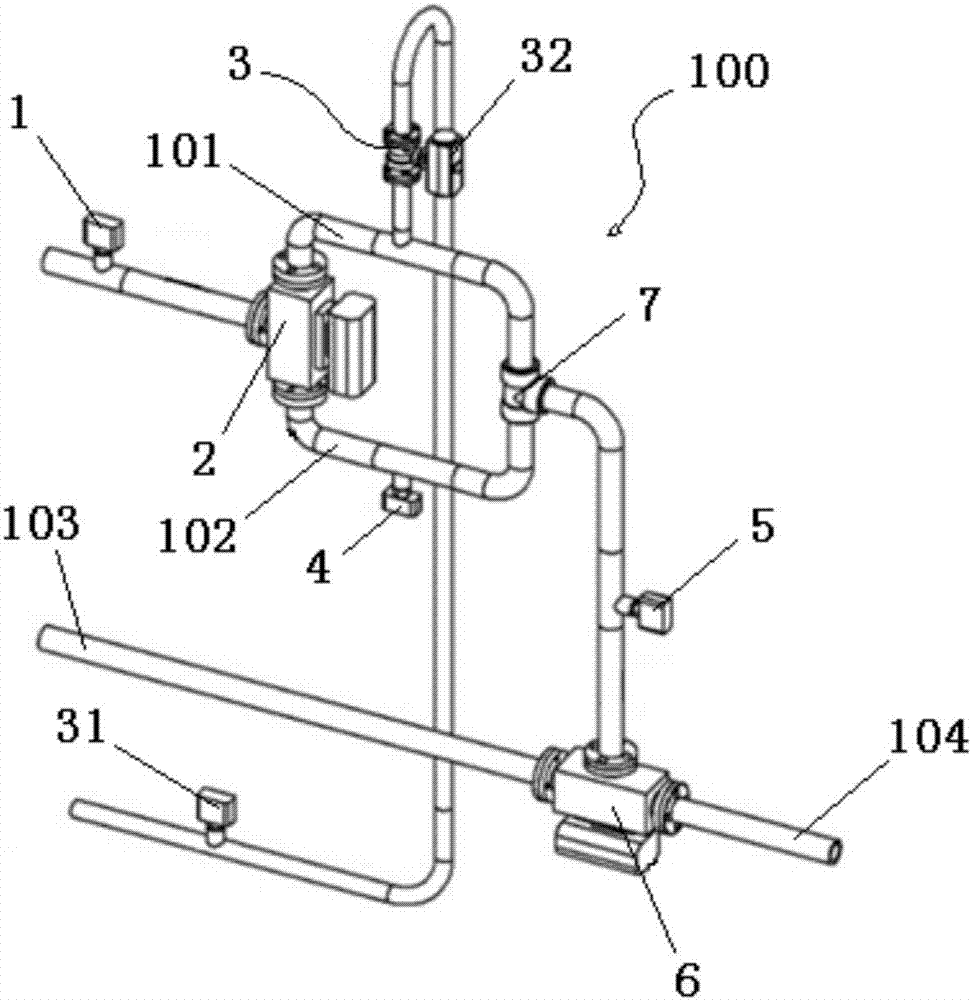
[0041] Such as figure 1As shown, the present invention provides a laboratory steam dryness monitoring device 100, which is used to monitor and control the steam dryness of the output steam, so that the output steam dryness accurately meets the set value. The laboratory steam dryness monitoring device 100 includes a first detection device 1 , a first electromagnetic three-way valve 2 , a water adding device 3 , a heating device 4 , a second detection device 5 and a second electromagnetic three-way valve 6 . The first detection device 1 is connected to the steam generator through a pipeline, and is used for detecting the steam dryness of the steam output by the steam generator. Preferably, the first detection device 1 adopts a fiber-optic steam dryness meter; the first detection device 1 has a measurement channel for steam to pass through. The fiber-optic steam dryness meter is one of the existing measuring devices for measuring steam dryness. It has high detection precision an...
Embodiment 2
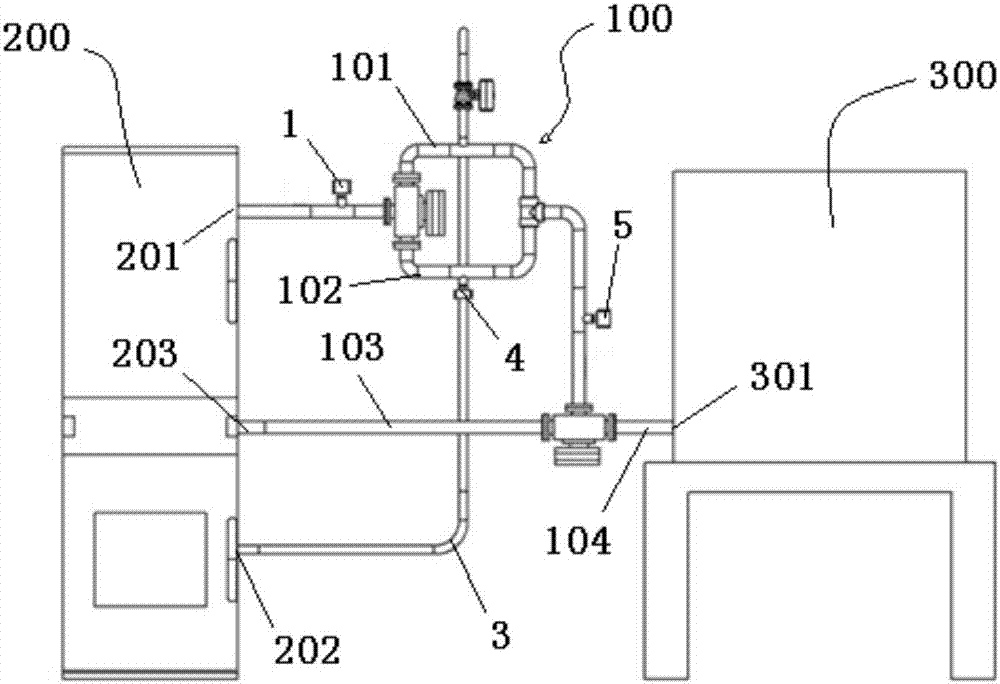
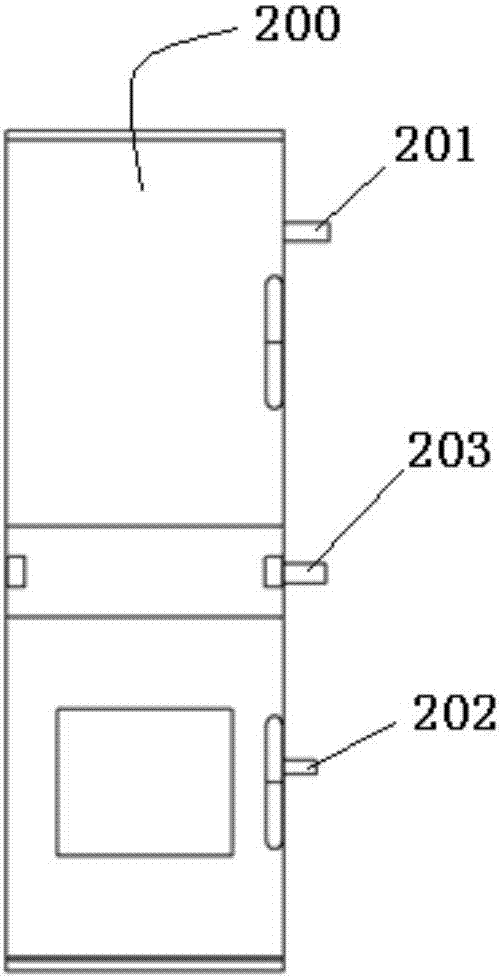
[0051] Such as figure 2 , image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides a laboratory steam flooding experimental device for performing steam flooding simulation experiments in the laboratory, which uses the laboratory steam dryness monitoring device 100 described in Embodiment 1, The laboratory steam flooding experimental device also includes a steam generator 200 and a steam flooding model 300 . The steam generator 200 can adopt existing technology, including a steam output port 201 , a soft water output port 202 and a steam recovery port 203 . The steam outlet 201 is connected to the first detection device 1 through a pipeline. The soft water output port 202 is connected to the water adding device 3 through a pipeline. The steam recovery port 203 is connected to the steam recovery pipeline 103 . The steam flooding model 300 can adopt an existing experimental model, which has a steam injection port 301 , and the steam injection port 301 is connected to the s...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for monitoring laboratory steam dryness, Figure 5 The steam parameter test devices in the figure represent the first detection device and the second detection device respectively; the injector model represents the injection of steam into the steam flooding model. The laboratory steam dryness monitoring method adopts the laboratory steam dryness monitoring device 100 described in Embodiment 1, comprising the following steps:
[0055] S1. Detect the steam dryness of the steam output from the steam generator 200 .
[0056] S2. Distribute steam according to the steam dryness value detected in step S1; if the detected steam dryness value is less than the set steam dryness value, then distribute the steam to the heating pipeline 102 to heat the steam; if If the detected steam dryness value is greater than the set steam dryness value, the steam is distributed to the water adding pipeline 101, and distilled water ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com