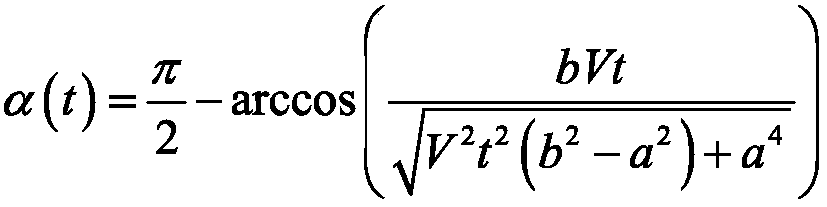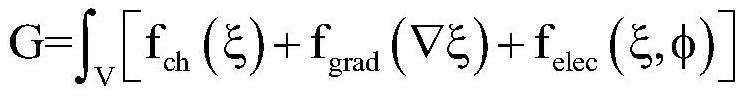Patents
Literature
58 results about "Phase field models" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phase field model is a mathematical model for solving interfacial problems. It has mainly been applied to solidification dynamics, but it has also been applied to other situations such as viscous fingering, fracture mechanics,, vesicle dynamics, etc.
Phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in welding process in transient state
ActiveCN106407623ASimplify the initialization processDeepen understanding of the evolution processSpecial data processing applicationsMolten stateEngineering
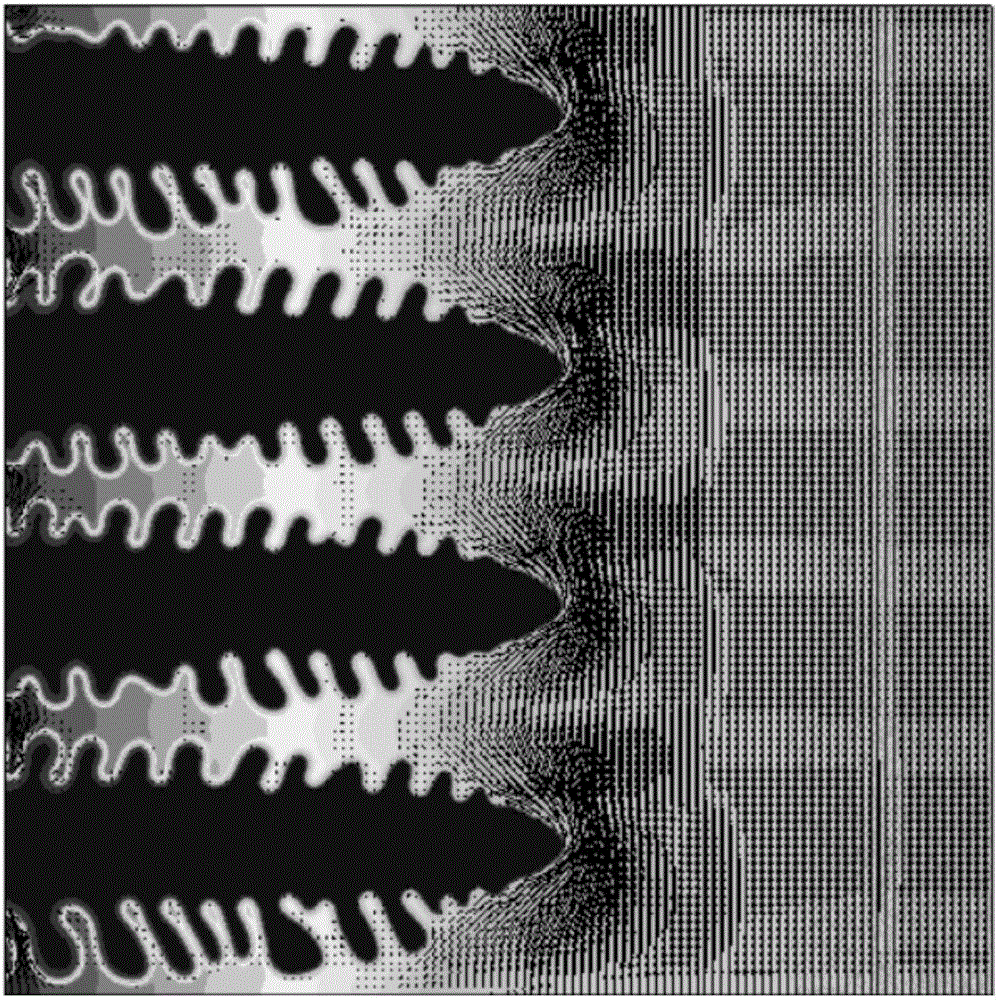
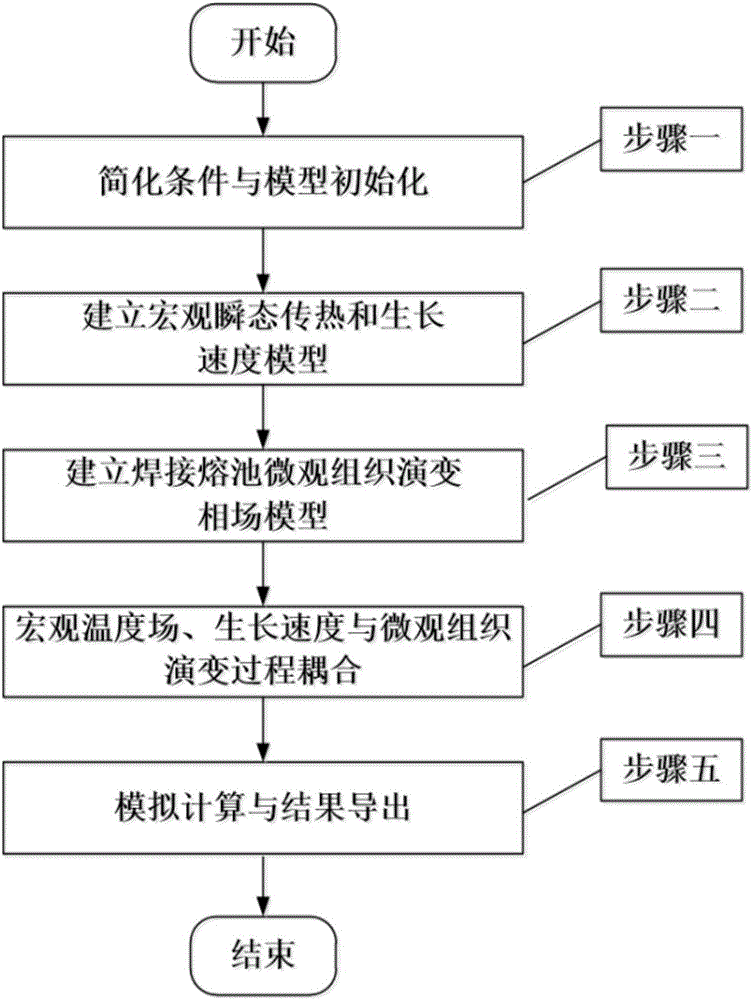
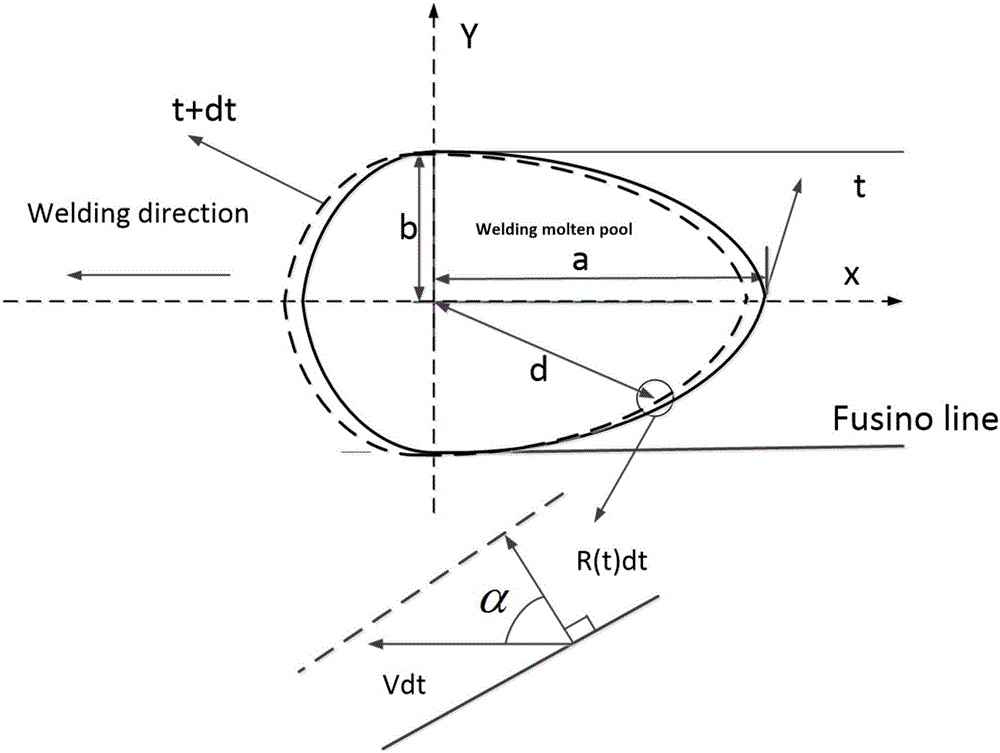
The invention provides a phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in a welding process in a transient state. The phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in the welding process in the transient state comprises the following steps of simplifying conditions and initializing a model, building the model according to parameters of a solidification process of a welding pool; building a macro transient heat transfer and growth rate model, wherein the welding pool is regarded to be formed by combining two semi-elliptical spheres, one semi-elliptical sphere is in a molten state and the other semi-elliptical sphere is in a solidified state in the welding process; building the macro transient heat transfer and growth rate model on the basis of hypotheses; building a microstructure evolution model and building a phase-field model of simulating microstructure evolution of the welding pool on the basis of the Ginzburg-Landau theory; and carrying out macro-micro coupling calculation, introducing a transient temperature gradient and a dendrite growth rate into the model, calculating a macro-micro coupled phase-field model and obtaining a microstructure evolution simulation result of the welding pool.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Real-time detection method of soft abrasive flow abrasive group
InactiveCN102830121AEfficient detectionAccurate extractionInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsField functionRunge–Kutta method
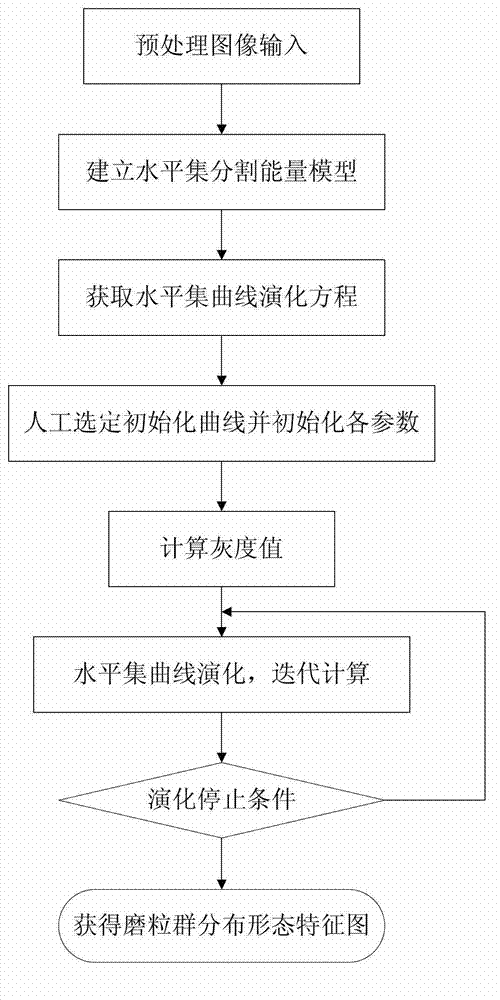
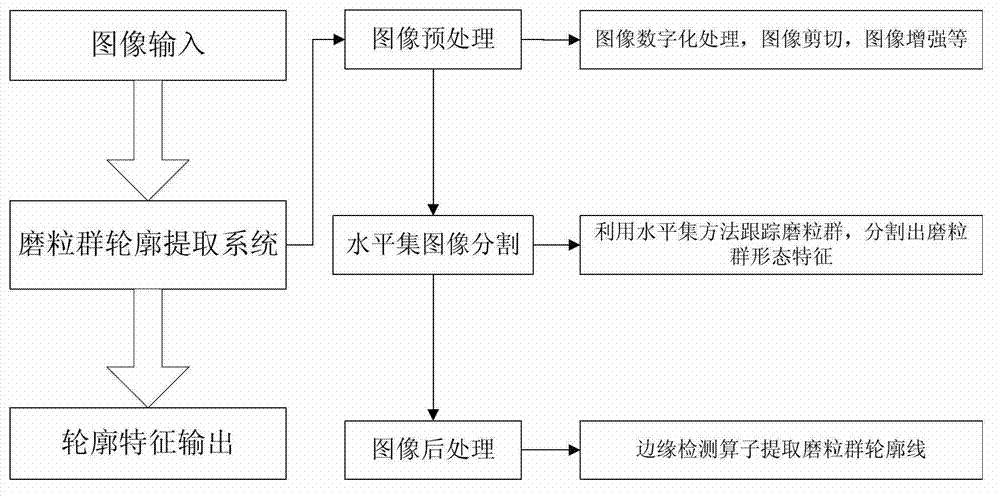
A real-time detection method of a soft abrasive flow abrasive group comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a phase-field model two-phase interface mixed energy equation according to the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group, also establishing a control equation of the phase-field function evolution, finally approximating a viscous phase and a surface pressure phase by a traditional second order center difference scheme, performing spatial discretization reconstruction of the control equation by a fifth order WENO scheme, performing discretization in the time direction by a Runge-Kutta method with a TVD property, and thus solving the two-phase interface to obtain a theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution; 2) performing real-time image processing of the distribution area of the abrasive group in a constraint channel obtained by a soft abrasive flow image acquisition device according to the obtained theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution, and thus extracting a contour feature of the abrasive group distribution area to obtain the change condition of the abrasive group dynamic boundary. The invention effectively detects the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for simulating dendritic crystal growth of laser welding pool
InactiveCN107309543ADeepen understanding of evolution mechanismDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMelting tankCoupling
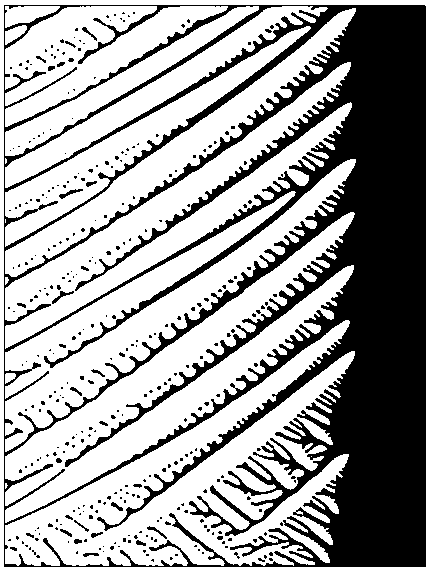
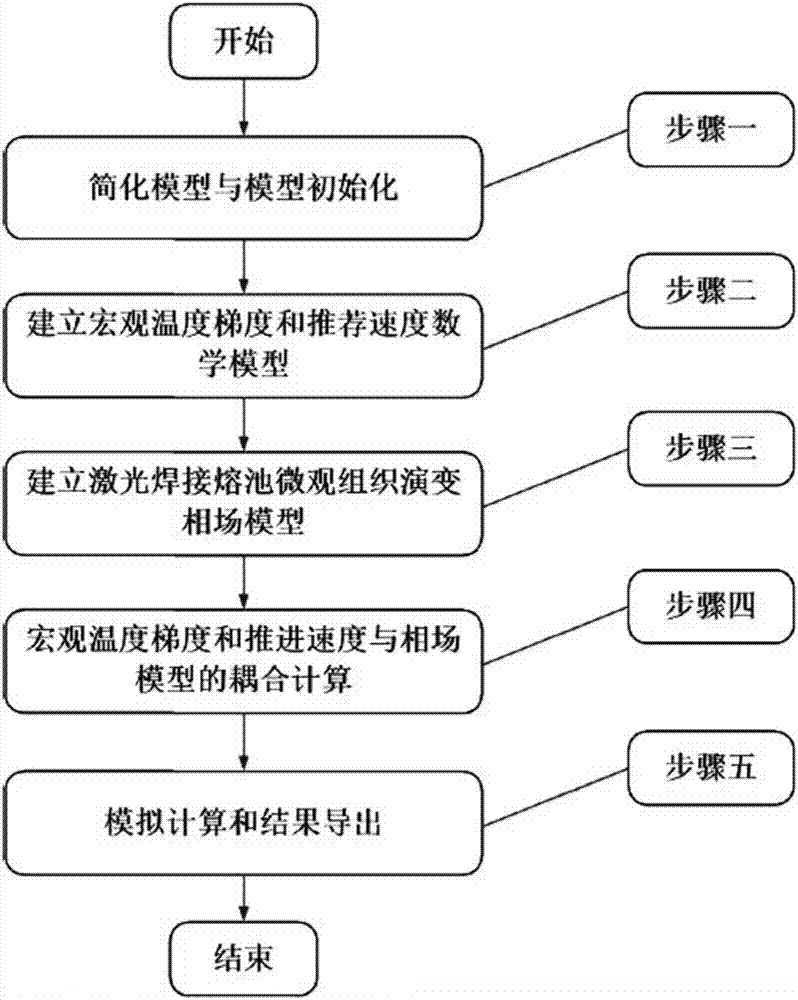
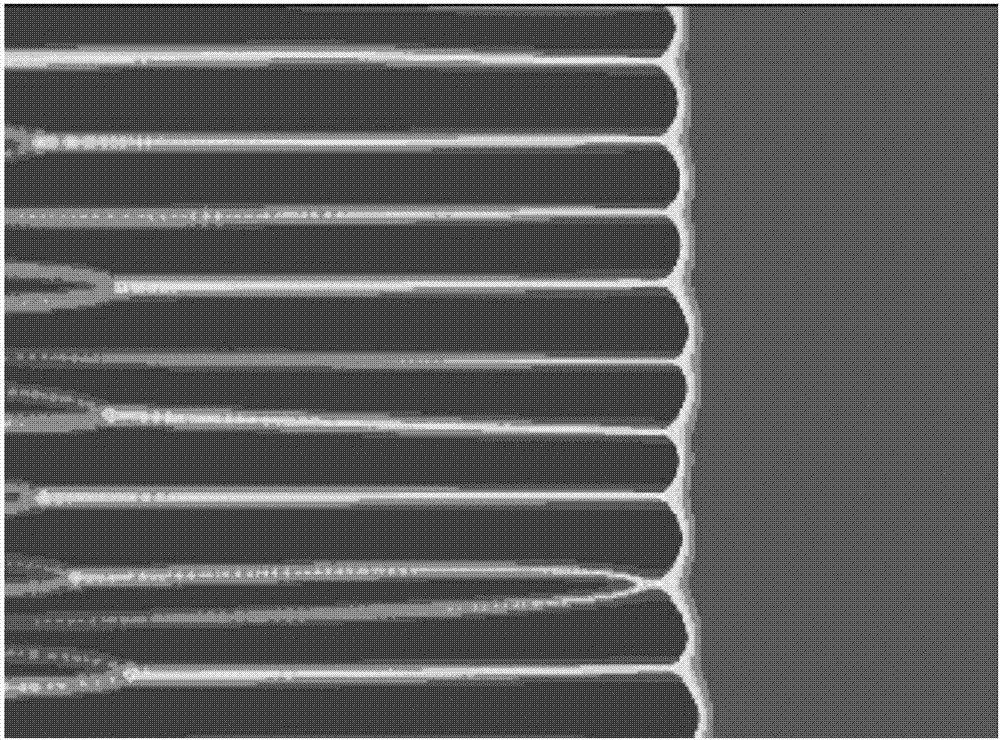
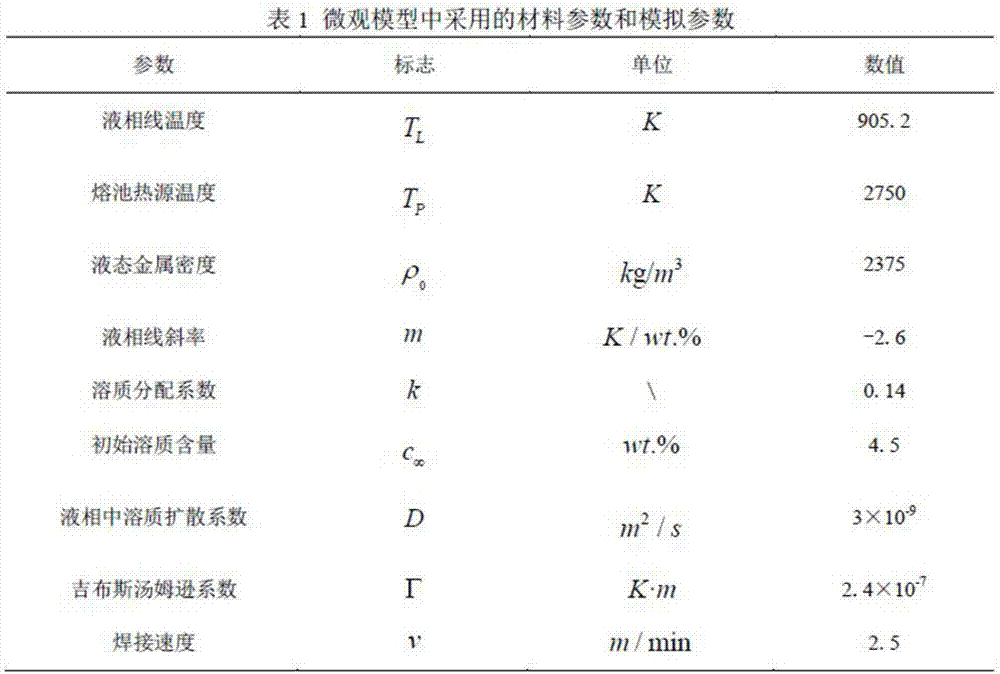
The invention discloses a method for simulating dendritic crystal growth of a laser welding pool. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, simplifying conditions and initializing a microcosmic model; 2, establishing a macroscopic model of the temperature gradient and propulsion speed; 3, establishing a phase-field model of dendritic crystal growth; 4, carrying out macroscopic-microcosmic coupling calculation; and 5, carrying out analog computation and exporting results. According to the method, the simulation of the dendritic crystal growth and evolution in the solidification process of the laser welding pool can be quantitatively carried out, the dendritic crystal growth process in the solidification process of the laser welding pool can be dynamically reproduced, so that deepening understanding of the microstructure evolution mechanism of the laser welding pool is facilitated, and a foundation is laid for researching the solidification process of the laser welding pool and optimizing the welding process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for researching influence on formation of surface microstructure on basis of irradiating different materials by laser
InactiveCN108318485AShort processing cycleProcessing method is easy to controlMaterial analysis by optical meansNanotechnologyField methodsHeat conducting
The invention relates to a method for researching influence on formation of a surface microstructure on the basis of irradiating different materials by laser. The method comprises the following steps:irradiating a silicon substrate by utilizing femtosecond laser and enabling the silicon substrate to form surface bulges; 2, based on phase field model theory, establishing a mathematic model and performing simulated analysis on a silicon substrate bulge forming experiment; 3, selecting other material substrates with different heat-conducting coefficients and repeating the step 1 and the step 2 to obtain the bulge forming rules of different material substrates. The silicon substrate is irradiated by the femtosecond laser to form surface bulges, and the laser forming silicon-based surface formis simulated and predicted by using a three-dimensional numerical model, namely a phase field method, so that invention thought whether the bulges formed by irradiating other materials by the femtosecond laser accords with the same forming rule or not is provided.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
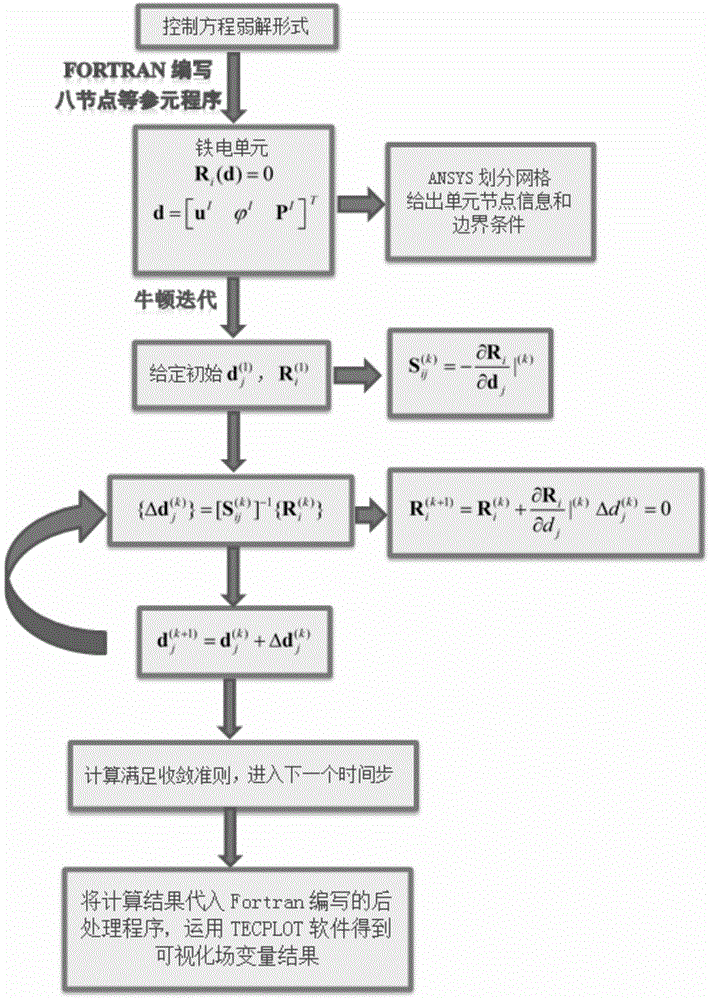
Finite element prediction method of electrode-containing ferroelectric single crystal based on phase-field method analysis
ActiveCN104361167AClear understanding of failure behaviorSimple processSpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldSingle crystal
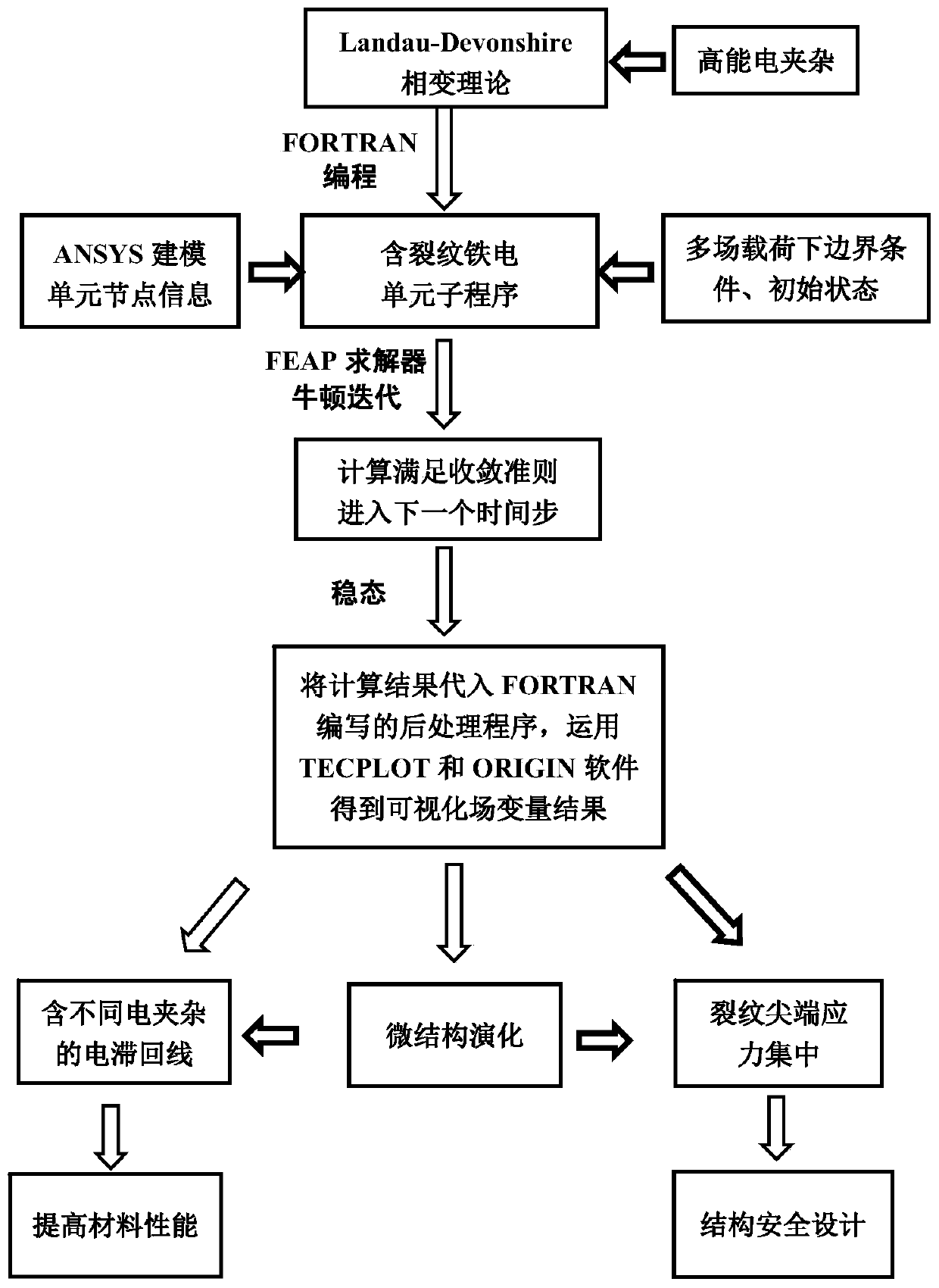
The invention discloses a finite element prediction method, under the action of force-electricity-heat multi-field coupling, of electrode-containing ferroelectric single crystal based on phase-field method analysis. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a new phase-field model with the multi-field coupling based on a Landau theory and an expansion interface model; obtaining the model establishment and the grid division of the electrode-containing ferroelectric single crystal by using ANSYS finite element software, and extracting node information and unit information; importing the obtained node information, the obtained unit information and considered different boundary condition information, and realizing a solution to the force-electricity-heat nonlinear coupling problem of the electrode-containing ferroelectric single crystal by using an FEAP fast solver; importing field variables which are obtained through FEAP finite element solution into a postprocessing program which is written by Fortran, and obtaining visual field variable results by using TECPLOT software. According to the method provided by the invention, not only is the process simple, but also the adaptability and the stability are good; a commercial finite element program can be developed to flexibly adapt to problem changes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
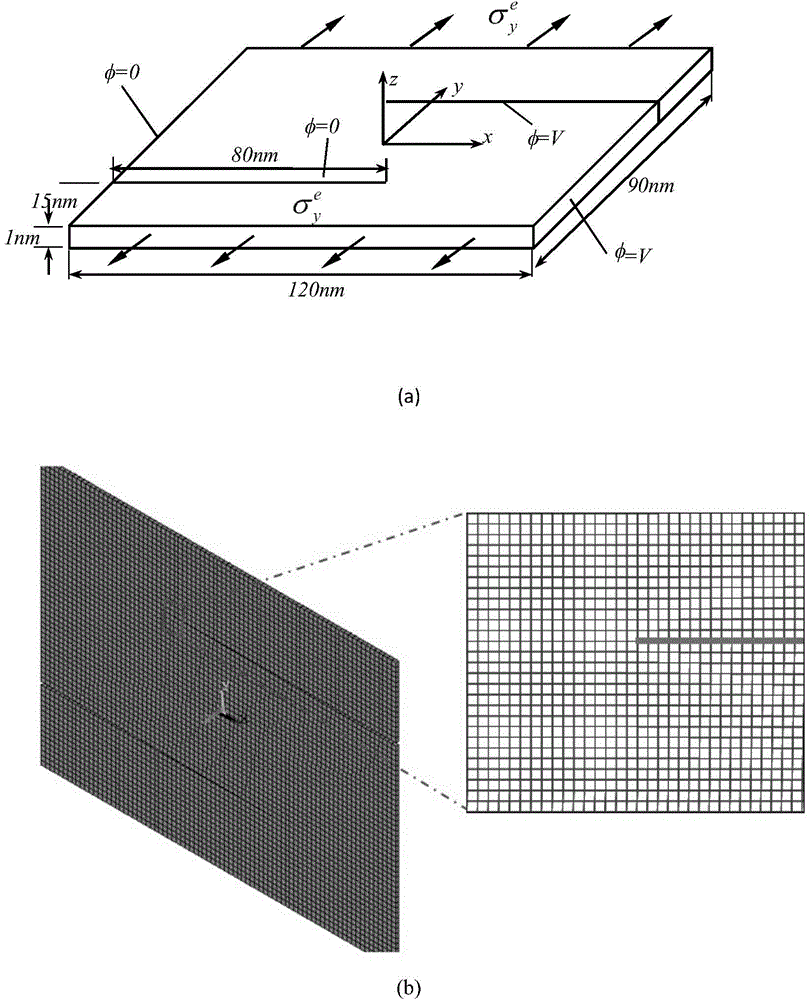
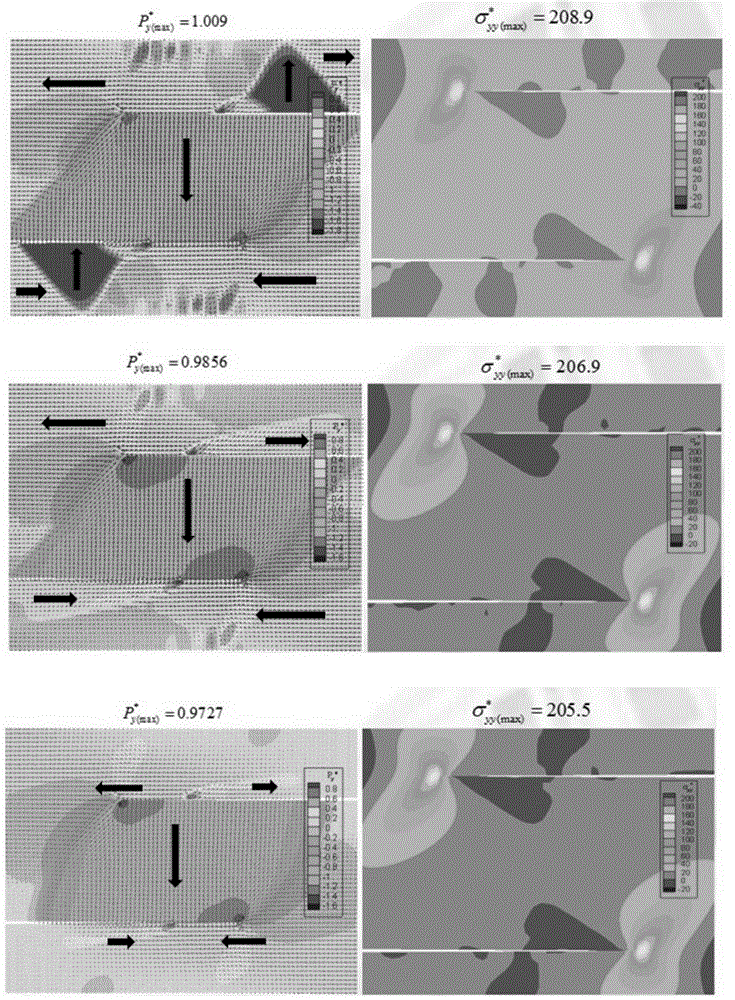
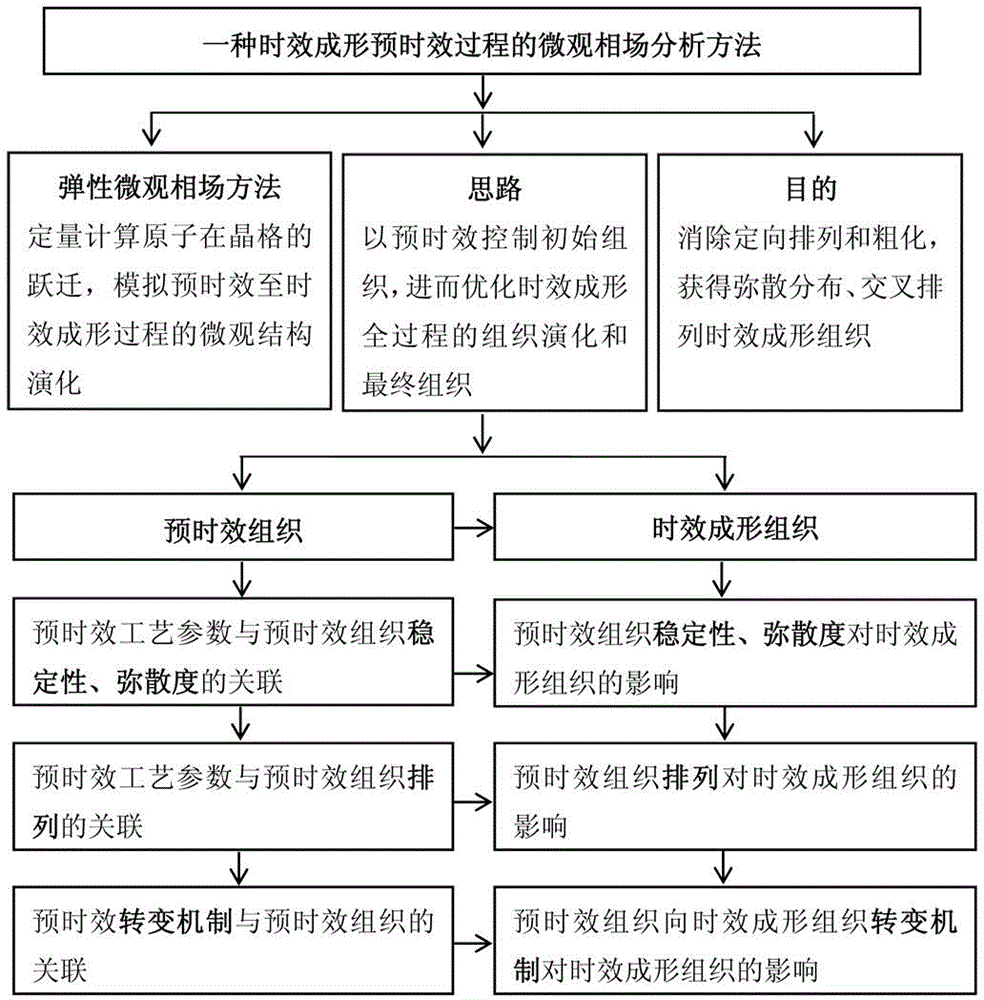
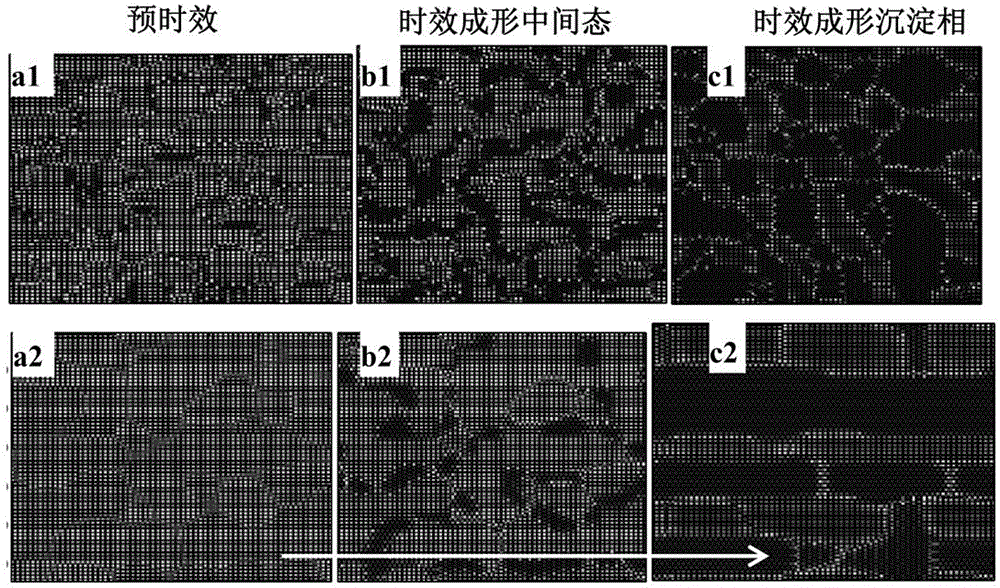
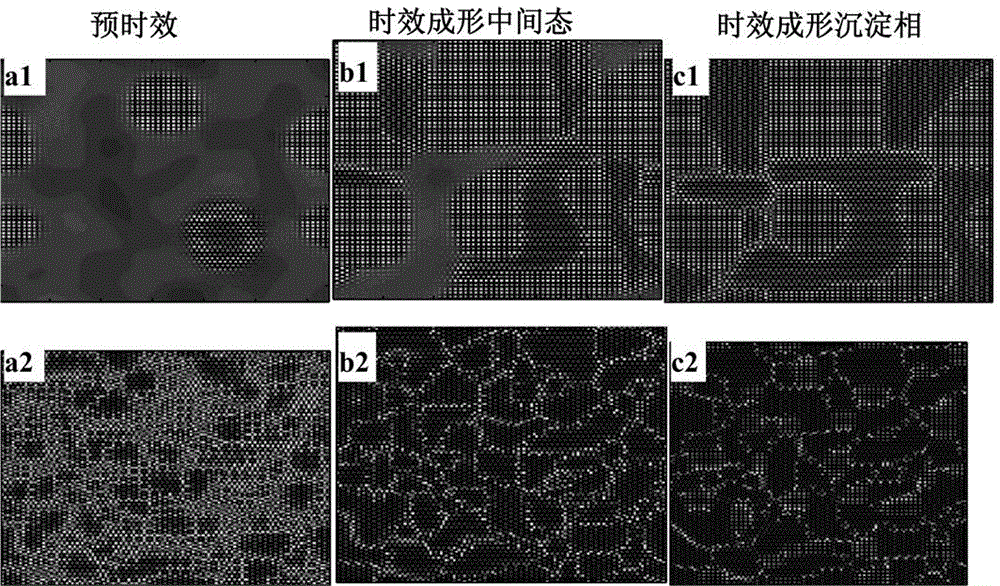
Microcosmic phase field analysis method in age forming and pre-ageing process
The invention discloses a microcosmic phase field analysis method in the age forming and pre-ageing process. A phase field model with the atomic scales of a macroscopic / nano stress field coupled is adopted, pre-ageing tissue hereditary of age forming is simulated, the influence rule of a pre-ageing tissue forming mechanism to a pre-ageing tissue structure is analyzed according to different precipitation tissue transformation mechanisms, the influence of the pre-ageing tissue forming mechanism and the mechanism used for transforming pre-ageing tissue to age forming tissue on the hereditary effect is obtained, and the response relation of the age forming tissue dispersity and layout is obtained. The method includes the step of first pre-ageing tissue control and the step of the hereditary effect of the second pre-ageing tissue on the age forming tissue. According to the method, the age forming precipitated phase early-stage shape is changed fundamentally, hence, age forming ending tissue is optimized, crystalline grain largeness and orientation arrangement are eliminated, and the tissue shape of dispersion distribution and cross arrangement with the refined crystalline strengthening effect and the dispersion strengthening effect is achieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
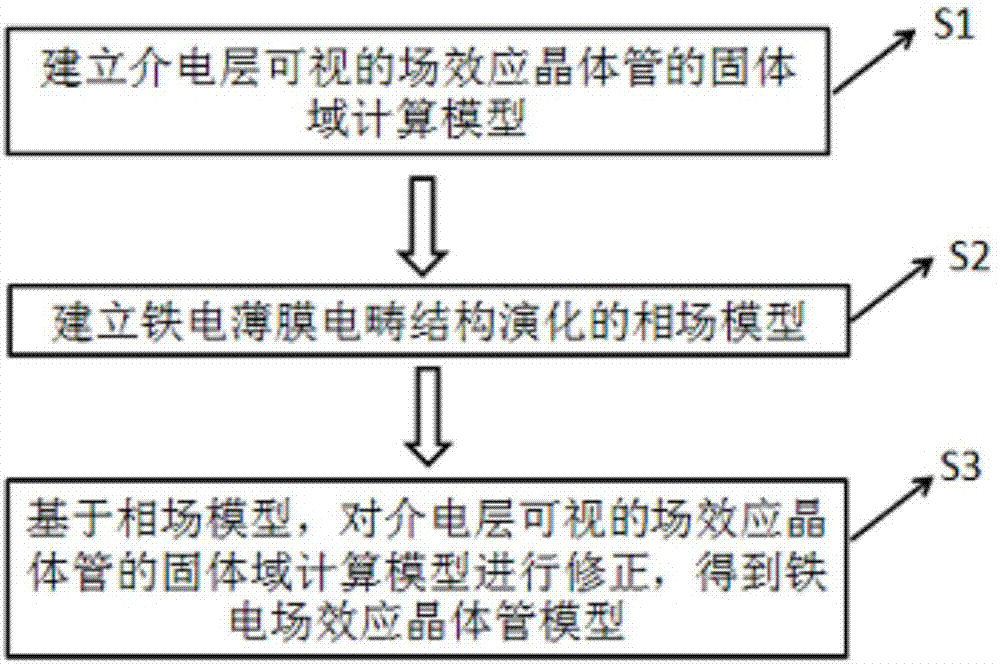
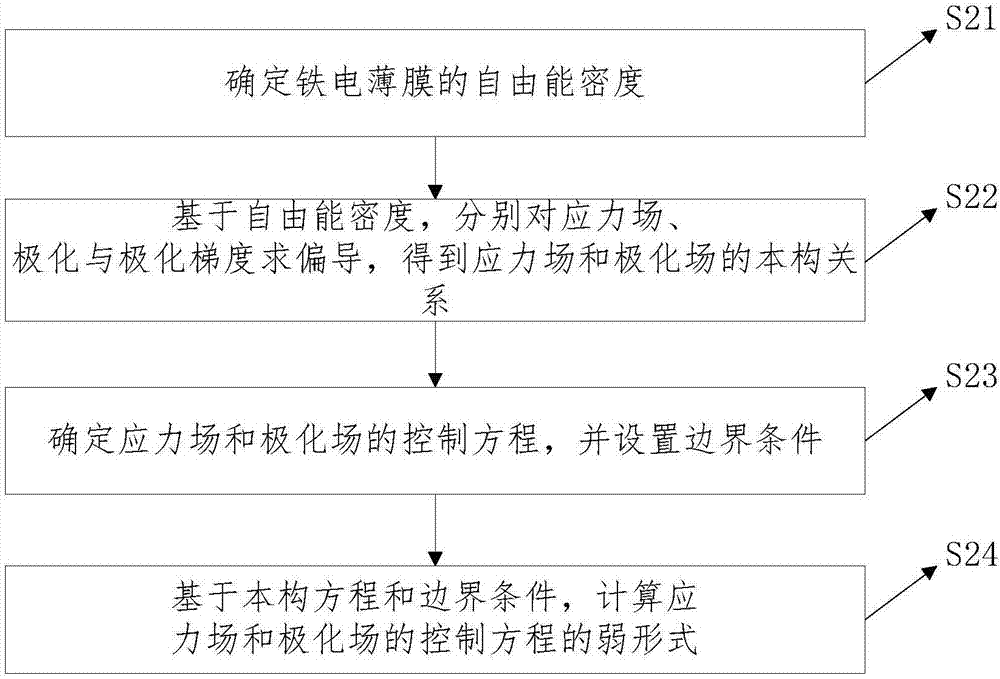
Building method and system for ferroelectric field effect transistor model
ActiveCN107423463AAvoid failureSimulation is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsCharge carrierElement modeling
The invention relates to a building method and system for a ferroelectric field effect transistor model, and belongs to the technical field of finite element modeling. The method comprises the steps of building a solid domain calculation model of a field effect transistor with a visible dielectric layer; building a phase field model of an electric domain of a ferroelectric film; and based on the phase field model, performing correction on the solid domain calculation model to obtain the ferroelectric field effect transistor model. Therefore, the electric domain evolution process of the dielectric layer under the action of an electric field can be accurately simulated and the domain structure and the domain switching condition of the dielectric layer can be observed; and moreover, the reflection of the macro-performance of the transistor and the potential distribution and carrier concentration distribution conditions under different domain structures can be simulated.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
SON (Silicon on Nothing) deformation mechanism study method based on phase field model at high temperature
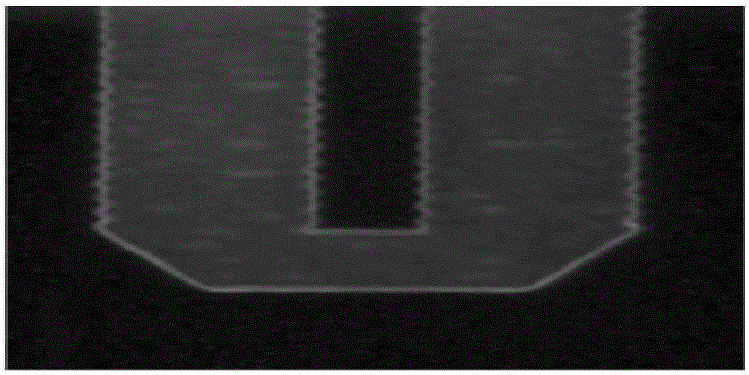
ActiveCN105956249AObserve molding changesEffective Dynamic Deformation ProcessSpecial data processing applicationsStudy methodsAtomic diffusion
The invention discloses an SON (Silicon on Nothing) deformation mechanism study method based on a phase field model at a high temperature. The method comprises the following steps of 1, putting a sample, i.e., an SON material at a certain temperature so that the sample becomes soft, and then making the sample into a U-shaped cylindrical hole shape; 2, putting the SON material into a high-temperature environment to be processed for several minutes for obtaining the SON form change state in different time periods; and 3, building a system model of the SON at the high temperature. According to the method, the SON deformation mechanism at the high temperature is studied by the method of integrating the experiment study and the simulation model for the first time. The SON forming process is controlled by using the high-temperature atomic diffusion motion; through the simulation model, the SON forming change can be more directly observed; and thus, a novel idea for processing the SON is provided.
Owner:嘉兴华吉环保科技有限公司
Universal phase field method for simulating different failure modes of a brittle material
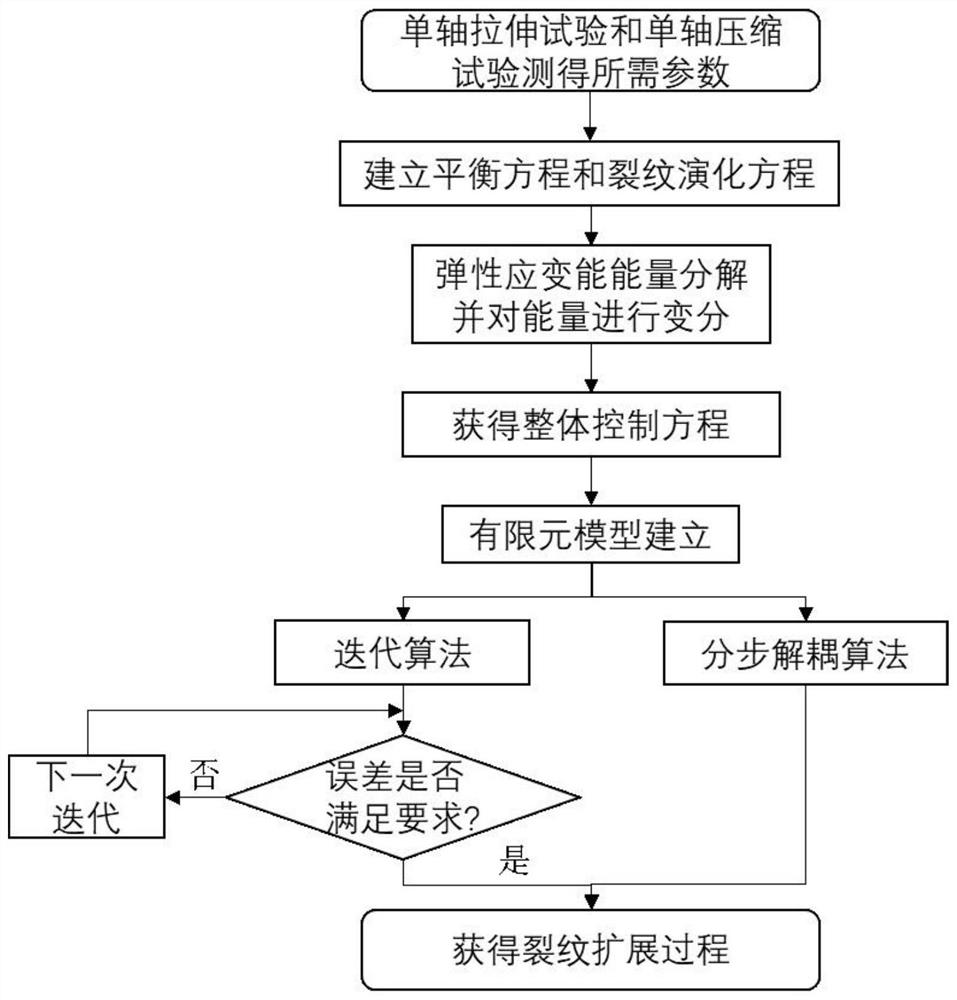
ActiveCN112051142ASimulation is accurateSolve the problem of inaccurate prediction of crack development directionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUniaxial compressionElement model
The invention discloses a universal phase field method for simulating different failure modes of a brittle material. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining material parameters requiredby a numerical simulation process through a uniaxial tensile test and a uniaxial compression test, substituting the measured material parameters into an established finite element model, carrying outenergy decomposition on the elastic strain energy of the test sample, carrying out variation on the energy, further establishing a universal balance equation and a crack evolution equation so as to obtain an overall control equation, and solving by adopting an iterative method or a distributed decoupling algorithm, so that accurate simulation of the crack propagation process, the crack propagation direction and the crack propagation path of the brittle material under complex stress is realized. According to the invention, the application range of a phase field model is greatly expanded; the simulation precision of the crack propagation process is greatly improved, and the problem of inaccurate prediction of the crack development direction of a traditional model is solved; and the solvingefficiency is improved, and the risk of non-convergence in the iterative solving process is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
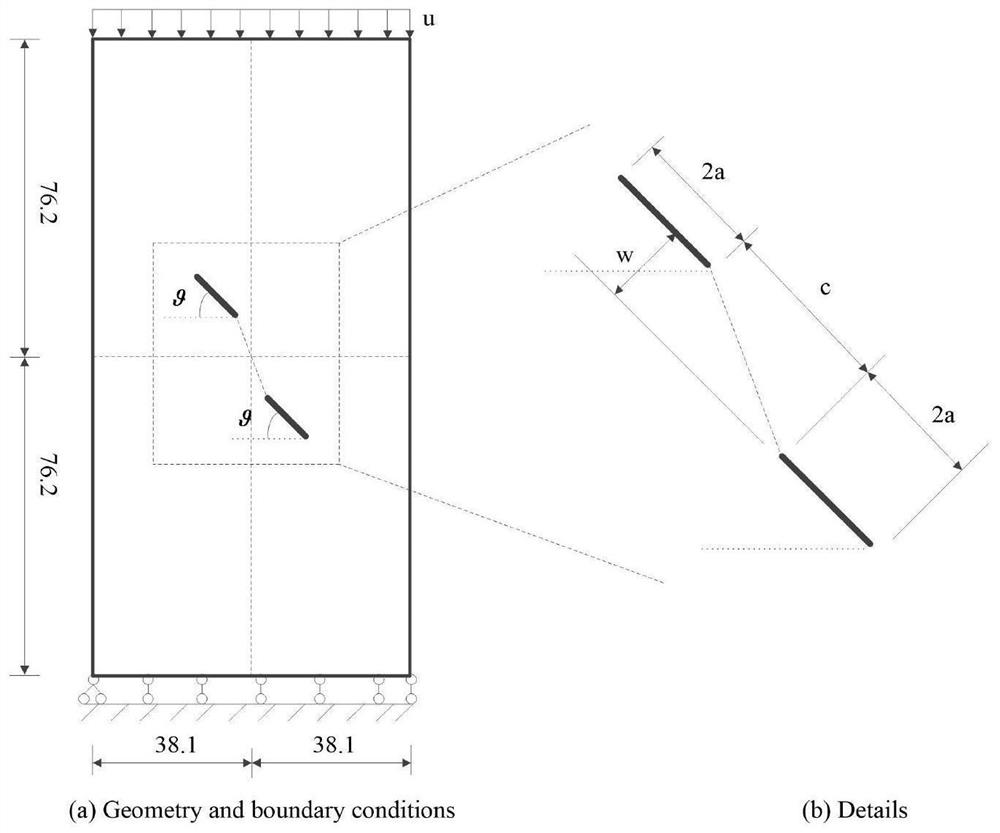
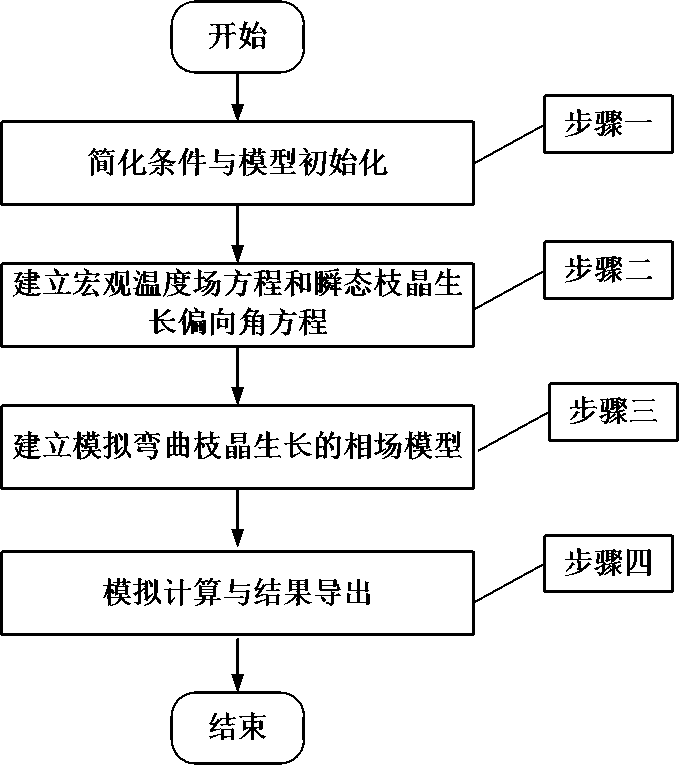
Phase-field method-based bending dendritic crystal growth simulation method
InactiveCN108254485ADeepen understanding of the evolution processChemical methods analysisProcess optimizationField methods
The invention relates to a phase-field method-based bending dendritic crystal growth simulation method. The phase-field method-based bending dendritic crystal growth simulation method comprises the following steps: simplifying conditions and initializing a model; establishing a macroscopic temperature field equation and a transient dendritic crystal growth deviation angle equation; establishing amicrostructure evolution model and establishing a phase field model for simulating bending dendritic crystal growth based on a Ginzburg-Landau theory; and performing macroscopic-microcosmic coupling calculation, introducing a macroscopic temperature field and a dendritic crystal growth deviation angle into the field phase model, and calculating the growth process of the bending dendritic crystal to finally obtain the shape of the bending dendritic crystal. According to the phase-field method-based bending dendritic crystal growth simulation method, formation of the bending dendritic crystal inthe solidification process can be simulated and predicted quantitatively, the formation process of the solidified microstructure dynamically reappears, deep understanding of the evolution process ofthe solidified microstructure is facilitated, and basis is laid for microstructure evolution research and process optimization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
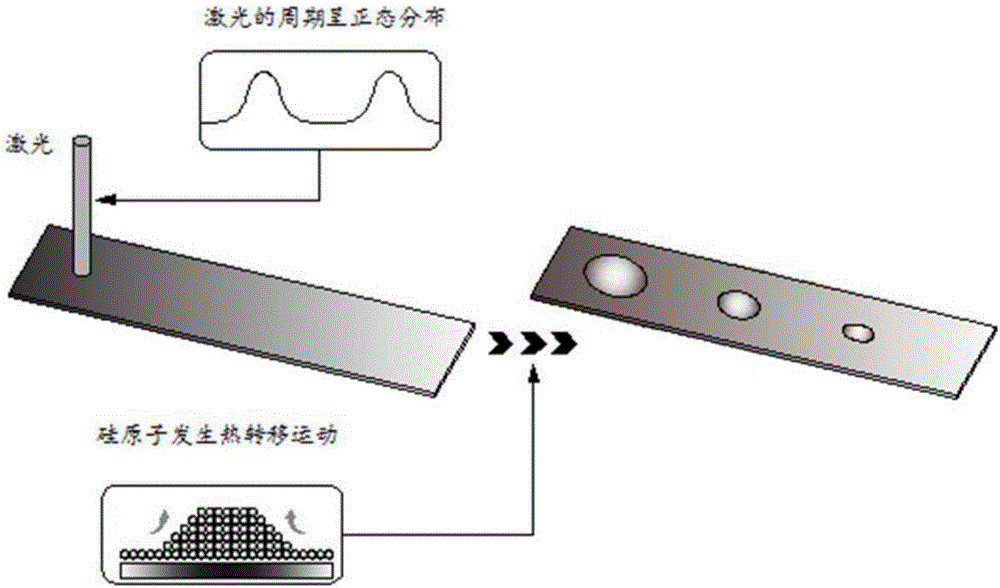
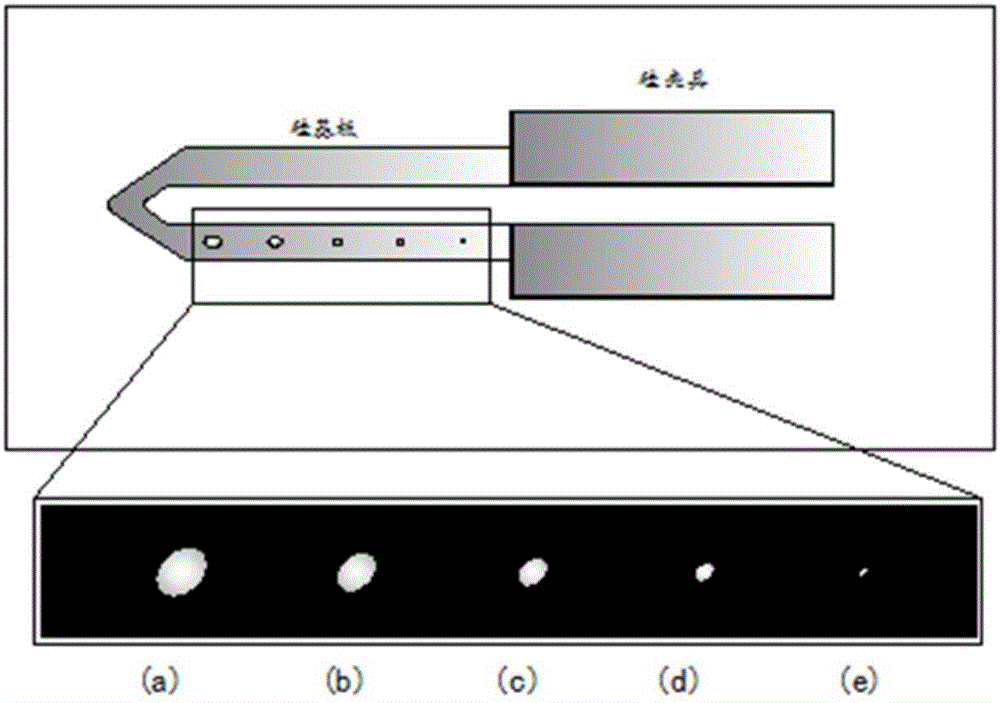
Phase-field-model-based study method of using laser to control silicon substrate surface morphology
The invention discloses a phase-field-model-based study method of using laser to control silicon substrate surface morphology. The method comprises the first step of adopting a silicon clamp to clamp a silicon substrate with a micro-nano structure under an atomic force microscope; the second step of using the laser to irradiate a suspending end of the silicon substrate for seconds, and observing the silicon substrate surface morphology of the silicon substrate and measuring the corresponding dimension; the third step of simulating a silicon atom diffusion behavior based on irradiation of the laser and the evolution process of the silicon substrate surface morphology of a nano structure under a phase-field model.
Owner:芜湖数字信息产业园有限公司
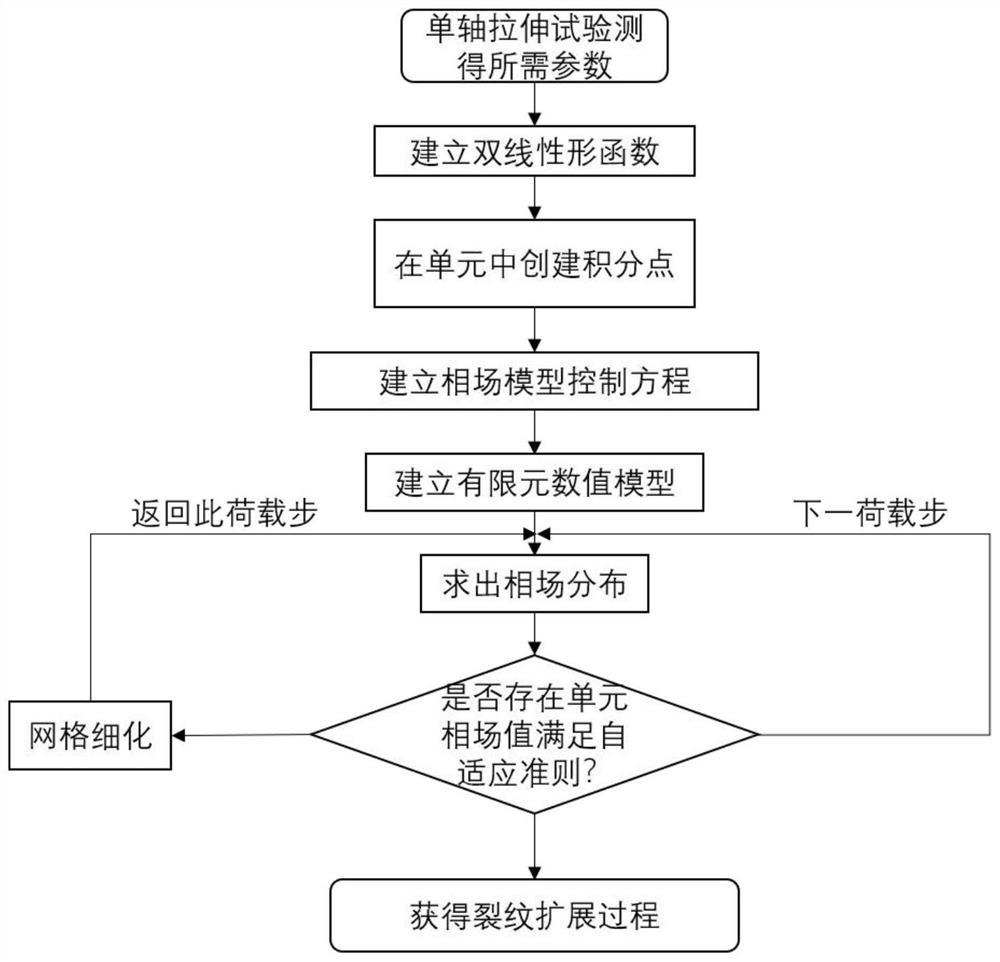
Bilinear adaptive phase field method for simulating brittle material damage
ActiveCN112036060ASolve the problem that it is difficult to rationalize the sub-gridImprove division efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCrazingClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a bilinear adaptive phase field method for simulating brittle material damage, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining material parameters required by a numerical simulation process through a uniaxial tensile test, creating a bilinear quadrilateral unit or a bilinear triangular unit, and establishing a phase field model control equation, establishing a finite element numerical model and endowing the finite element numerical model with material parameters, boundary conditions and finite element grids so as to solve a control equation to obtain phase field distribution, judging whether a unit needs to be adaptively divided or not according to a phase field value, if so, solving the original load step again after grid refinement, otherwise, carrying out the next step of solving, and otherwise, carrying out the next step of solving; therefore, accurate simulation of the crack propagation process, the crack propagation direction and the crack propagation path of the brittle material under complex stress is finally realized. According to the invention, the calculation efficiency of the phase field model is greatly improved; the simulation precision of the crack propagation process is greatly improved, and a series of problems caused by the fact that a traditional model cannot reasonably divide grids are solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
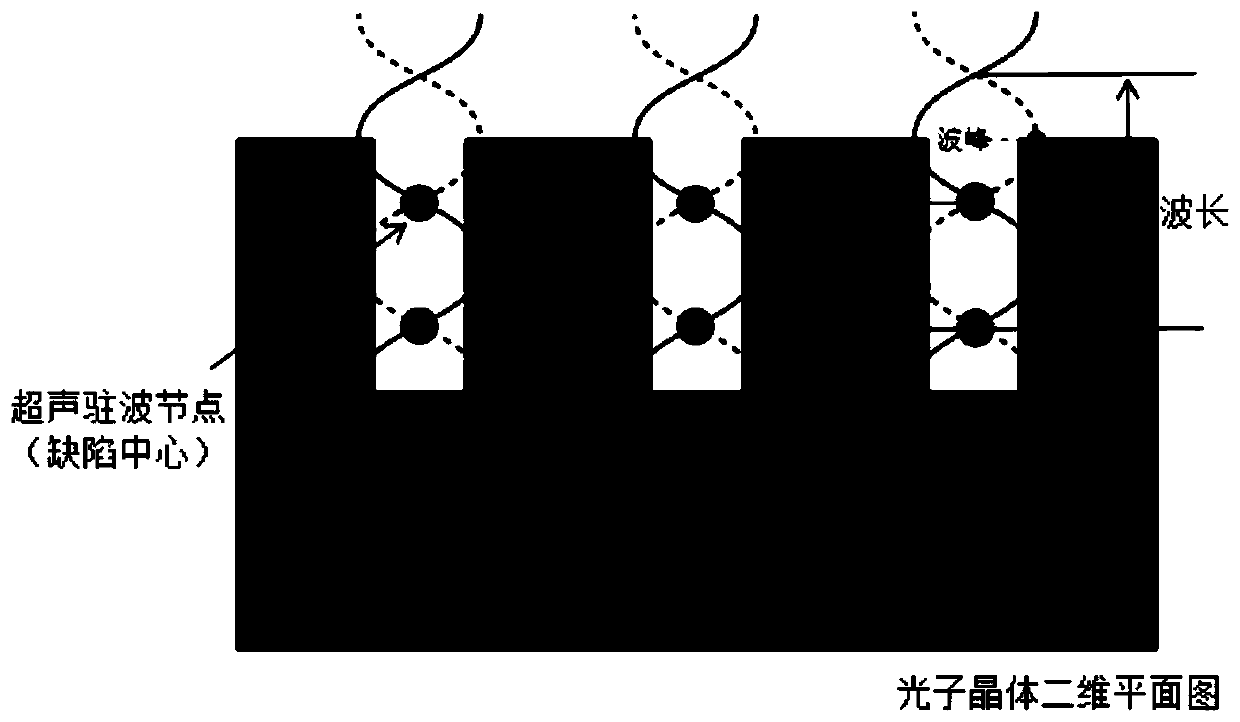
Modeling method for forming and positioning internal defects of three-dimensional photonic crystal
ActiveCN110008650ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelPhotonics
The invention relates to a modeling method for forming and positioning internal defects of a three-dimensional photonic crystal. The modeling method comprises the following steps: defining size parameters of two-dimensional array cylindrical holes in a silicon-based three-dimensional photonic crystal; adjusting the parameter variable of the ultrasonic wave to position the center position of the internal defect of the silicon-based three-dimensional photonic crystal; establishing an ultrasonic temperature field mathematical model equation; and according to the size parameters of the two-dimensional array cylindrical holes, adjusting the ultrasonic length to control the directional movement of silicon-based atoms, and based on an ultrasonic temperature field mathematical model equation, controlling the forming of silicon-based internal defects. The directional movement mechanism of acoustic radiation force to silicon-based atoms is utilized; based on the phase field model, the magnitudeof acoustic radiation force is changed to control positioning of internal defects; an ultrasonic temperature field mathematical model is established, the magnitude of acoustic radiation force is adjusted by changing parameters of external ultrasonic standing waves, the change mechanism of defect positions in the three-dimensional photonic crystals is studied, and a new idea is provided for numerical simulation of the three-dimensional photonic crystals which are periodically and regularly arranged.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for simulating influence of heating technology on premelting and melting of crystal boundaries by aid of crystal phase-field process
The invention relates to a method for simulating the influence of a heating technology on premelting and melting of crystal boundaries by the aid of a crystal phase-field process, and belongs to the field of technologies for simulating crystals. The method includes steps of (1), building a crystal phase-field model, in other words, building the crystal phase-field model on the basis of an idea of the traditional phase-field process, introducing a periodic function form into the model, and setting periodic partial-time average atomic densities as order parameters to obtain a free energy function expression of crystals; (2), determining a numerical process and calculation parameters. The method has the advantages that premelting and melting microstructure morphology at different heating rates is researched by the aid of a simulated calculation process and the crystal phase-field process, the widths of liquid-phase films at the crystal boundaries are quantitatively calculated by an excess mass process when the crystal boundaries are premelted and melted at the different heating rates, accordingly, the widths of the liquid-phase films at the crystal boundaries are quantified when the crystal boundaries are premelted and melted, structural relations among numerical values of the widths of the liquid-phase films and the atomic crystal boundary structures are illustrated, and an effect is perfect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Measurement method for oil-water two-phase interference pressure gradient
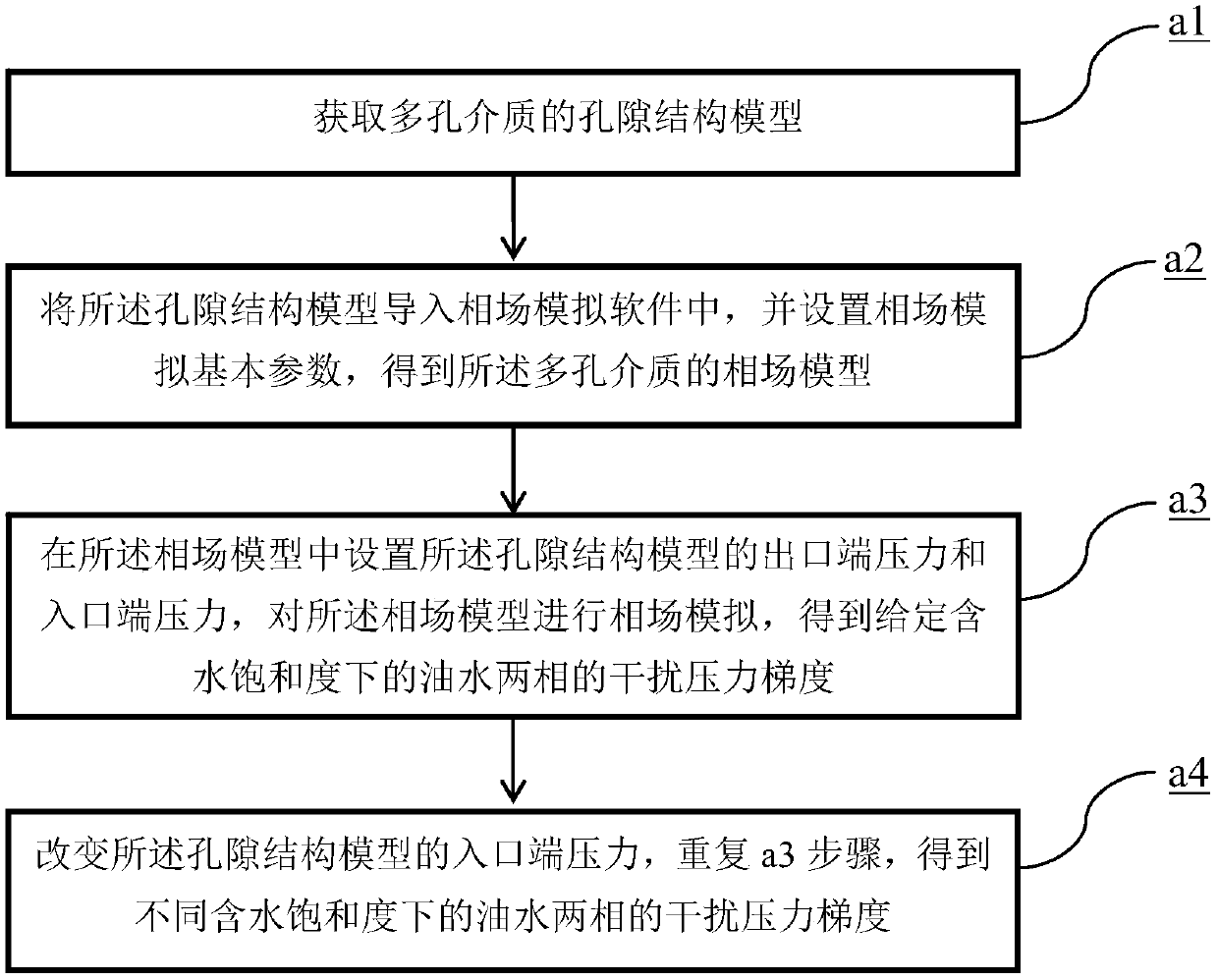
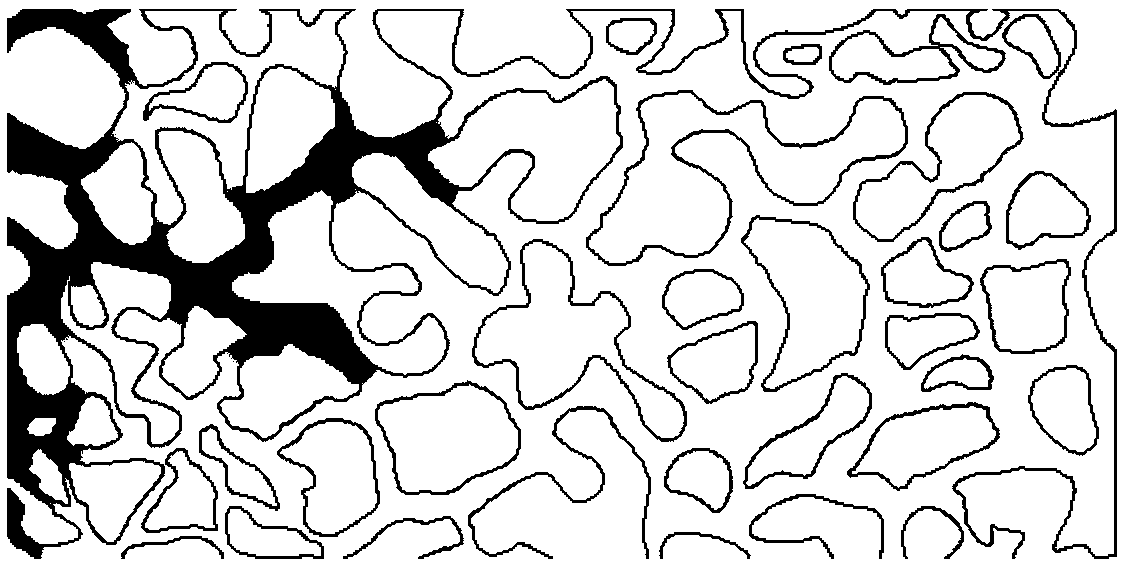
ActiveCN109556996ASolve the unmeasurableTruly reflect the law of seepageSurface/boundary effectPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesPorous mediumOperability
The invention relates to the technical field of oil and gas field development, and discloses a measurement method for an oil-water two-phase interference pressure gradient. The method comprises the following steps that: a1: obtaining the pore structure model of porous media; a2: importing the pore structure model into phase field simulation software, and setting phase field simulation basic parameters to obtain a phase field model of the porous media; a3: in the phase field model, setting the outlet end pressure and the inlet end pressure of the pore structure model, carrying out phase field simulation on the phase field model, and obtaining the oil-water two-phase interference pressure gradient under given water saturation; and a4: changing the inlet end pressure of the pore structure model, and repeating the step a3 to obtain the oil-water two-phase interference pressure gradient under different water saturations. The measurement method disclosed by the invention is convenient, effective and high in operability, can truly reflect the permeability rule of two-phase fluid in the porous media and can provide technical support for the accurate prediction of oil deposit development dynamics and the design of a development and regulation scheme.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
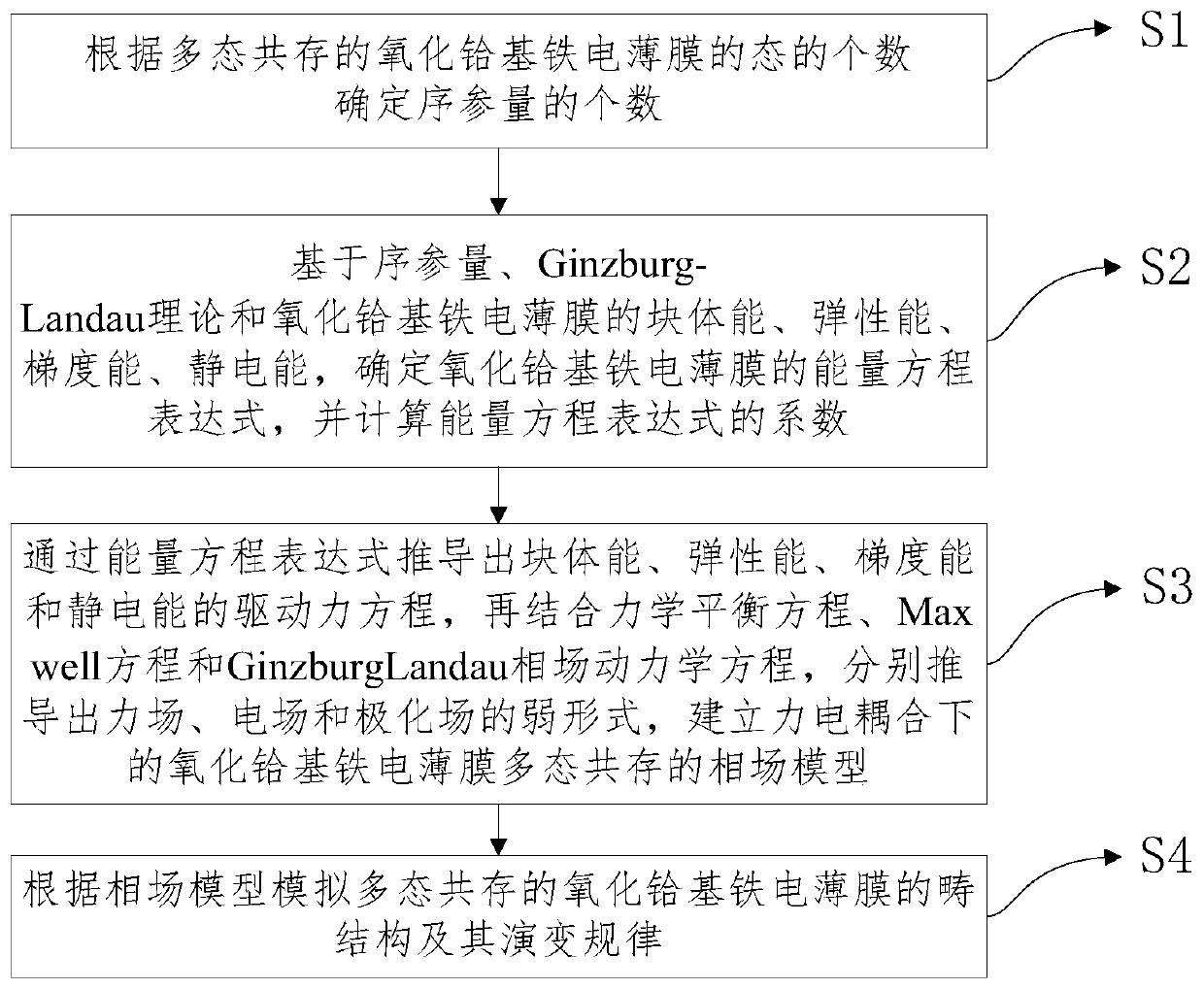
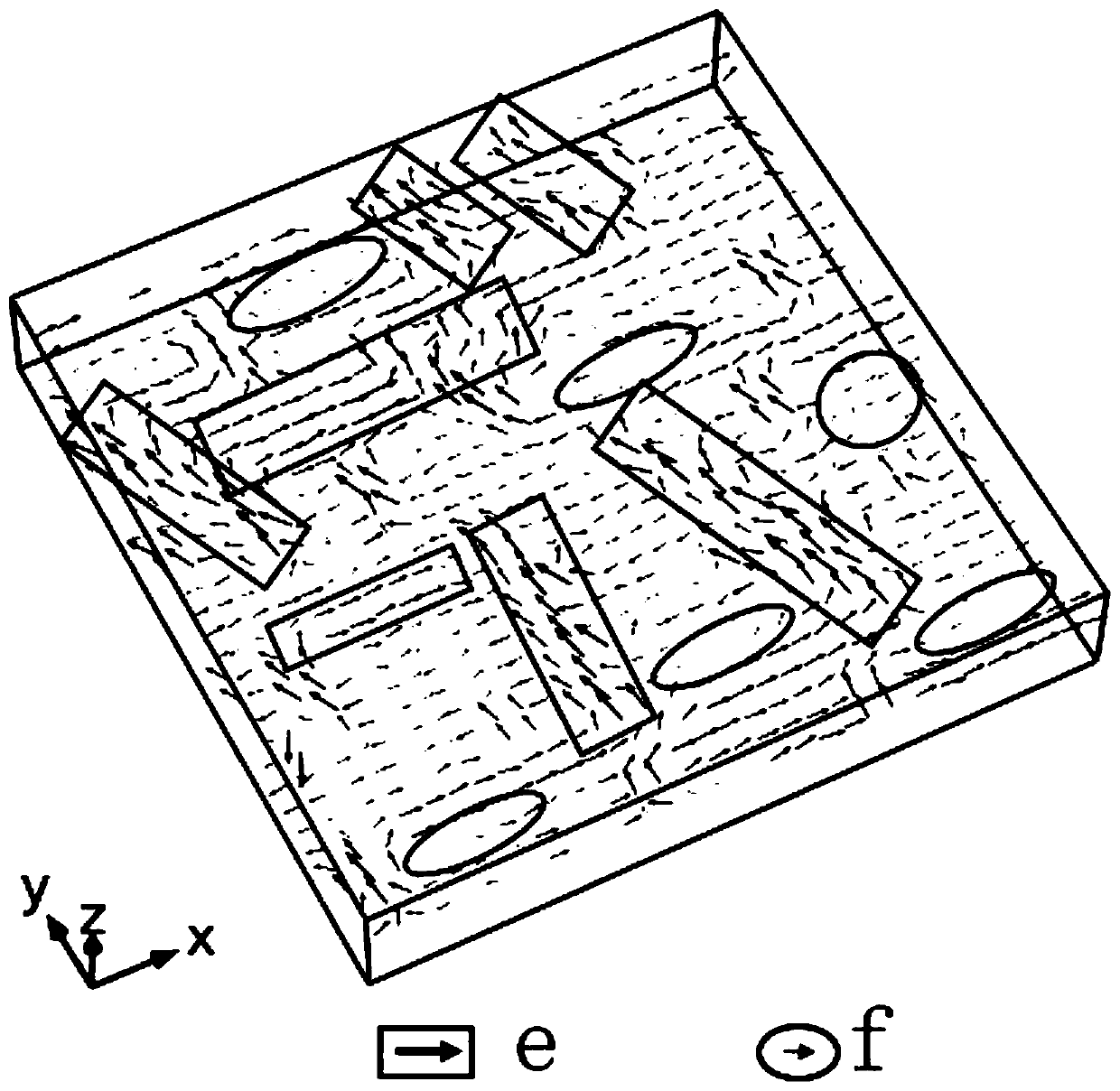
Polymorphic coexistence-based phase field analysis method for hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film
ActiveCN110866349AFew parametersReduce difficultyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingChemical physicsFerroelectric thin films
The invention discloses a polymorphic coexistence-based phase field analysis method for a hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film. The method comprises the following steps: determining the number of sequence parameters according to the number of states of the polymorphic coexisting hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film; determining an energy equation expression and a coefficient of the ferroelectric film based on the sequence parameter, the Ginzburg-Landau theory and the block energy, the elastic energy, the gradient energy and the electrostatic energy of the ferroelectric film; in combinationwith a mechanical equilibrium equation, a Maxwell equation and a Ginzburg-Landau phase field kinetic equation, deducing weak forms of a force field, an electric field and a polarization field, and establishing a hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film polymorphic coexistence phase field model under force-electricity coupling; and simulating a domain structure and an evolution rule of the polymorphic coexisting hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film according to the phase field model. The formation and growth process of the domain structure of the HfO2-based ferroelectric film is dynamically simulated, the redistribution of the domain structure under the action of different external fields is researched, guidance is provided for experimenters, and the experiment cost is reduced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
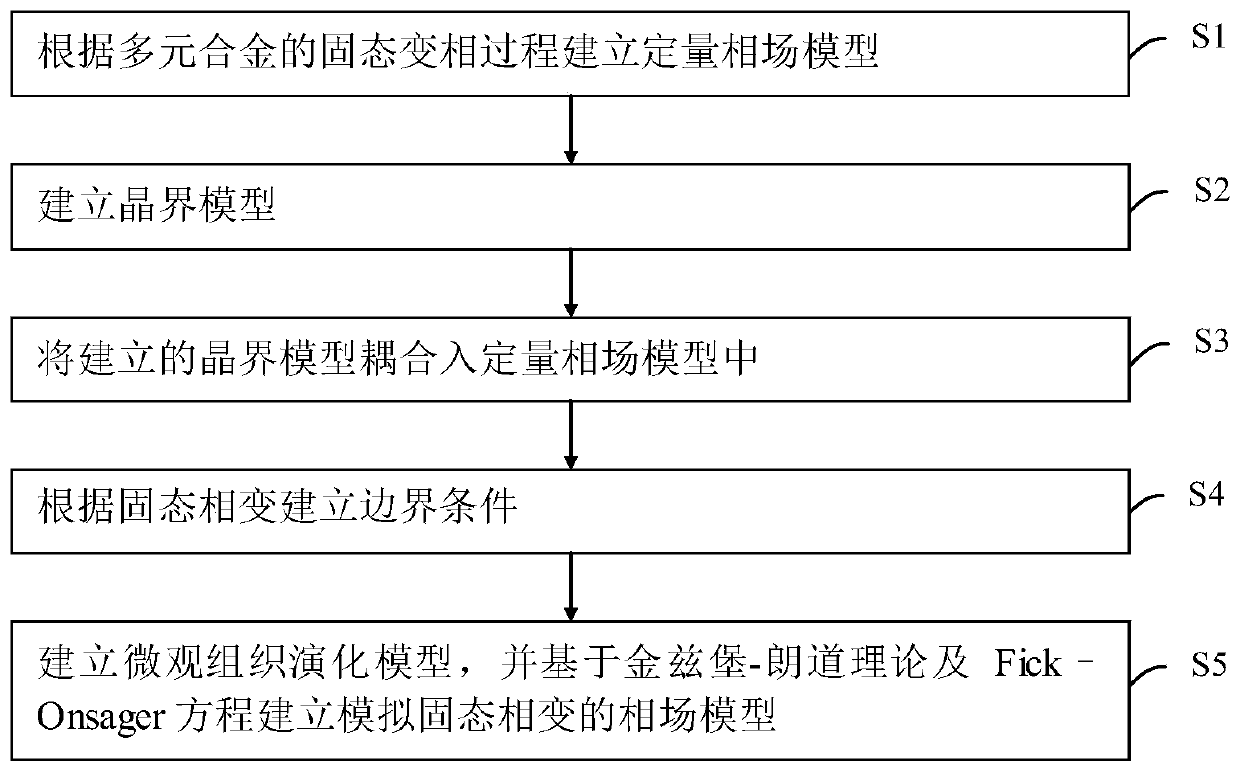
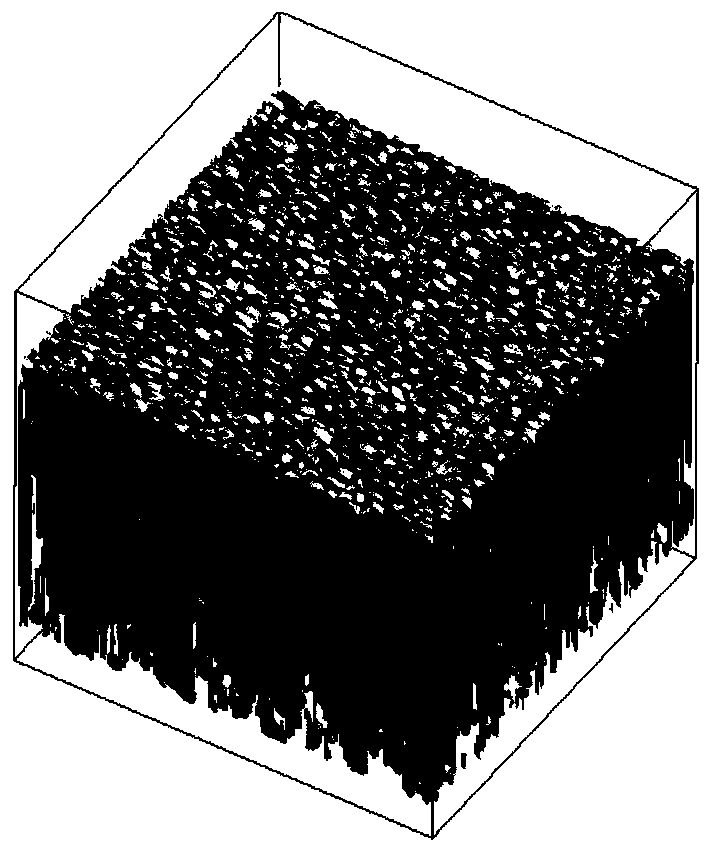
A multi-element alloy solid phase change simulation method based on a coupled grain boundary diffusion phase field method
ActiveCN109740205ARich Solid State Phase Transition TheoryOptimize heat treatment processSpecial data processing applicationsAlloyGrain boundary
The invention discloses a multi-element alloy solid phase change simulation method based on a coupled grain boundary diffusion phase field method. The multi-element alloy solid phase change simulationmethod comprises the steps of S1, establishing a quantitative phase field model according to the solid phase change process of multi-element alloy; S2, establishing a crystal boundary model; S3, coupling the established grain boundary model into a quantitative phase field model; S4, establishing boundary conditions according to solid-state phase change; S5, establishing a microstructure evolutionmodel, and establishing a microstructure evolution model based on Pittsburg-based on Pittsburg- And establishing a phase field model for simulating solid-state phase change according to a Lamble theory and a Fick-On equation. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a solid-solid phase change model coupled with grain boundary diffusion; The solid-state phase change microstructure evolution process in the multi-element alloy system is quantitatively simulated and predicted, the evolution behavior of the solid-state phase change microstructure can be deeply understood, the solid-state phase change theory is enriched, meanwhile, the heat treatment process is optimized, and guidance can be provided for microstructure evolution research and process optimization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
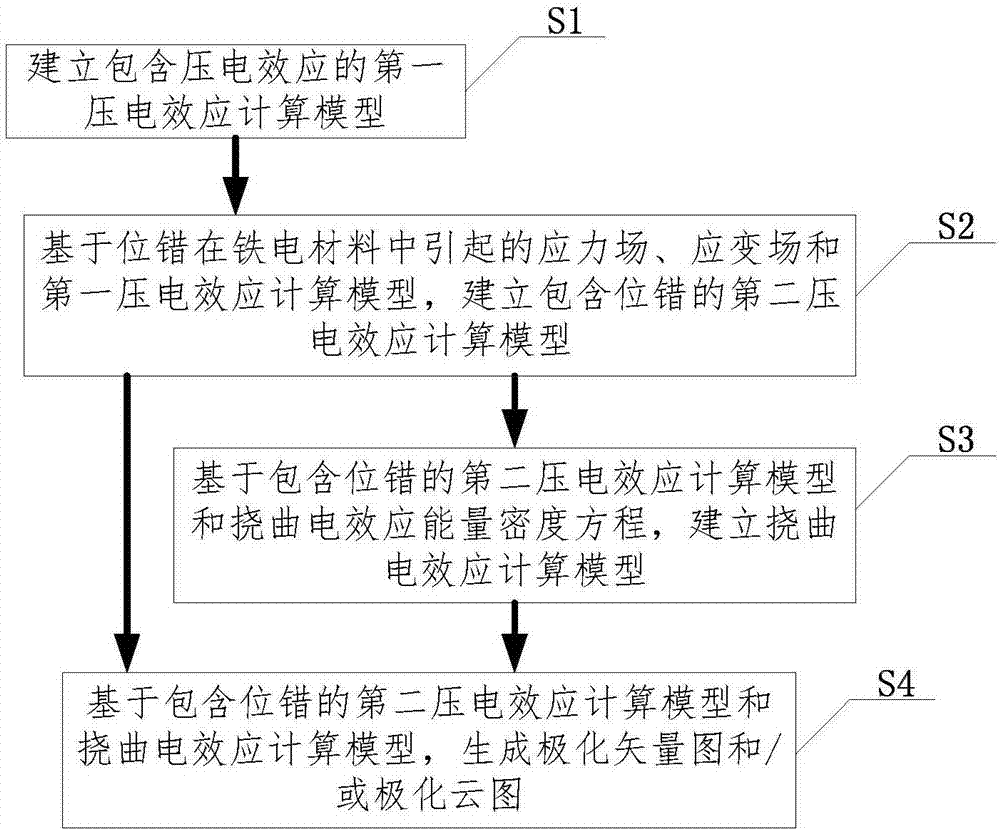
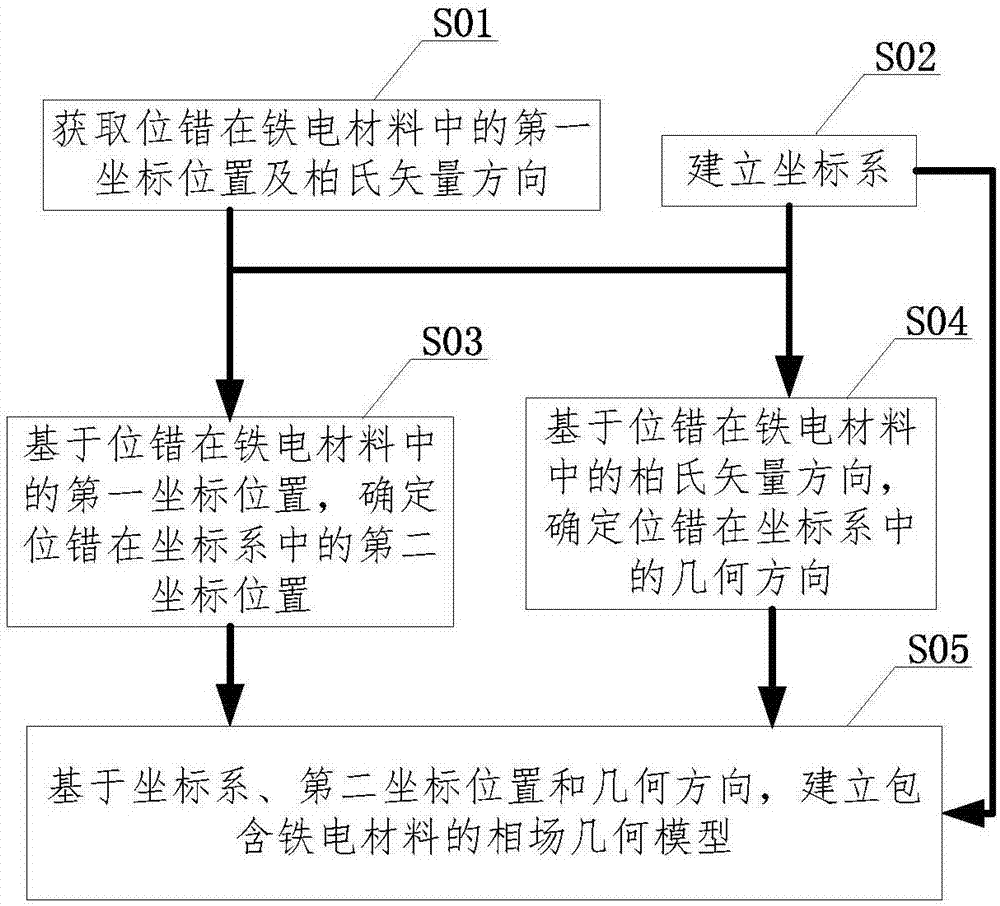
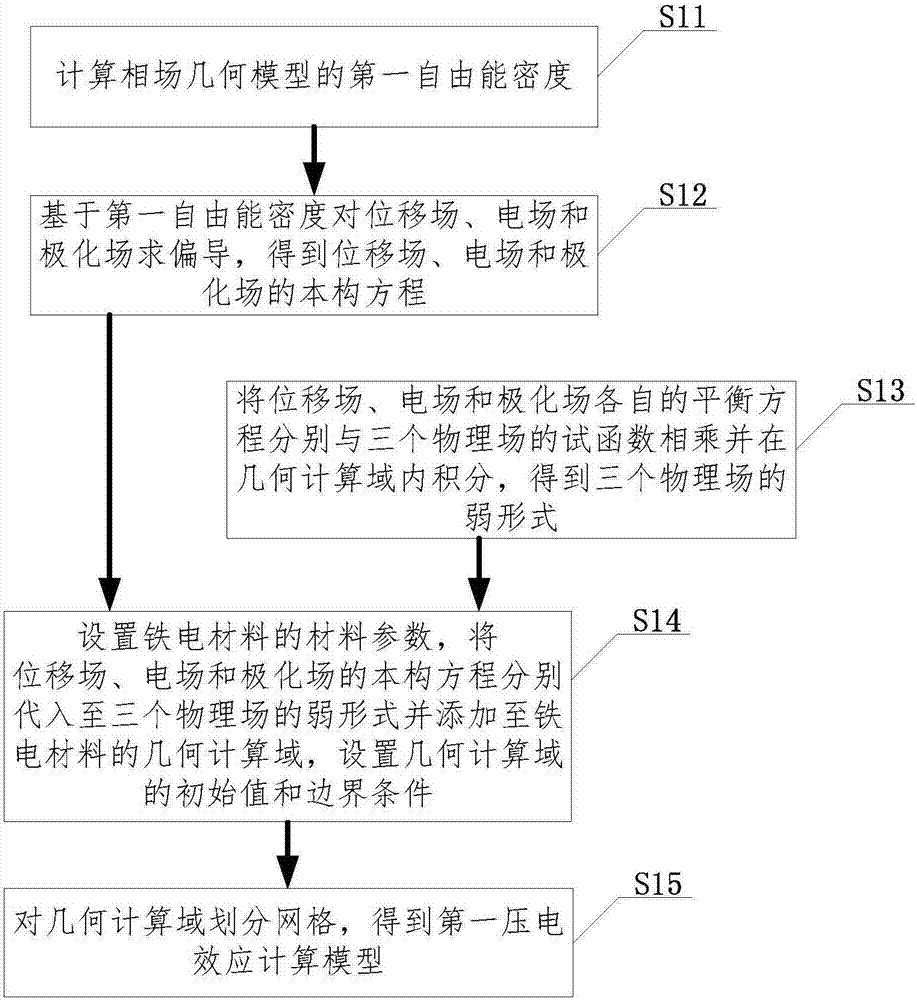
Method and system for analyzing influence mechanism of dislocation on ferroelectric materialdomain structure
ActiveCN107025339AThe simulation method is simple and efficientDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodComputer science
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a system for analyzing an influence mechanism of dislocation on a ferroelectric materialdomain structure. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, establishing a first piezoelectric effectcalculation model with a piezoelectric effect; S2, establishing a second piezoelectric effectcalculation model with the dislocation on the basis of a stress-strain field caused by the dislocation in a ferroelectric material as well as the first piezoelectric effectcalculation model; S3, establishing a flexoelectric effect calculation model on the basis of the second piezoelectric effectcalculation model with the dislocation and a flexoelectric effectenergy densityequation; S4, generating a polarization vector diagram and / or a polarizationcloud chart on the basis of the second piezoelectric effectcalculation model with the dislocation and the flexoelectric effect calculation model. Compared with a traditional dislocation phase field model only taking the piezoelectric effect into consideration, the embodiment of the invention takes the flexoelectric effect into consideration, and a simulated result more matched with an experimental result is obtained.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
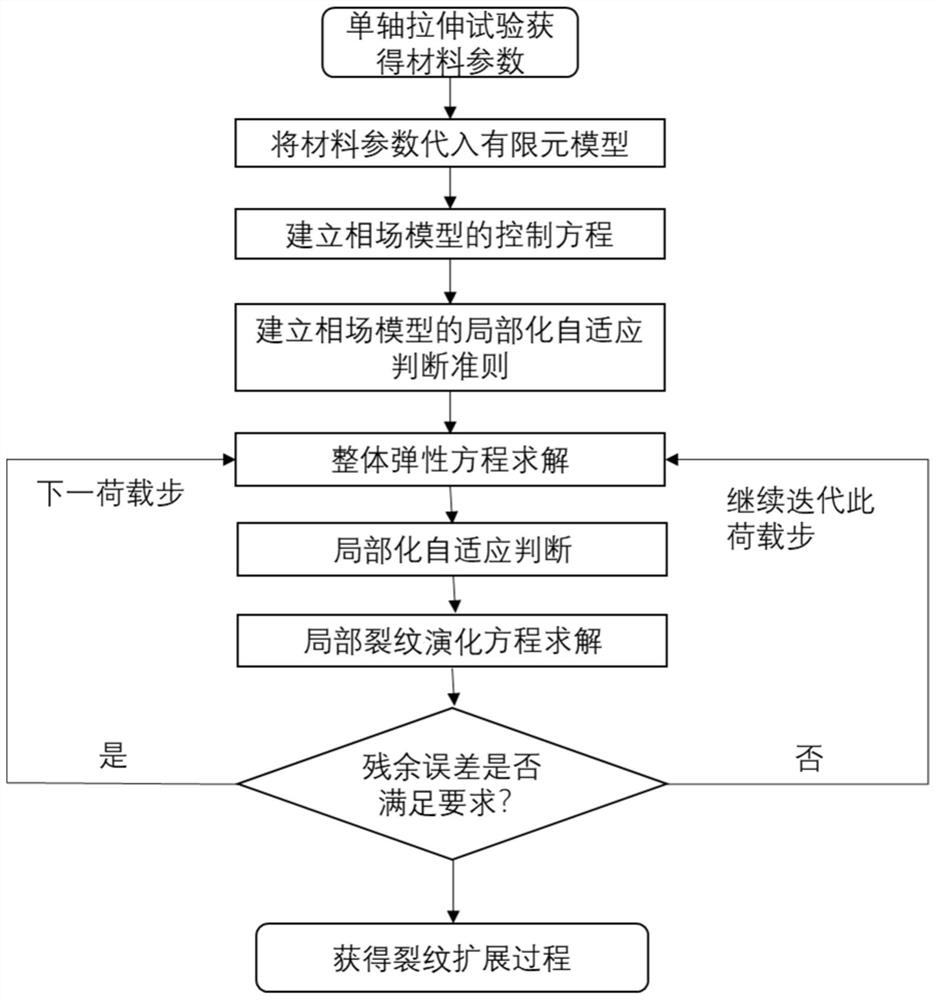
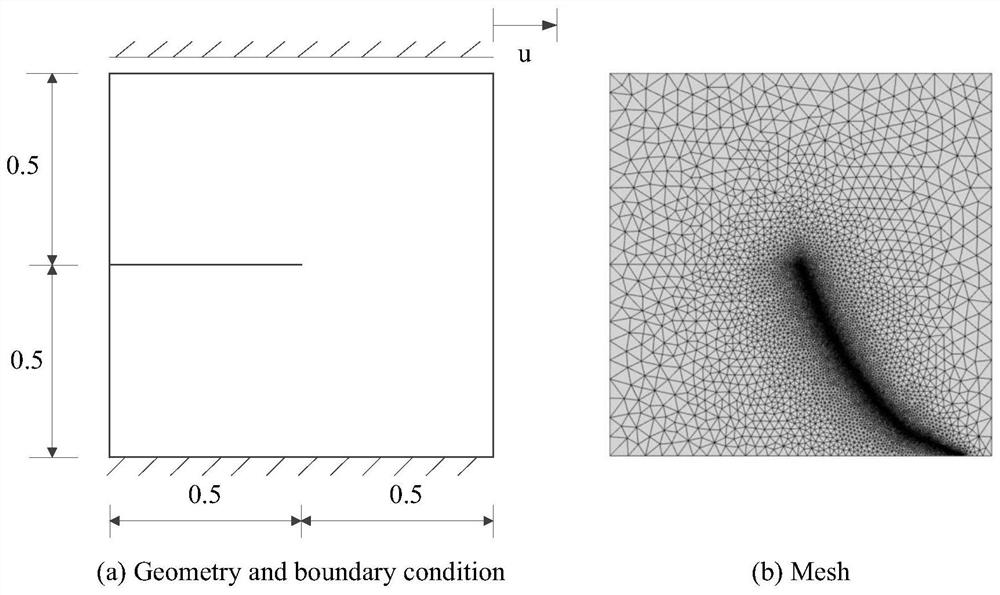
Phase field model localization adaptive algorithm for simulating material cracking
ActiveCN113094946ASmall amount of calculationBreak through difficult-to-simulate problemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelCrazing
The invention discloses a phase field model localization self-adaptive algorithm for simulating material cracking. The phase field model localization self-adaptive algorithm is suitable for tracking and simulating a material elastic-plastic failure process and greatly reducing the calculation amount. The algorithm comprises the following steps: obtaining material parameters required by a numerical simulation process through a uniaxial tensile test, substituting the measured material parameters into an established finite element model, further establishing an equilibrium equation and a crack evolution equation of a phase field model, establishing a localization self-adaptive judgment criterion of the phase field model, and carrying out overall-local staggered solution on the simulated object to realize rapid solution and simulation of the crack propagation process of the material under the action of external force. According to the method provided by the invention, the solving speed of the crack propagation process of the phase field model is greatly improved; meanwhile, the simulation precision of the damage process is guaranteed, and the problems that a traditional phase field model theory is large in calculation amount, slow in solving and limited in application are solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
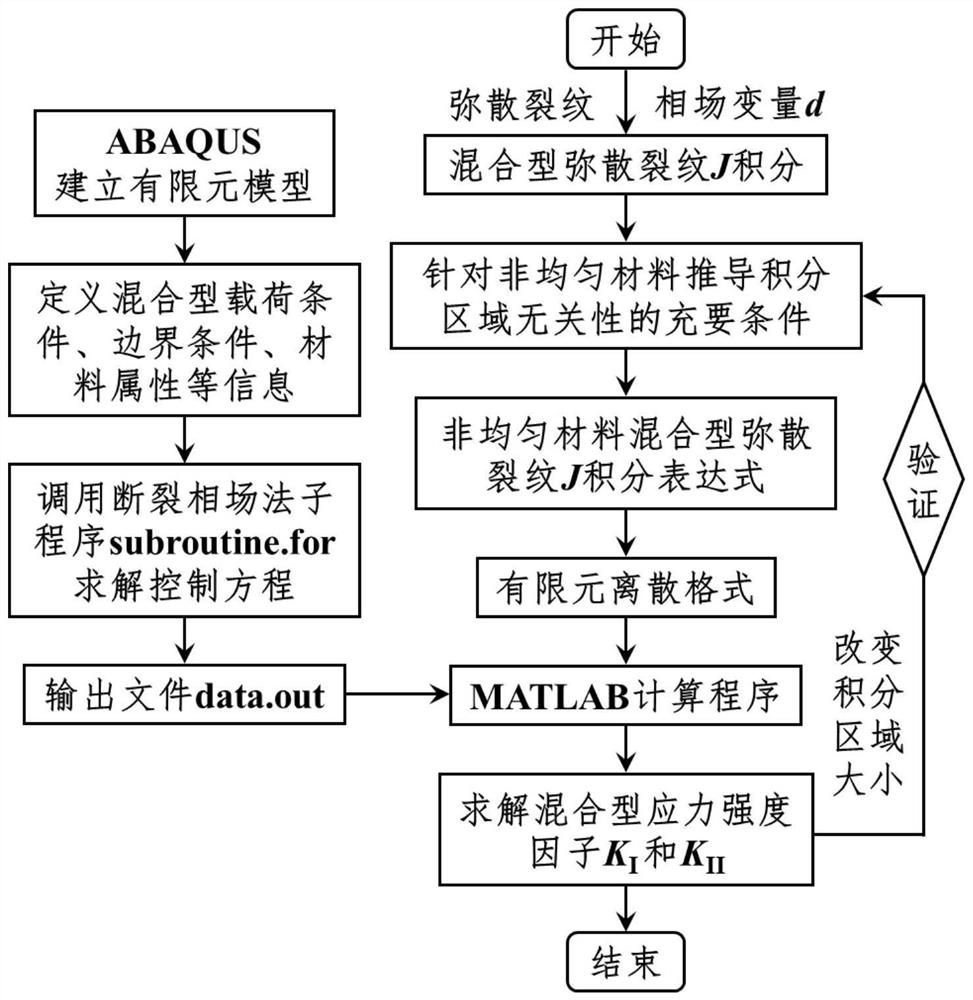
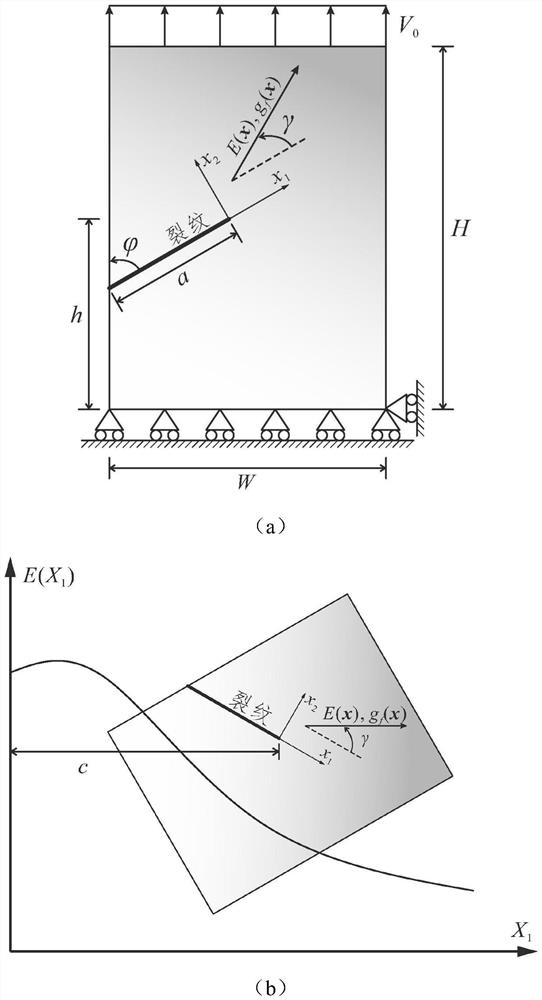
Non-uniform material dispersion crack J integration method based on fracture phase field method
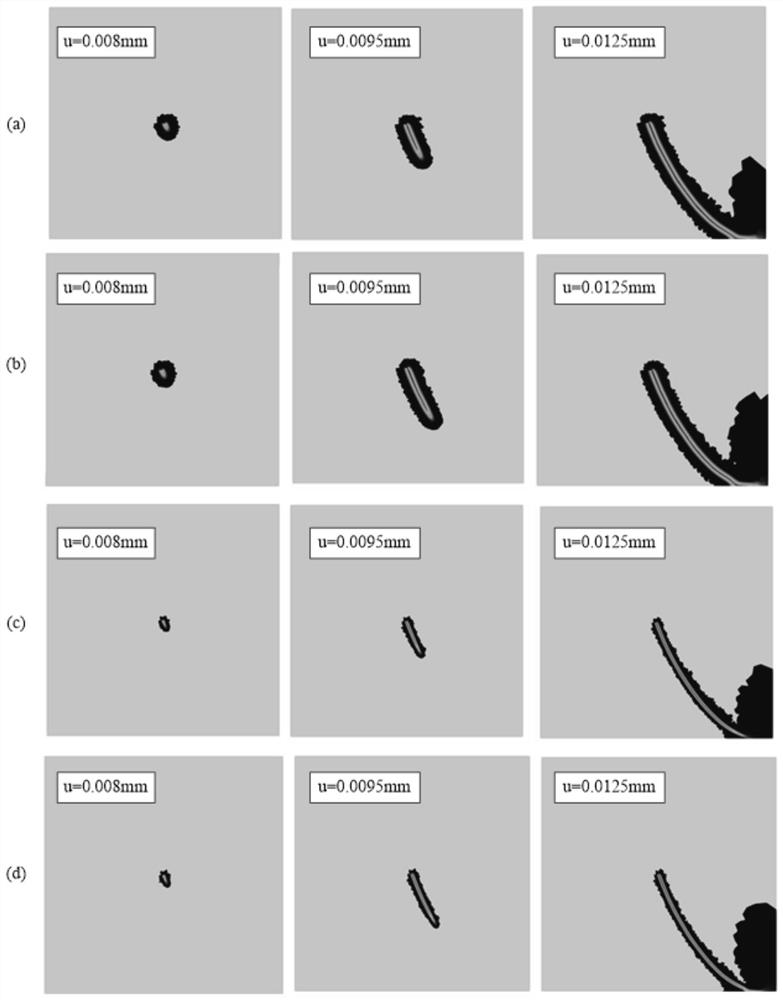
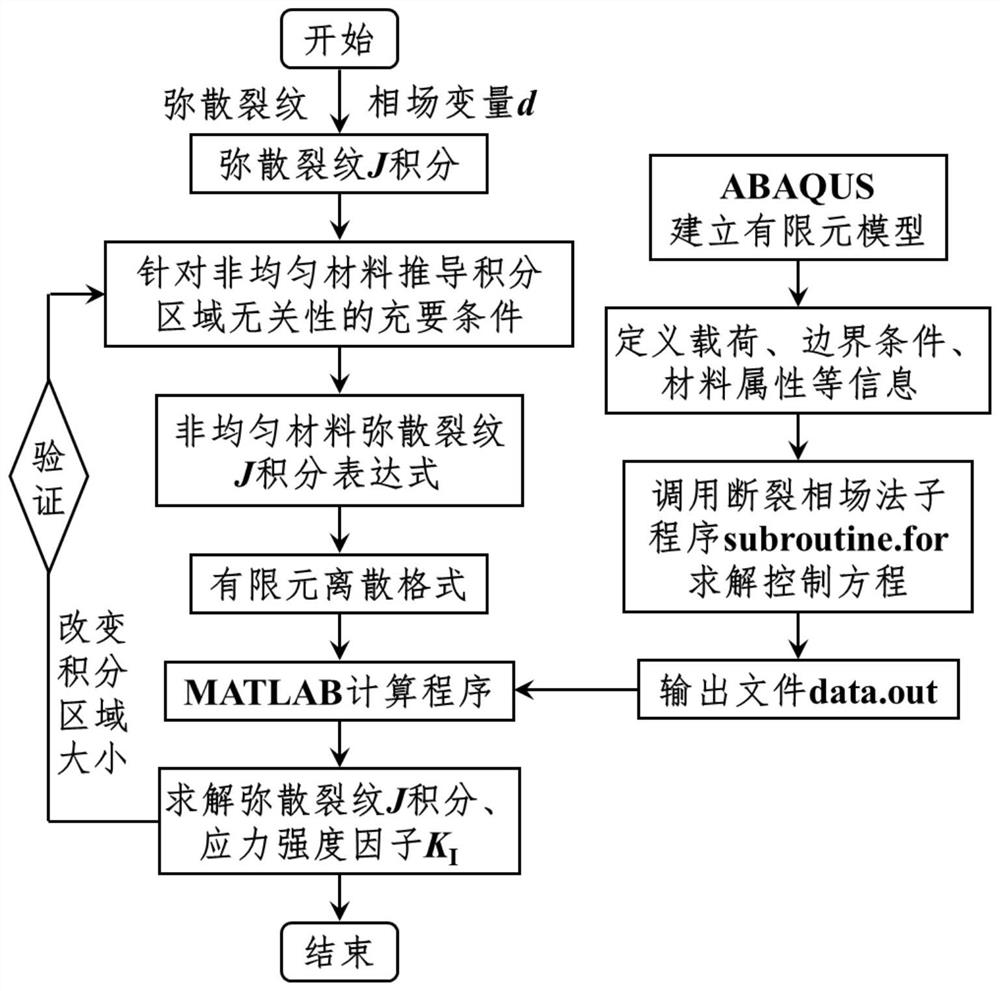
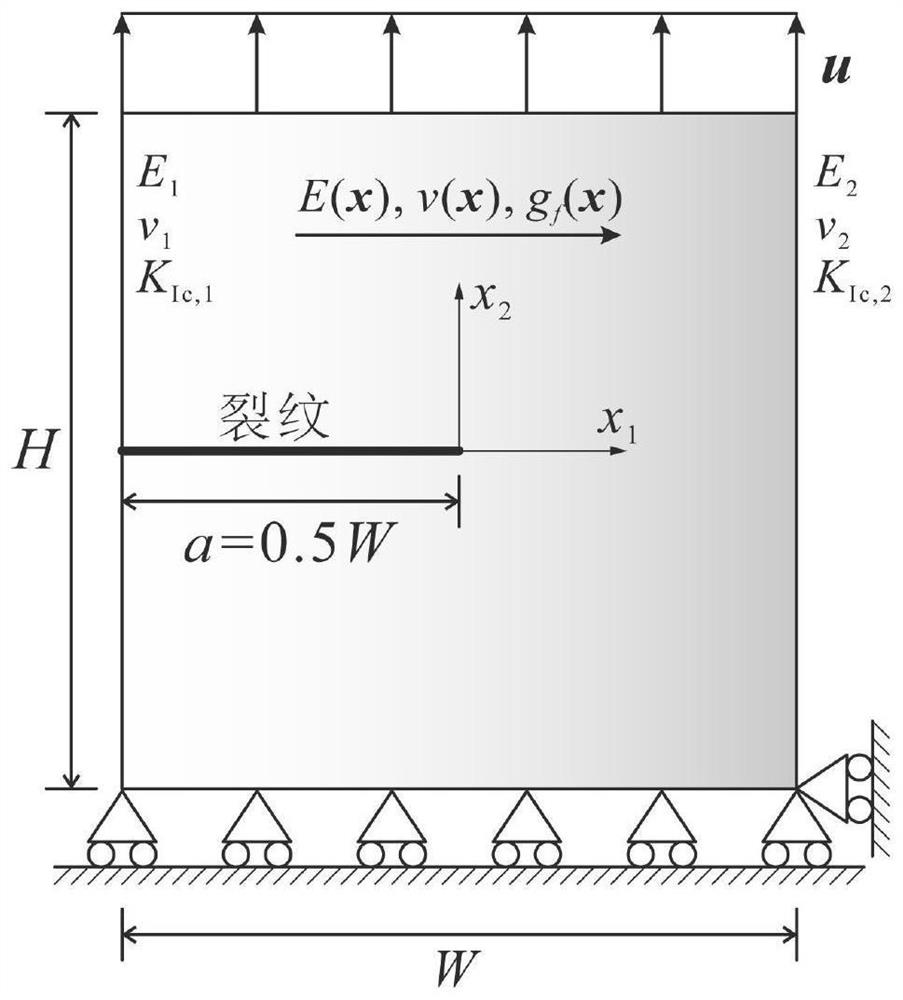
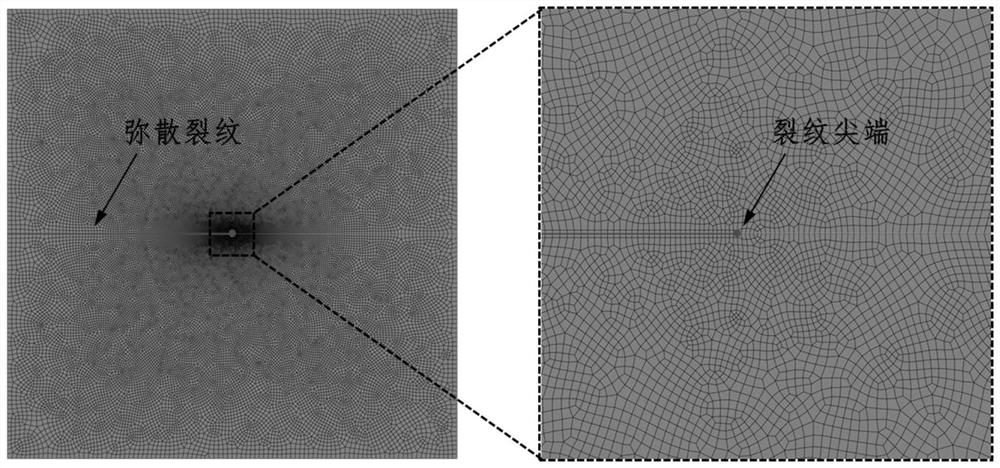
ActiveCN114491831AAccurate solutionImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationElement modelStress intensity factor
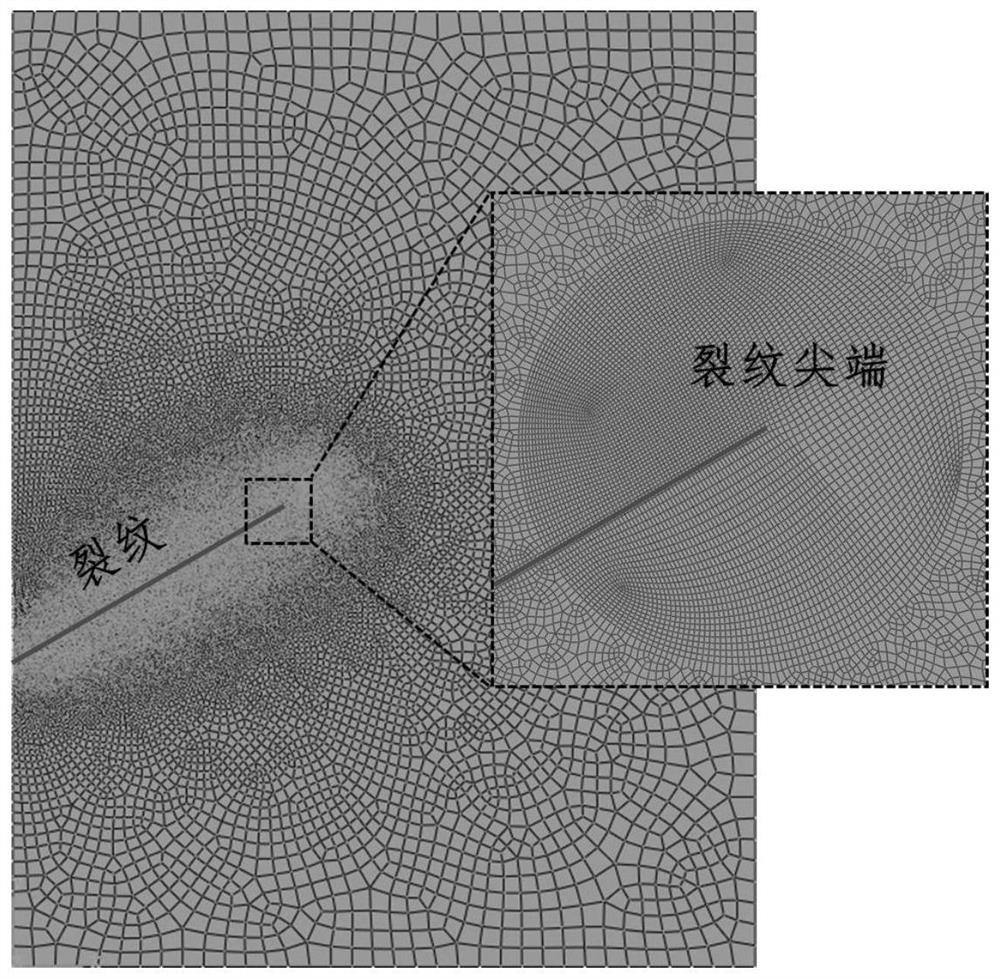
The invention discloses a non-uniform material dispersion crack J integral method based on a fracture phase field method, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, introducing a phase field variable d of a fracture phase field model, and determining a non-uniform material dispersion crack J integral expression with integral region independence and a corresponding finite element discrete format; 2, establishing a finite element model containing dispersion cracks and dividing finite element grids; 3, calling a calculation subprogram of the fracture phase field model, and solving a nonlinear control equation of the fracture phase field model by adopting a Newton-Raphson method; and 4, according to a finite element discrete format of the J integral of the dispersion crack of the non-uniform material, solving a characteristic quantity-stress intensity factor KI of the dispersion crack tip based on a finite element calculation result. According to the method, the characteristic quantity of the dispersion crack tip of the non-uniform material is accurately solved, and the defect that the stress state of the dispersion crack tip cannot be accurately described by a traditional fracture phase field method is overcome.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
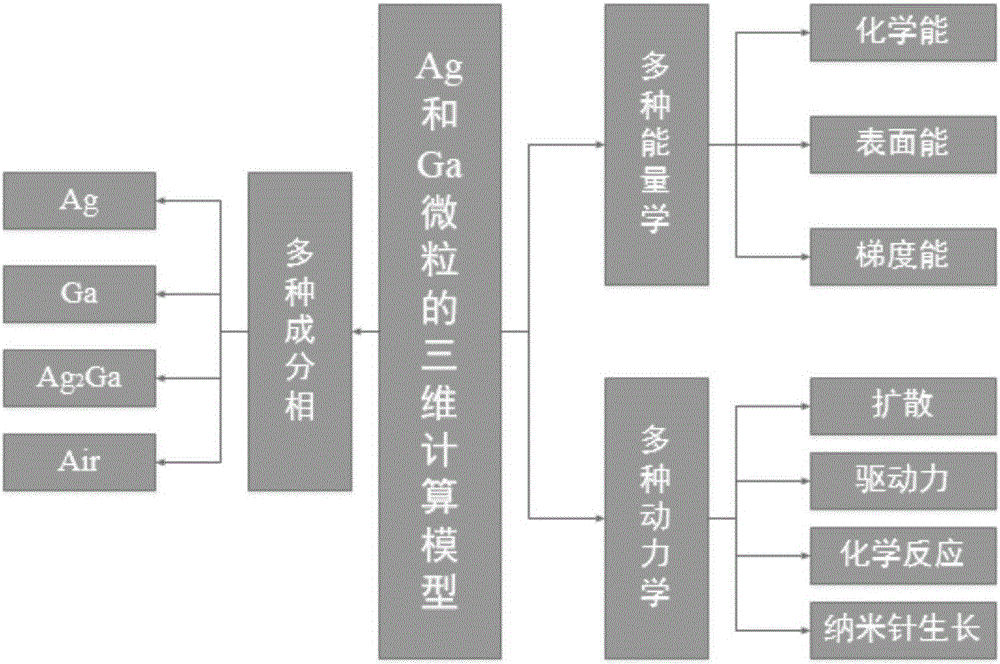
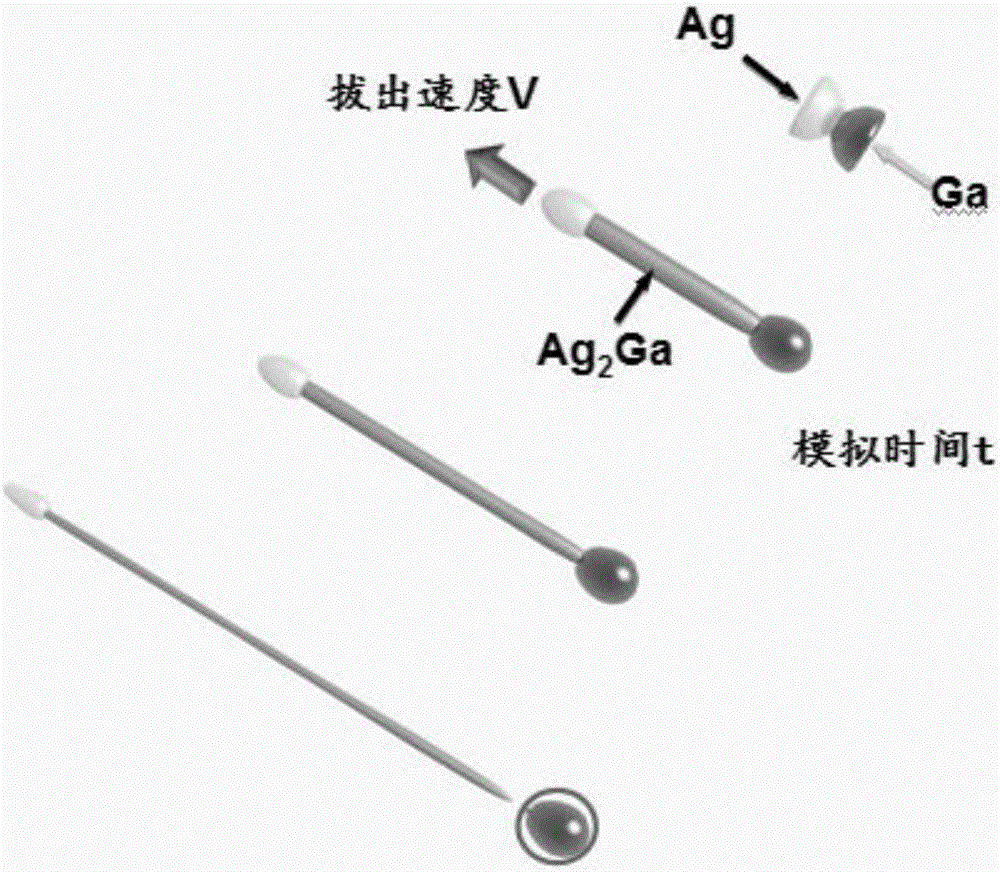
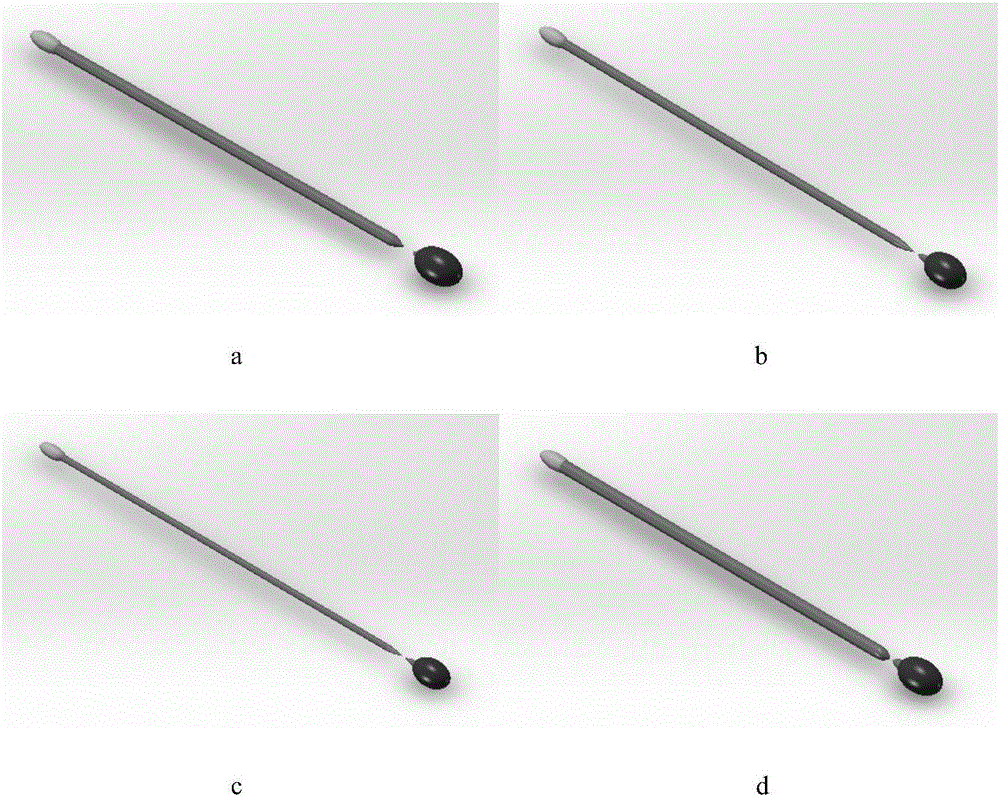
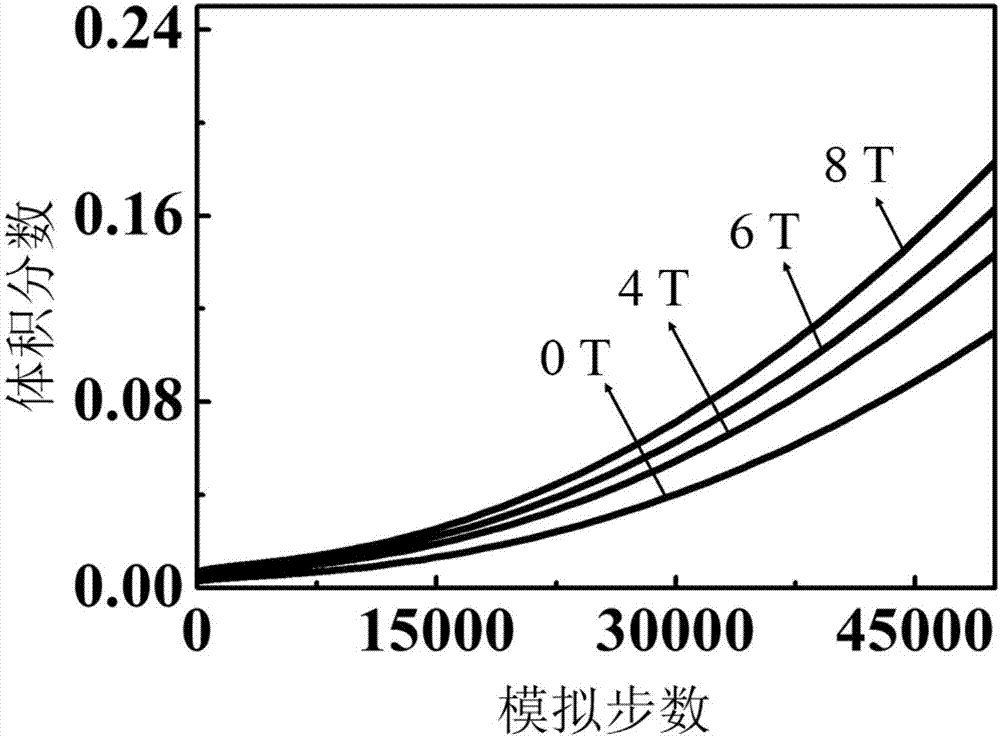
Research method of controlling draw ratio of Ag2Ga nano-needle based on phase field model
ActiveCN106055887AReduce complexityChemical processes analysis/designDesign optimisation/simulationDiffusionStudy methods
The invention discloses a research method of controlling draw ratio of an Ag2Ga nano-needle based on a phase field model. The method comprises following steps: firstly, constructing a three-dimensional calculation model of the Ag2Ga nano-needle; secondly, changing an experiment reaction condition and simulation time to shed light upon the changing rule of the draw ratio of the Ag2Ga nano-needle; diffusion between Ag particles and liquid Ga particles occurs at indoor temperature to generate Ag2Ga particles and form the Ag2Ga nano-needle by applying force to one end and pulling out; during the process, the condition of experiment reaction and simulation time are key factors in influencing the draw ratio of the Ag2Ga nano-needle; carrying out following operations: first operation: exploring influence of different particle concentrations on changes of draw ratio of the Ag2Ga nano-needle; second operation: exploring influence of different simulation time on changes of draw ratio of the Ag2Ga nano-needle; third operation: exploring influence of different pulling speed on changes of draw ratio of the Ag2Ga nano-needle.
Owner:嘉兴华吉环保科技有限公司
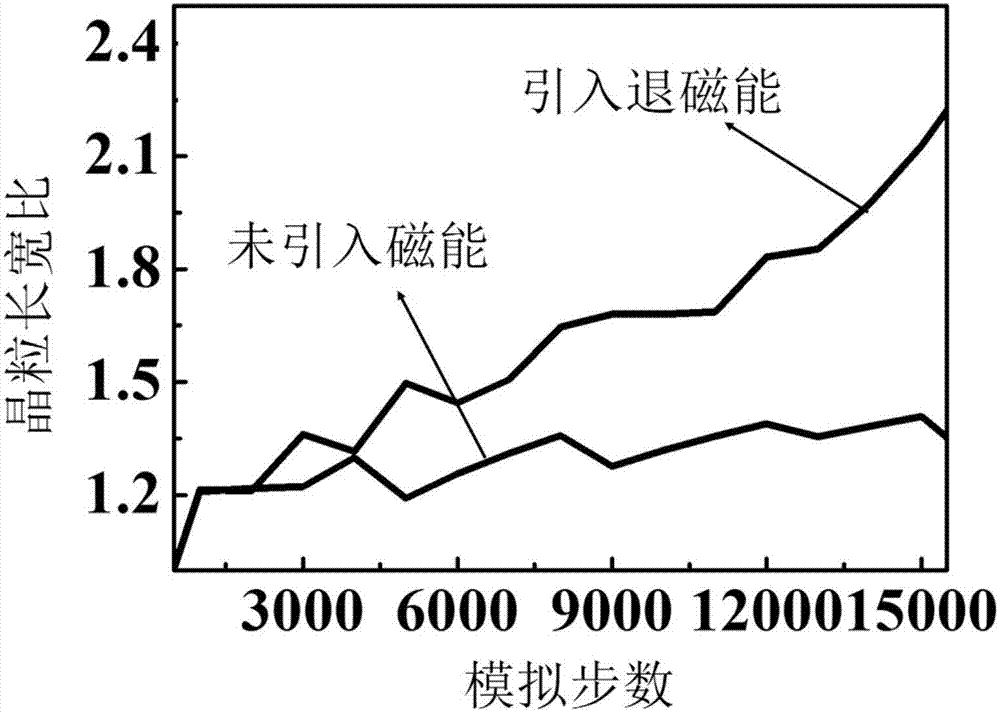
Phase field analysis method of ferromagnetic crystal grain evolution under magnetic field
InactiveCN107315913AVersatilityComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsZeeman energyField analysis
The invention discloses a phase field analysis method of ferromagnetic crystal grain evolution under a magnetic field. According to the method, micromagnetics magnetic-energy calculation formulas are combined to introduce magnetic energy, which is generated by ferromagnetic crystal grains under the action of the external magnetic field, into system free-energy on the basis of a classical phase field model, and a general model used for simulating evolution processes of the ferromagnetic crystal grains under the action of the external magnetic field is constructed. According to the model, influences of each magnetic energy item on ferromagnetic phase single-domain crystal grain evolution under different external magnetic field strength and a comprehensive influence of the total magnetic energy on the same can be studied through introducing the different magnetic energy terms (Zeeman energy, magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy and demagnetization field energy). The invention provides the phase field model of considering ferromagnetic crystal grain evolution under the action of the external magnetic field, and the model is applied to an Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet alloy to verify the feasibility thereof.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Numerical method for extracting hybrid dispersion crack tip parameters of non-uniform material
ActiveCN114169209AAccurate solutionRealize the solutionGeometric CADSustainable transportationElement modelMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a numerical method for extracting a tip parameter of a mixed type dispersion crack of a non-uniform material. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, determining a J integral expression of the mixed type dispersion crack of the non-uniform material with integral region independence and a corresponding finite element discrete format; 2, establishing a finite element model containing the mixed type dispersion cracks and dividing finite element grids; 3, solving a nonlinear control equation of the fracture phase field model by adopting a Newton-Raphson method; and 4, according to a finite element discrete format of the J integral of the mixed type dispersion crack of the non-uniform material, solving mixed type dispersion crack tip parameters-mixed type stress intensity factors KI and KII based on a finite element calculation result. According to the method, the parameters of the mixed type dispersion crack tip of the non-uniform material are accurately solved, and the defect that the stress state of the mixed type dispersion crack tip cannot be accurately described through a traditional fracture phase field method is overcome.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
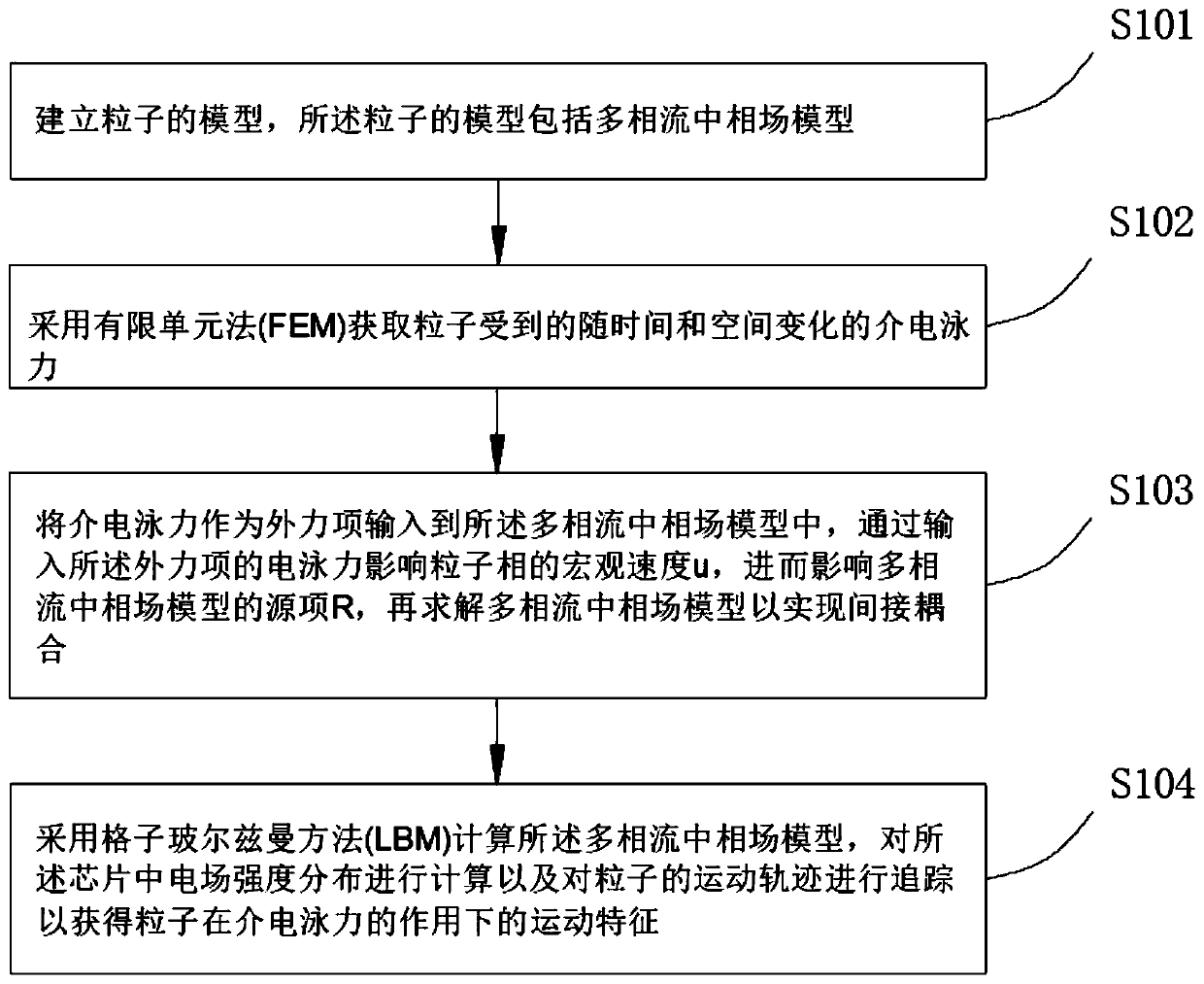
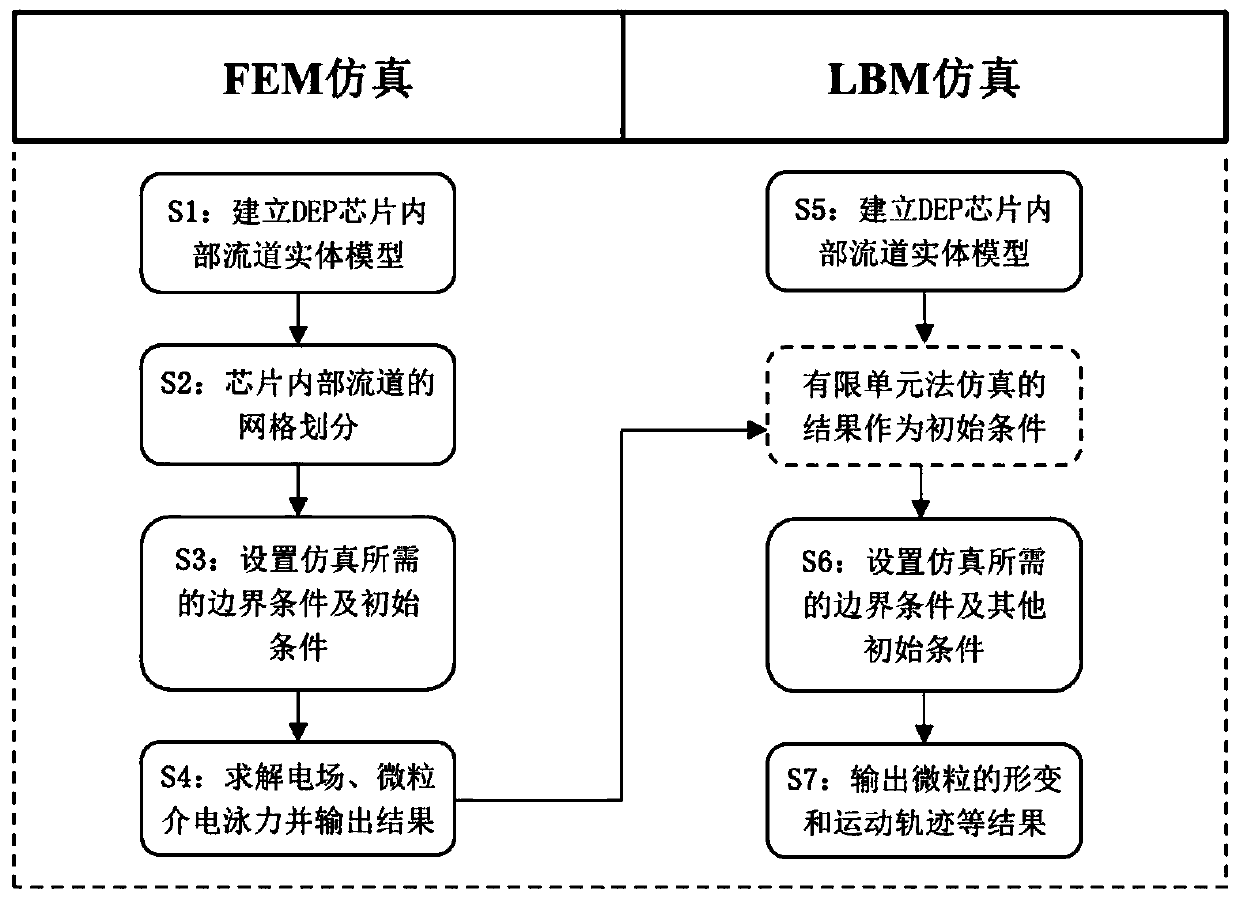
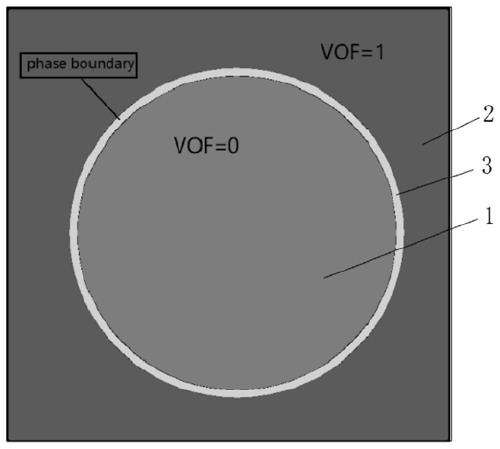
Indirect coupling simulation method of microfluidic dielectrophoresis sorting chip
PendingCN111475983ASimple structureDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryElectrical field strengthDielectrophoretic force
The invention discloses an indirect coupling simulation method of a microfluidic dielectrophoresis sorting chip, and relates to the technical field of dielectrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a phase field model in a multiphase flow; adopting a finite element method to obtain dielectrophoretic force which changes along with time and space and is borne by particles;inputting the dielectrophoresis force as an external force item into the phase field model in the multiphase flow, and solving the phase field model in the multiphase flow to realize indirect coupling; adopting a lattice Boltzmann method to calculate the phase field model in the multiphase flow, calculating electric field intensity distribution in a chip and track and characterize motion trails of the particles. The advantages of the finite element grid method for solving the electric field can be exerted, the advantages of the lattice Boltzmann method for solving micro-scale flow and flexible cell deformation can also be exerted, the chip structure can be optimized according to the simulation result, and a new thought is provided for design and manufacturing of the microfluidic dielectrophoresis chip.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
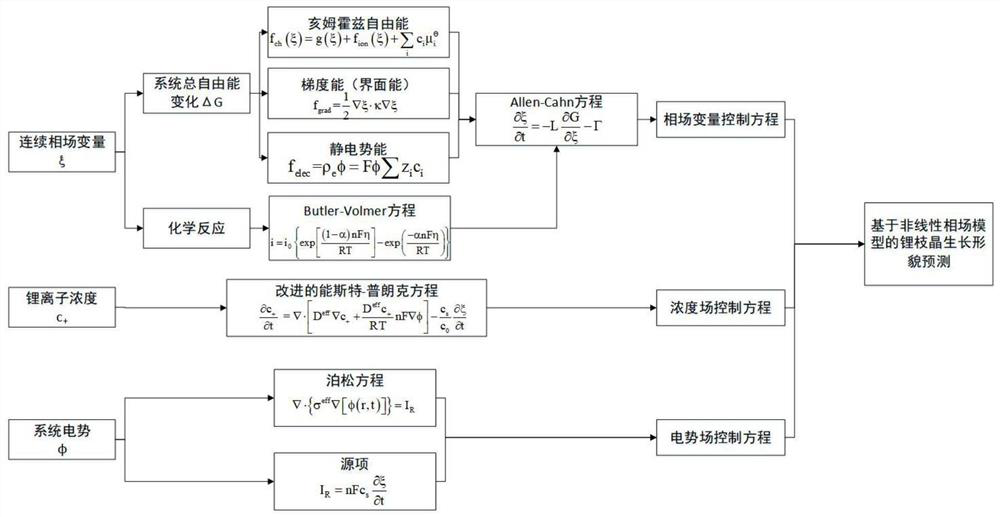
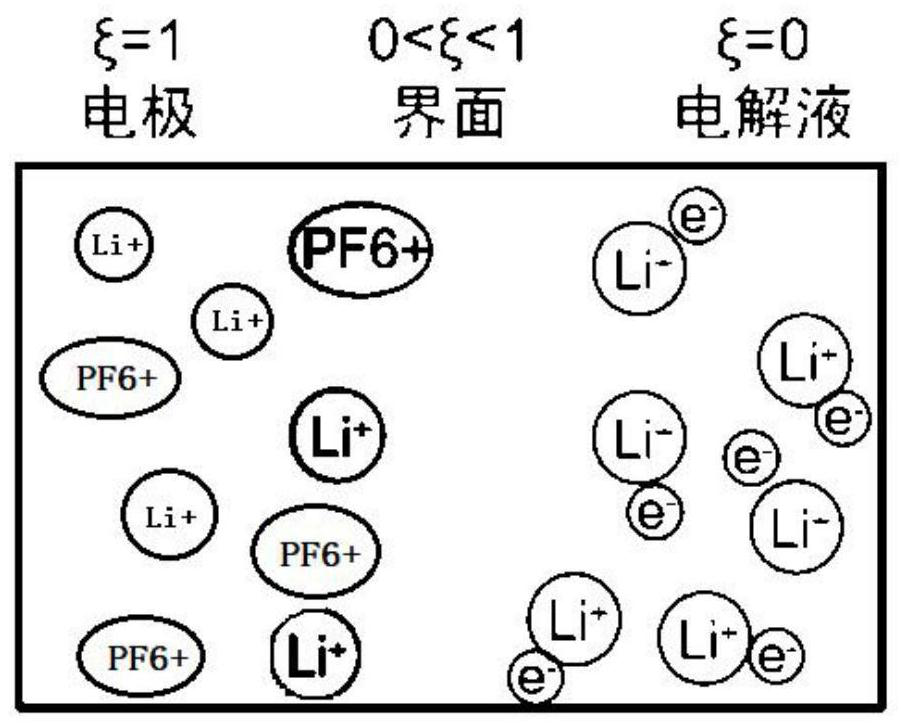
Lithium dendrite morphology growth prediction method and system based on nonlinear phase field model
ActiveCN113420472ASolve the problem of continuous trackingReduce computational complexityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrolytic agentComputation complexity
The invention provides a lithium dendrite morphology growth prediction method and system based on a nonlinear phase field model. The lithium dendrite morphology growth prediction method comprises the steps: 1, deducing according to a free energy change rule and reaction kinetics to obtain a phase field variable control equation, a lithium ion concentration field control equation and a potential field control equation in a lithium dendrite growth process; 2, collecting parameters in the growth process of the lithium dendrites; 3, inputting the parameters and the equation into finite element simulation software, determining the size of an electrolyte region needing to be calculated, performing grid division, setting a boundary condition, an initial condition, a calculation step length and calculation time, and performing transient solution of a control equation set; 4, outputting the change conditions of the phase field variable values in the calculation process and the calculation region as images to obtain the growth morphology of the lithium dendrites on the surface of the negative electrode of the lithium battery in the charging process. According to the method, the problem that a solid-liquid interface needs to be tracked continuously in a traditional model is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
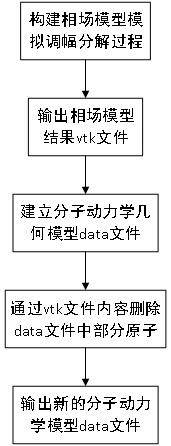
Construction method for molecular dynamics geometric model of spinodal decomposition distribution
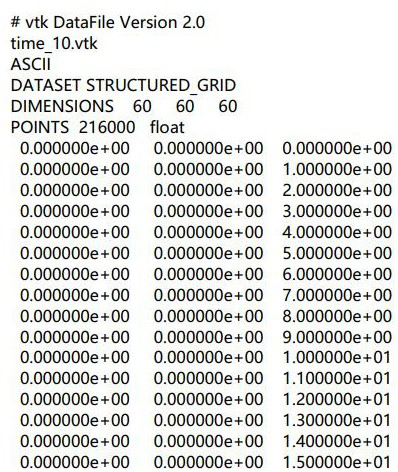
PendingCN111816261ADistributed embodimentReflect sizeDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryData fileMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular dynamics of materials, and particularly relates to a construction method for a molecular dynamics geometric model of spinodal decomposition distribution. The method comprises the following steps: 1, constructing a phase field model of spinodal decomposition of a system based on a Cahn-Hilliard model, iterating the phase field model by usingMATLAB, and finally, outputting target concentration data of a block in a vtk format; 2, based on a Python environment, calling a vtk format file of the block target concentration data, and storing the file in the form of a built-in type, namely a dictionary, of a sequence in Python; 3, creating data files of the molecular dynamics geometric model, establishing a corresponding relationship between atomic coordinates and coordinates of blocks in the dictionary, setting a concentration threshold of the blocks, arranging the data files of the molecular dynamics geometric model according to the concentration threshold of the block, and outputting a new data file of the molecular dynamics model; and step 4, inputting the new data file of the molecular dynamics model into LAMMPS to perform molecular dynamics simulation. The method can be used for carrying out molecular dynamics simulation research on a porous nano-metal material.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
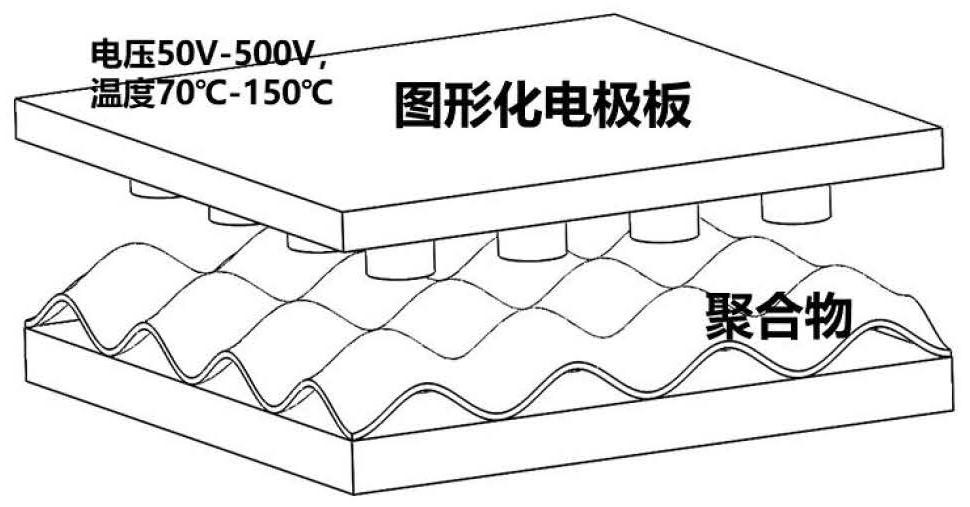
Polymer surface microstructure controllable forming mechanism research method based on phase field model
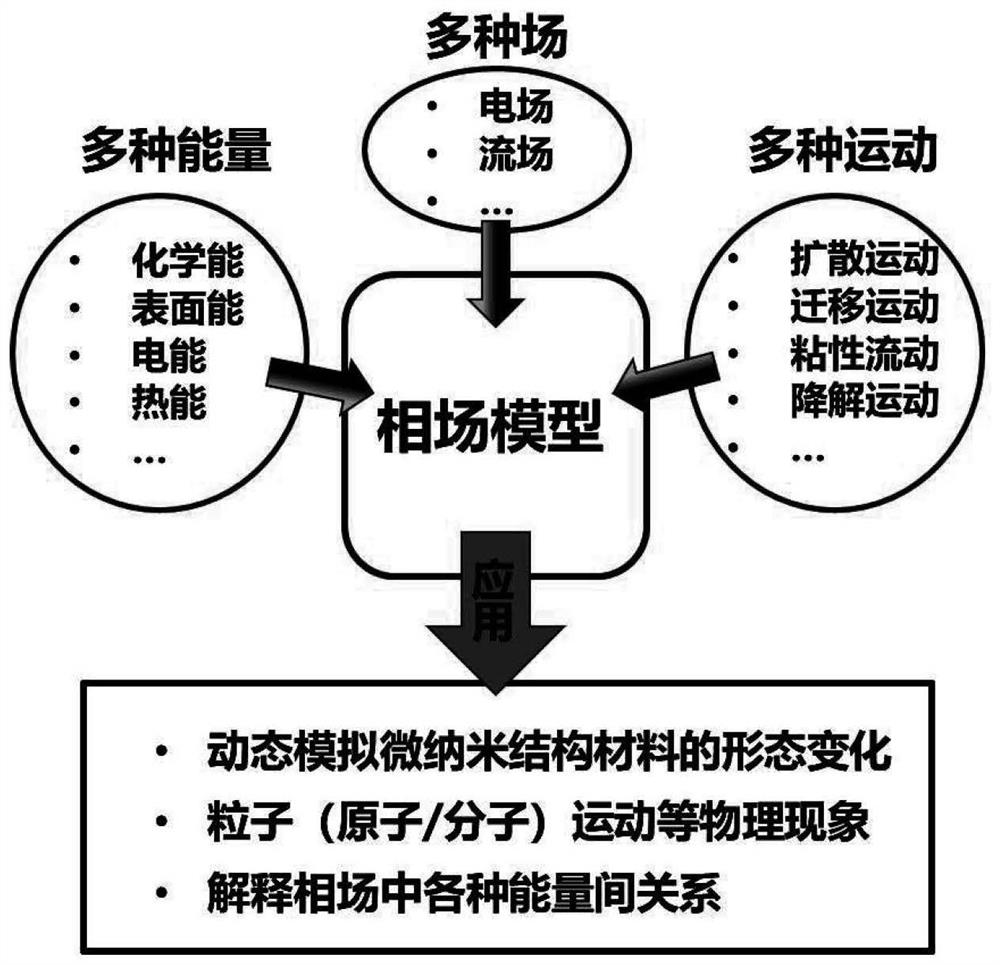
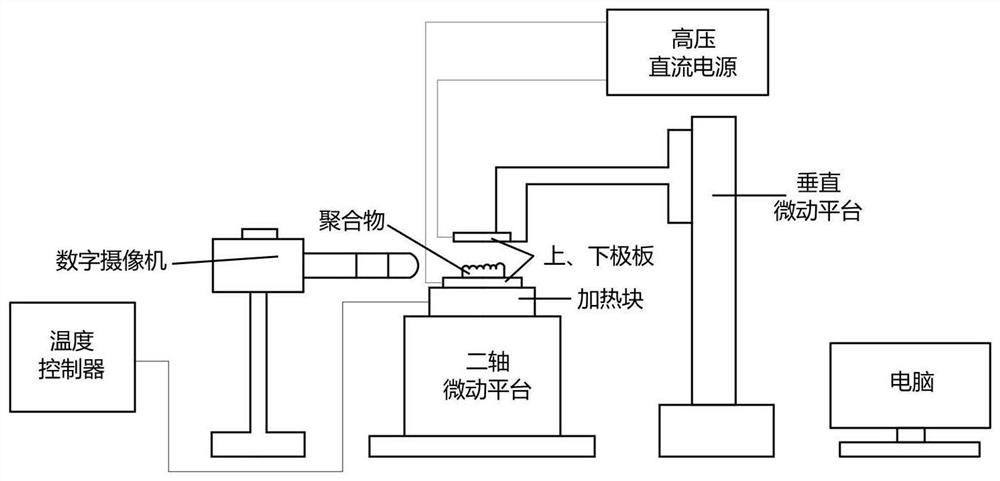
ActiveCN112895408AObserve the shape changeStudying Dynamic Deformation ProcessesPolymeric surfaceMolten state
The invention discloses a polymer surface microstructure controllable forming mechanism research method based on a phase field model. The method comprises the following steps of S1, heating a sample, namely a polymer material, at a certain temperature to reach a molten state; S2, applying an electric field to the polymer in the molten state, and inducing the surface microstructure of the polymer to form various array structures by patterning an electrode plate and setting different electric field intensities so as to obtain the morphological change conditions of the surface microstructure of the polymer at different time periods; S3, establishing a system model of an electric field induced polymer surface microstructure; and S4, compiling the differential equation in the model to obtain simulation data, and importing the simulation data into visual software for image display to obtain a corresponding analog simulation result. According to the method, the dynamic process that the electric field induces the formation of the polymer surface microstructure is simulated, so that the formation change of the polymer surface structure is more intuitively observed, and the influence of the shape, parameters, air gaps, polymer film thickness and the like of the electric field on an experiment is researched.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Research method for quantitative formation of internal spherical defects of three-dimensional photonic crystal
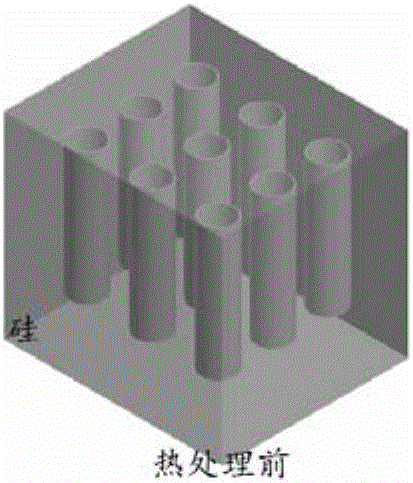
ActiveCN109933917ABuild inner connectionSpecial data processing applicationsPhotonic crystalSpherical shaped
The invention particularly relates to a research method for quantitative formation of internal spherical defects of a three-dimensional photonic crystal based on surface energy action. The surface ofthe three-dimensional photonic crystal is provided with two-dimensional array cylindrical holes, and the research method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a phase field model of thethree-dimensional photonic crystal; step 2, establishing a system surface energy equation; and step 3, selecting the diameter D and the aperture distance Ds of the two-dimensional array cylindrical holes to be unchanged, continuously changing the depth H of the cylindrical holes, and adjusting the limit conditions of H / D to obtain the quantitative relationship between the system surface energy ofthe three-dimensional photonic crystal and the formed spherical defect cavity. According to the invention, the thermal diffusion motion of three-dimensional photonic crystal medium particles is utilized. The research on the quantitative forming of the spherical defects in the photonic crystal is realized under the action of the surface energy of the system, the internal relation between the surface energy E of the system and the number N of the spherical defect cavities is established, and a new idea method is provided for the stable forming of the internal microstructure of the three-dimensional photonic crystal.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for analyzing and predicting strength of crack-containing ferroelectric material under effect of force-electricity-heat coupling field
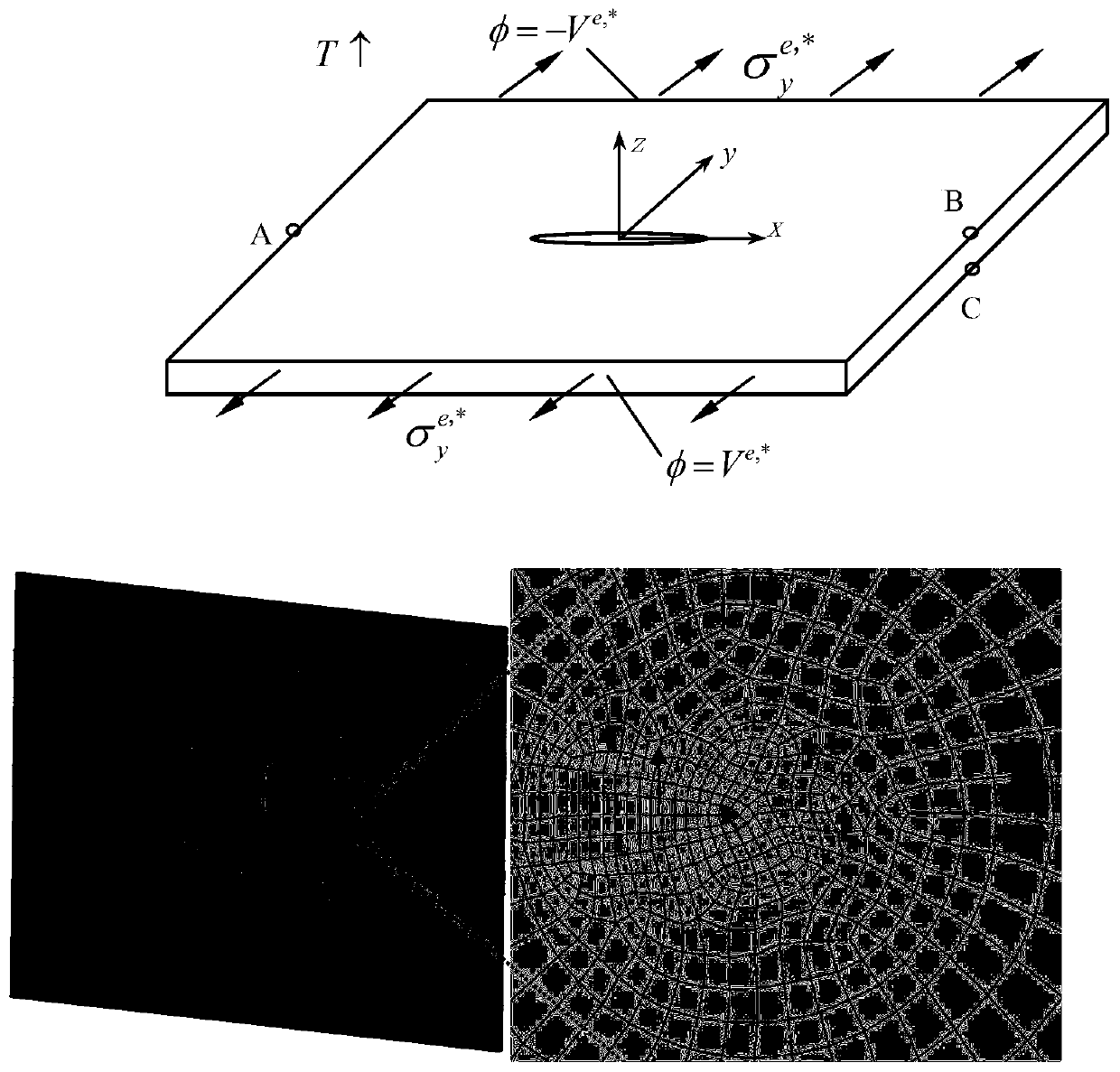
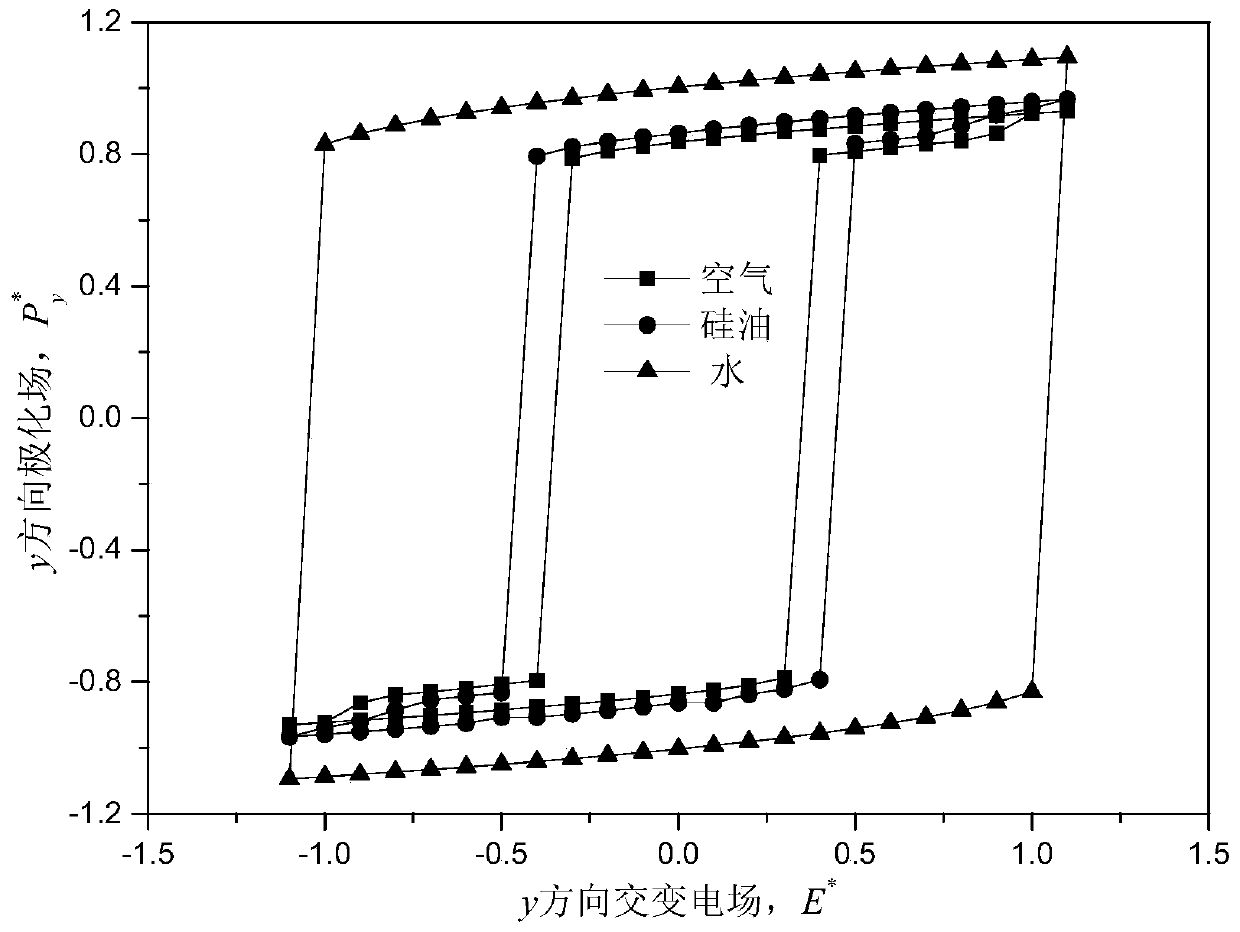
InactiveCN111105848ASimple processImprove adaptabilityChemical property predictionCheminformatics data warehousingDielectricStress concentration
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and predicting the strength of a crack-containing ferroelectric material under the effect of a force-electricity-heat coupling field. The method comprises the steps: building a new phase field model of multi-field coupling by considering oval cracks in the ferroelectric material as electric inclusions; solving a force-electricity-heat multi-field coupling problem of crack-containing ferroelectric single crystal; giving hysteresis loops of different electric inclusion models, and controlling the dielectric constant of electric inclusion to improvethe material performance or prevent degradation of the material performance; and obtaining domain structures and stress field distribution of ferroelectric single crystals of different electric inclusion models under the effect of a given electromechanical load in different temperature environments. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the correlation between the evolution of the micro domain structure and the macroscopic local stress concentration of the crack-containing ferroelectric material under the action of the force-electricity-heat coupling field is uniformly expressedby using the effective model. Therefore, a theoretical basis is provided for structural safety design and health prediction of a ferroelectric component under a complex or extreme environmental load.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Substance evolution simulation method based on exponential time difference format solution
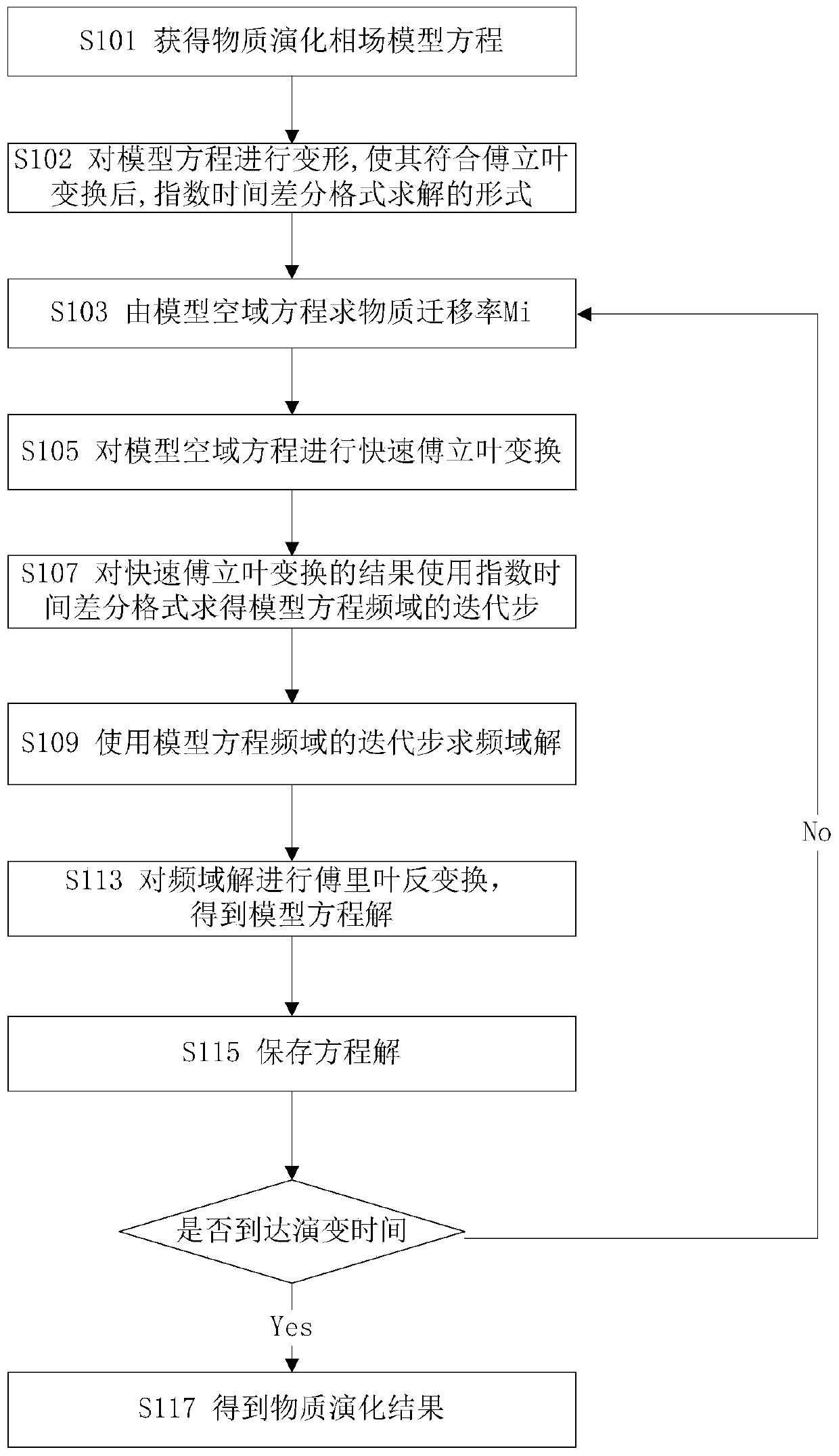
ActiveCN110717271ASimplify complexityQuick solveDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformConcurrent computation
The embodiment of the invention provides a substance evolution simulation method based on exponential time difference format solution. A substance evolution model is established based on a phase fieldmodel, the phase field model does not need to carry out prior assumption on a crystal grain structure evolution path, the position of a crystal grain interface does not need to be tracked explicitly,and the complexity of simulation calculation is greatly simplified. The equation of the substance evolution model is solved by using an exponential time difference format, namely, in the solving process, a frequency domain equation of the equation is obtained through fast Fourier transform, the frequency equation is solved by using the exponential time difference format, and Fourier inverse processing is performed on a solving result to finally obtain an equation solution. When the method is used for solving the phase field model, the method is rapid, stable and accurate, parallel computing can be carried out, and the method is suitable for solving a large-scale equation set by utilizing a computer.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com