Method and system for analyzing influence mechanism of dislocation on ferroelectric materialdomain structure
A ferroelectric material and domain structure technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of difficult to directly measure the influence mechanism of dislocation, and achieve the effect of simple simulation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
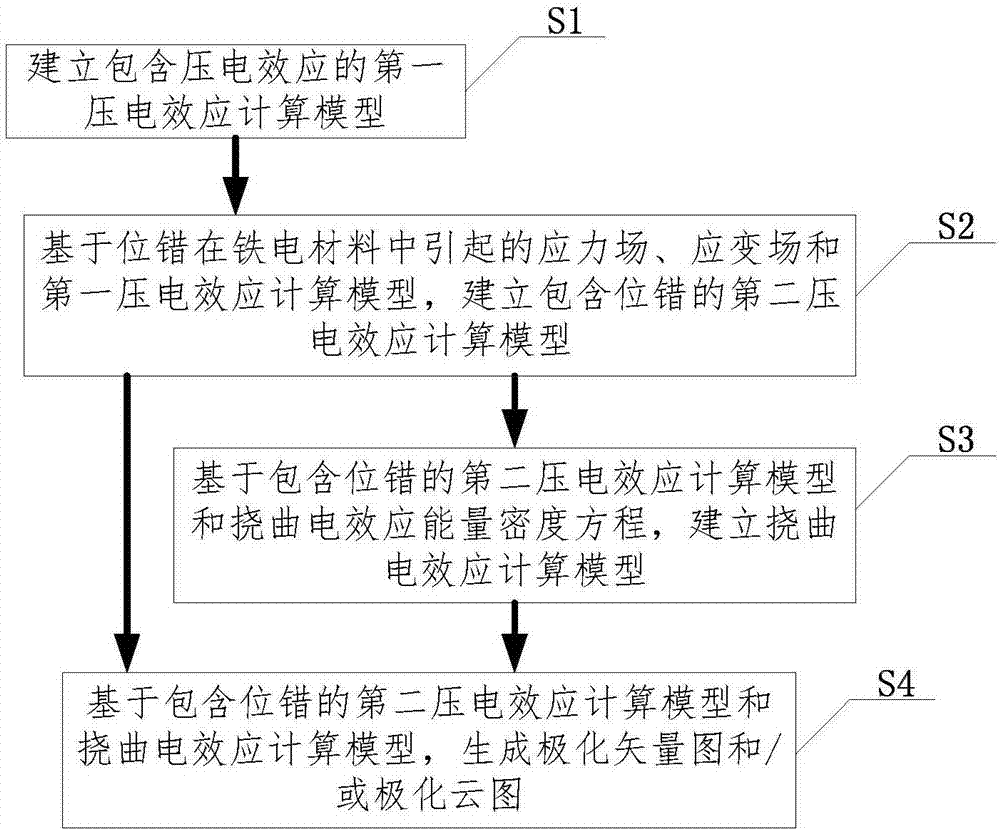
[0065] figure 1 It is a schematic flow chart of the analysis method for the mechanism of the influence of dislocations on the domain structure of ferroelectric materials provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for analyzing the influence mechanism of dislocations on the domain structure of ferroelectric materials provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes:
[0067] Step S1, establishing a first piezoelectric effect calculation model including the piezoelectric effect. In this step, firstly, calculate the first free energy density of the geometric model of the phase field, calculate the partial derivatives of the displacement field, electric field and polarization field according to the first free energy density, and obtain the constitutive equations of the displacement field, electric field and polarization field , further, multiply the equilibrium equations of the displacement field, electric field an...
Embodiment 2
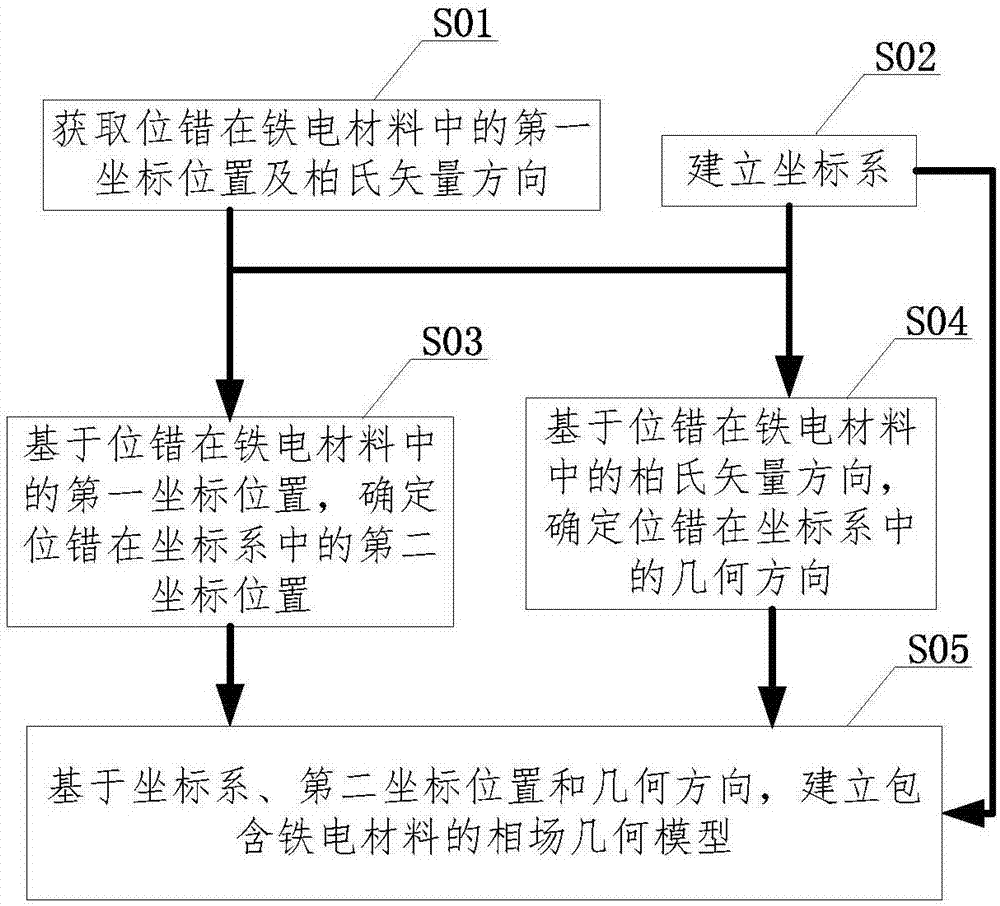
[0077] figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of establishing a phase field geometric model including ferroelectric materials according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0078] Such as figure 2 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1 of the present invention, before step S1, it also includes: establishing a phase field geometric model including ferroelectric materials, which includes:
[0079] Step S01, obtaining the first coordinate position and Burgers vector direction of the dislocation in the ferroelectric material.
[0080] In this step, the first coordinate position of a certain dislocation (there may be multiple dislocations in the ferroelectric material) in the ferroelectric material and the Burgers vector direction of the dislocation are obtained. The first coordinate position is the coordinate position of the dislocation in the ferroelectric material, the Burgers vector is the direction of the dislocation in the ferroelectric material, and the determinatio...
Embodiment 3
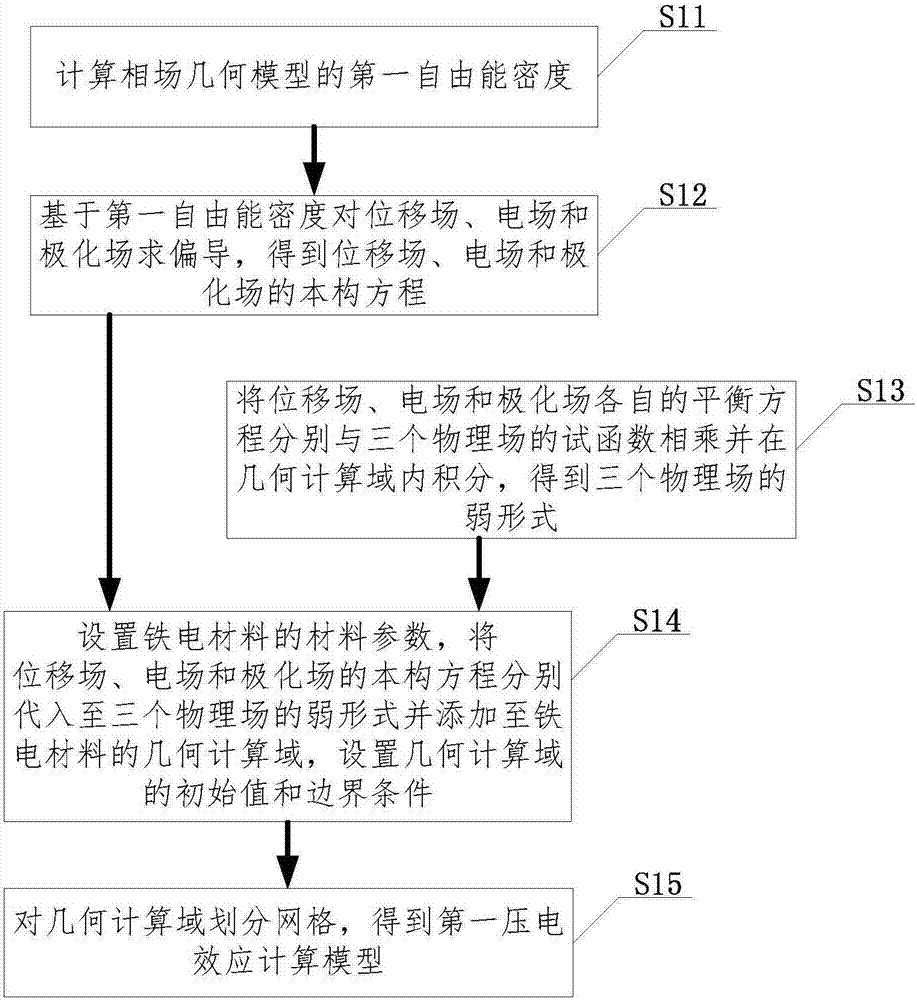
[0097] image 3 is a schematic flowchart of step S1 provided according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0098] Such as image 3 As shown, on the basis of the first embodiment of the present invention, the step S1 provided in the third embodiment of the present invention further includes:
[0099] Step S11, summing the bulk free energy density, elastic strain energy density, coupling energy density of polarization and strain, gradient energy density and electrostatic energy density of the ferroelectric material to obtain the first free energy density h of the phase field geometric model.
[0100] Specifically, the first free energy density h is calculated according to the following formula:
[0101] h=f landau +f strain +f coup +f grad +f elec (1.1)
[0102] Among them, f landau Indicates the bulk free energy density, f strain Indicates the elastic strain energy density, f coup Indicates the coupling energy density of polarization and strain, f grad Indic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com