Prevention and treatment of inflammatory conditions
A technology for inflammatory conditions, hepatitis, applied in the field of compositions that modulate type II and/or type I NKT cells, and can solve problems such as the lack of effective treatment methods for the disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
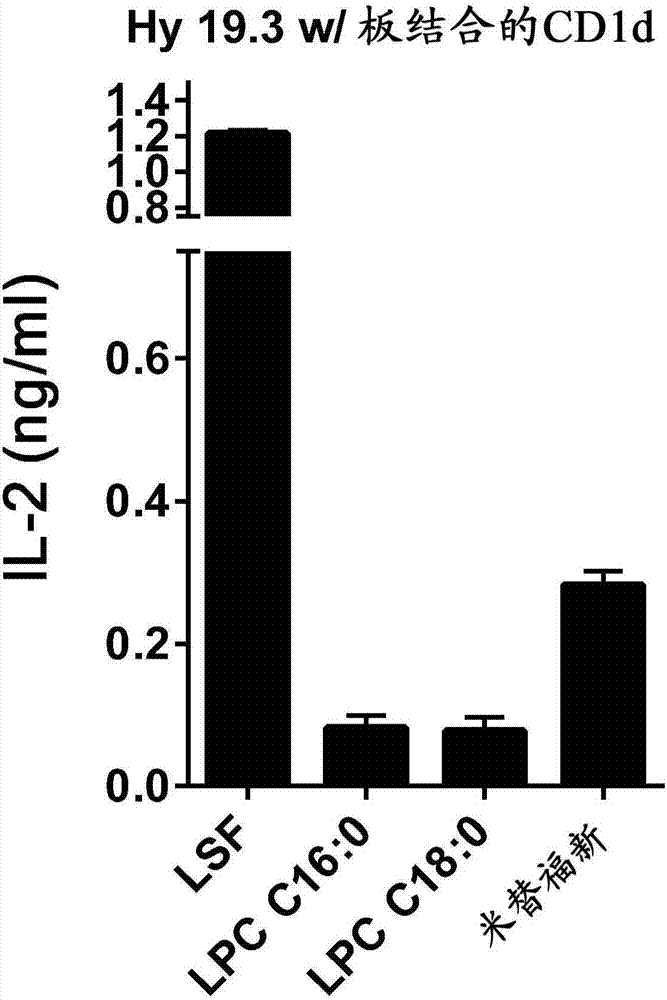
[0535] Miltefosine was able to stimulate the type II NKT cell hybridoma Hy19.3 in a plate-bound CDld assay. CDld protein-coated 96-well plates were incubated with the indicated liquids for 6 hr, washed and added with type II NKT cells Hy 19.3 (50,000 cells / well), and IL-2 in the supernatant was measured after 16 hr. LSF, lysosulfatidyl; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine.
[0536] These data show that miltefosine, an analog of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), can bind CDld molecules and stimulate type II NKT cells.
Embodiment 2
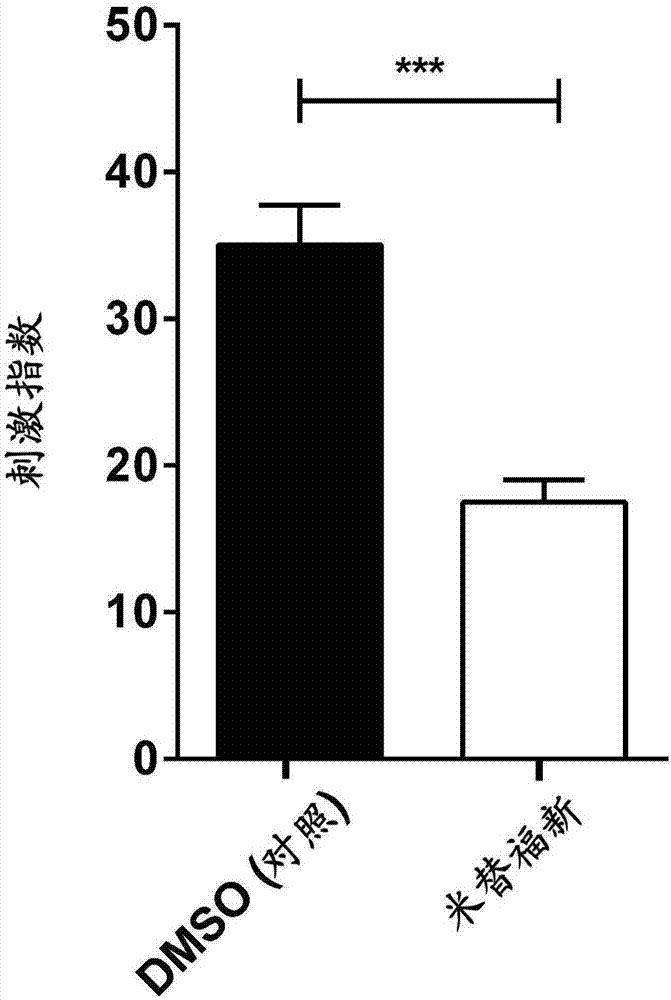
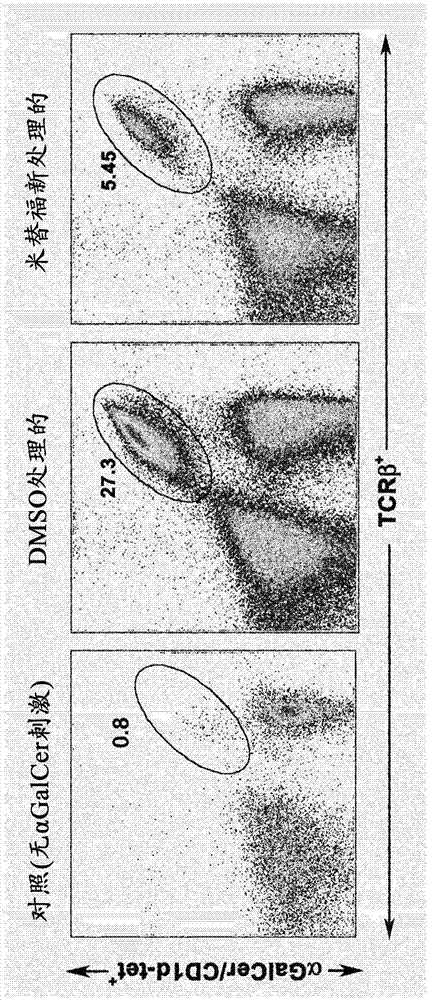
[0538] Naive B6 mice were treated daily for 7 days with DMSO (control) or miltefosine 1 mg (dissolved in DMSO and diluted into PBS) by oral gavage. Splenocytes were cultured in vitro for 90 hr in the presence or absence of α-GalCer. Stimulation (as a stimulation index) and expansion (using α-GalCer / CD1d) of type I NKT cells at a concentration of α-GalCer of 10 ng / ml - Tetramer + cells, as FACS staining), are shown in Figure 2A with Figure 2B middle.
[0539] Figure 2A with Figure 2B The data in show that there is a marked inhibition of type I NKT cell proliferation and expansion in the presence of its cognitive ligand α-GalCer in miltefosine-treated animals.
[0540] These data are consistent with the fact that other lipids such as sulfatides (glycolipids) or lysophosphatidylcholines (LPC, phospholipids) activate type II NKT cells, leading to inactivation or inhibition of type I NKT cells.
Embodiment 3
[0542] 12 hr before ConA administration, DMSO / PBS or miltefosine was administered to the BL / 6 mouse group, and liver injury was determined by H&E staining of liver sections and detection of liver enzymes (such as ALT in serum) after 24 hr ( Figure 3A and Figure 3B ). Data shown represent 2 independent experiments.
[0543] like Figure 3B As shown, in liver sections treated with con A, staining indicative of necrosis (red H&E staining)1 was observed, but in liver sections treated with con A and miltefosine, staining indicative of attenuated necrosis was observed (diminished red H&E staining)2.
[0544] Thus, suppression of ConA-induced hepatitis was observed following treatment with miltefosine. These data show that, similar to sulfatide or LPC, treatment of mice with miltefosine resulted in a significant inhibition of liver injury following Con A injection.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com