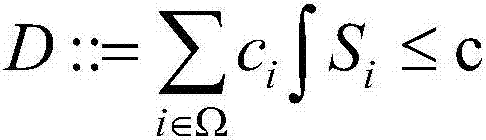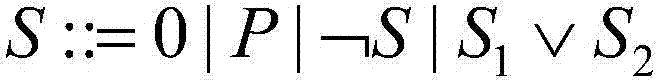Bounded model inspection method based on expanded linear time invariance
A model checking and period technology, applied in the field of bounded model checking, to achieve good efficiency, eliminate sampling error, and low algorithm complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
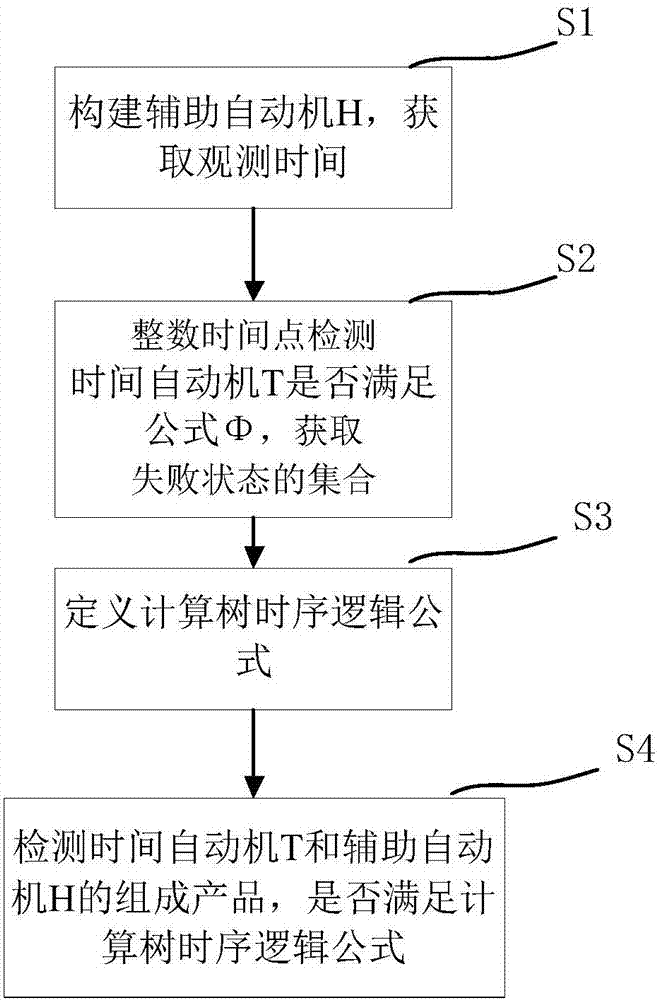
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, a bounded model checking method based on the extended linear period invariant includes the following steps:
[0044] S1, according to the timed automaton T and the extended linear period invariant formula Φ under the given discrete time semantics, construct the auxiliary automaton H, which is used to calculate the observation time of the auxiliary automaton H for the timed automaton T;
[0045] S2, within the range set by the observation time, detect whether the time automaton T at each integer time point satisfies the formula Φ, and obtain the set of states that do not satisfy the formula Φ;
[0046] S3, defining a computational tree temporal logic formula for describing the properties of the set obtained in step S2;
[0047] S4. Check whether the product composed of the timed automaton T and the auxiliary automaton H, namely T||H, satisfies the temporal logic formula of the calculation tree obtained in step S3. If not, the timed automaton T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com