3D printing device and method of tissue engineering scaffolds
A tissue engineering scaffold and 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems that it is difficult to realize complex structural scaffolds with multiple or even all tissue combinations, simple scaffold structures, single shapes, etc., to achieve mechanical The effect of excellent strength, reasonable structure and composition, and strong manufacturing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below. It should be emphasized that the following description is only exemplary and not intended to limit the scope of the invention and its application.
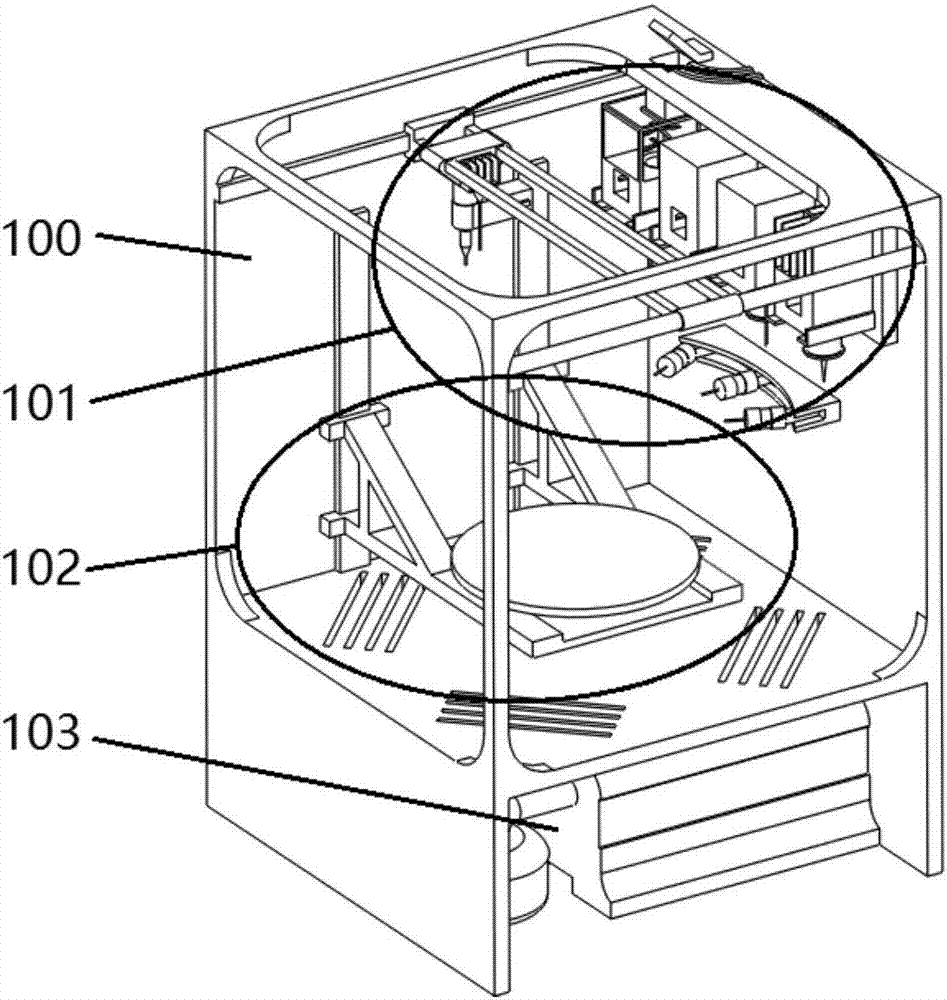
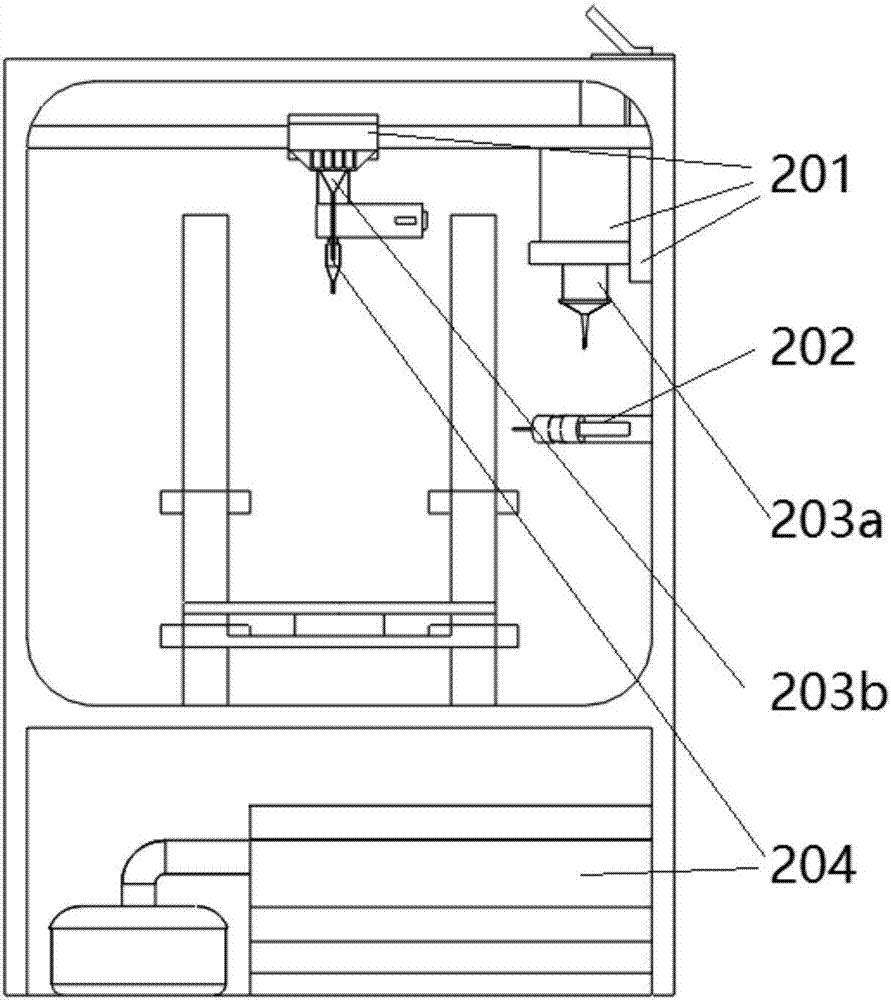
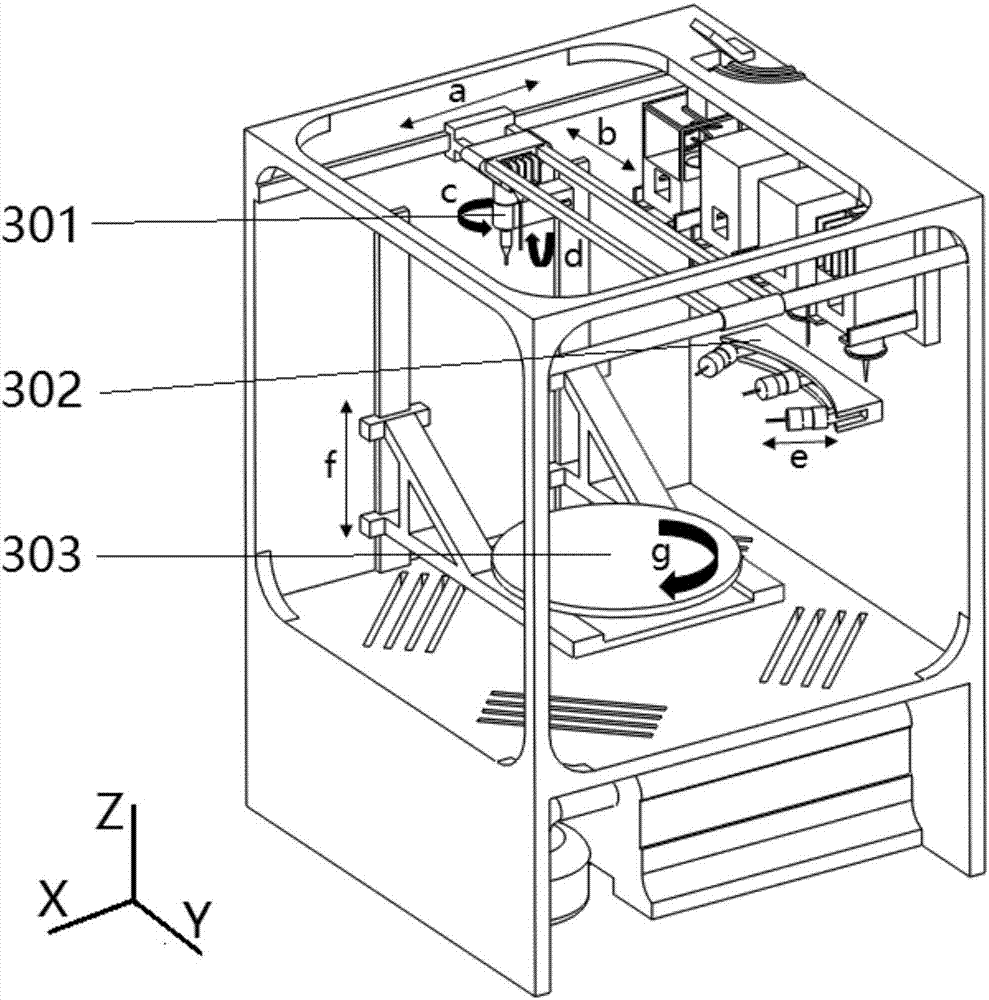
[0033] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 8 , in one embodiment, a 3D printing device for tissue engineering scaffolds, including a printing module 201, a spraying module 202, cell implantation modules 203a, 203b, a printing platform 303 and a temperature control module; the printing module 201 has An extrusion printing device of one or more nozzle devices 403, used for extrusion printing to form a tissue engineering scaffold with a three-dimensional macroscopic structure; the spraying module 202 is a spraying device with one or more nozzles, used for forming a two-dimensional Macrostructure tissue engineering scaffold; the cell implantation module 203a, 203b is an inkjet printing device with one or more nozzles, used to eject micro-droplets containing seed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com