T-spline and isogeometric analysis-based die surface springback compensation method
A technology of isogeometric analysis and mold surface, which is applied to mold surface springback compensation for geometric analysis. Surface springback compensation refers to reducing the accuracy of the model in the fields of sheet metal stamping, eelements, NURBS, and exactgeomet. Error, model refinement analysis error, discrete and other issues, to achieve the effect of ensuring smoothness, accuracy and effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
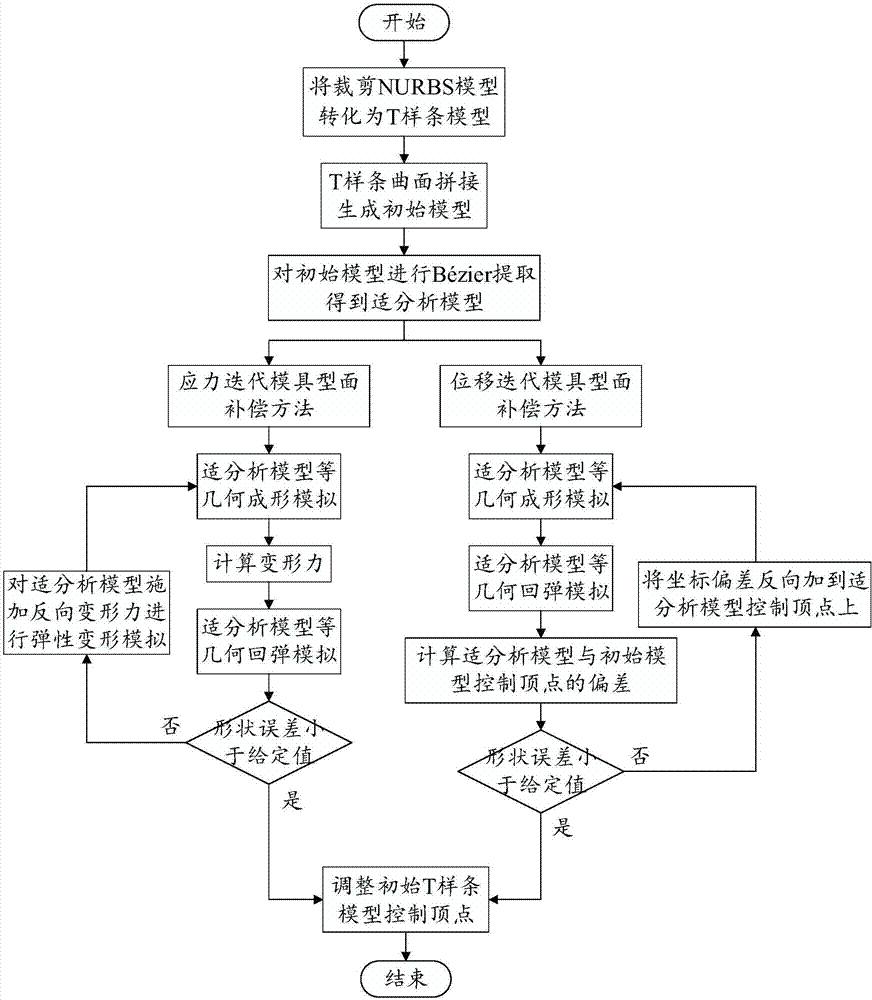
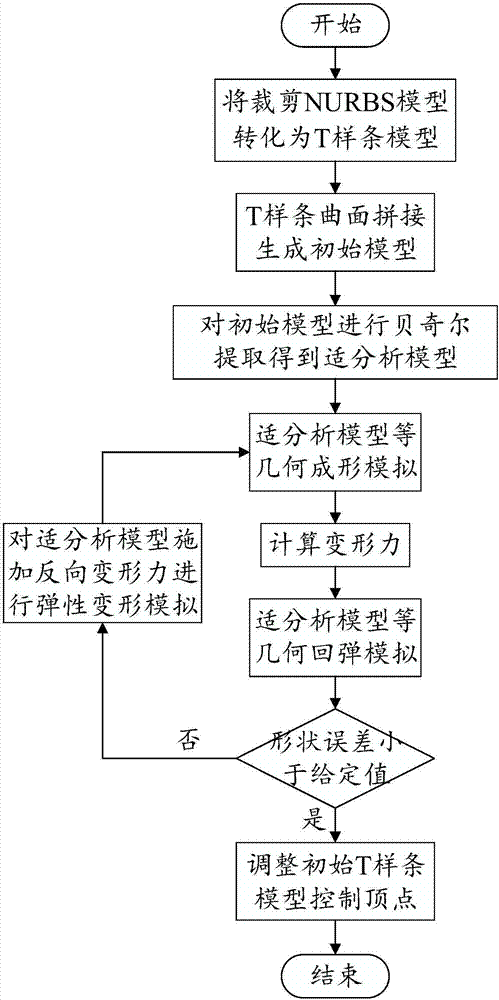
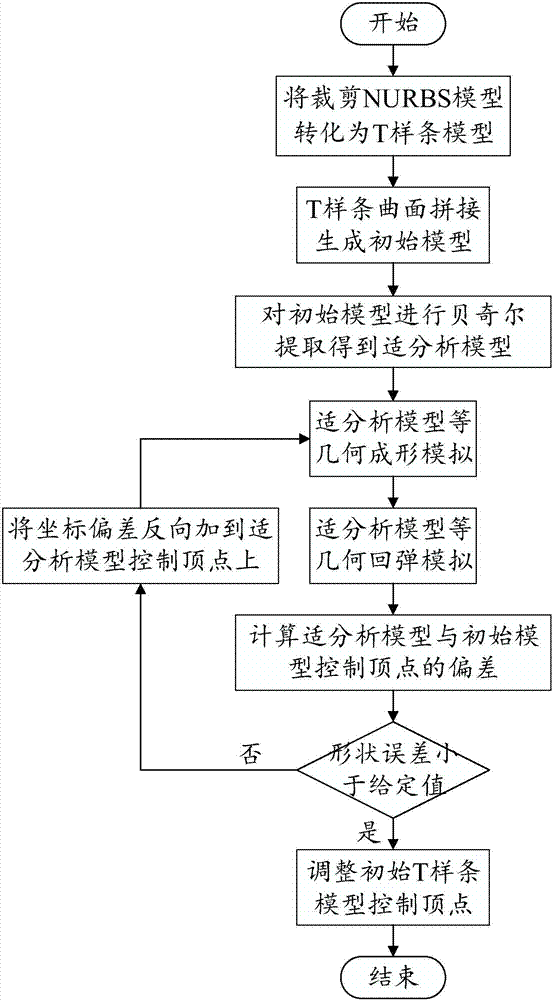
[0052] The present invention provides a mold surface springback compensation method based on T-spline and isogeometric analysis, which can be carried out in two different ways: a stress iterative mold surface compensation method and a displacement iterative mold surface compensation method. These two methods are described in detail below.
[0053] [1] Stress iterative mold surface compensation method mainly includes the following steps:
[0054] Step 1 converts the stamping part model represented by the clipped NURBS surface into multiple non-clipped T-spline models. At present, the design models of large and complex stamping parts such as automobile panels in CAD software are mostly represented by clipping NURBS, and they need to be converted into non-clipping T-spline surfaces first.
[0055] Step 2 splicing multiple non-cut T-spline models to generate a single T-spline surface model as the initial model of the mold surface. For the specific implementation method of conver...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com