Workflow scheduling method based on critical path task prospects
A technology of critical path and scheduling method, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve problems such as increasing time complexity, poor scheduling effect, and small sum of computing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] The invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
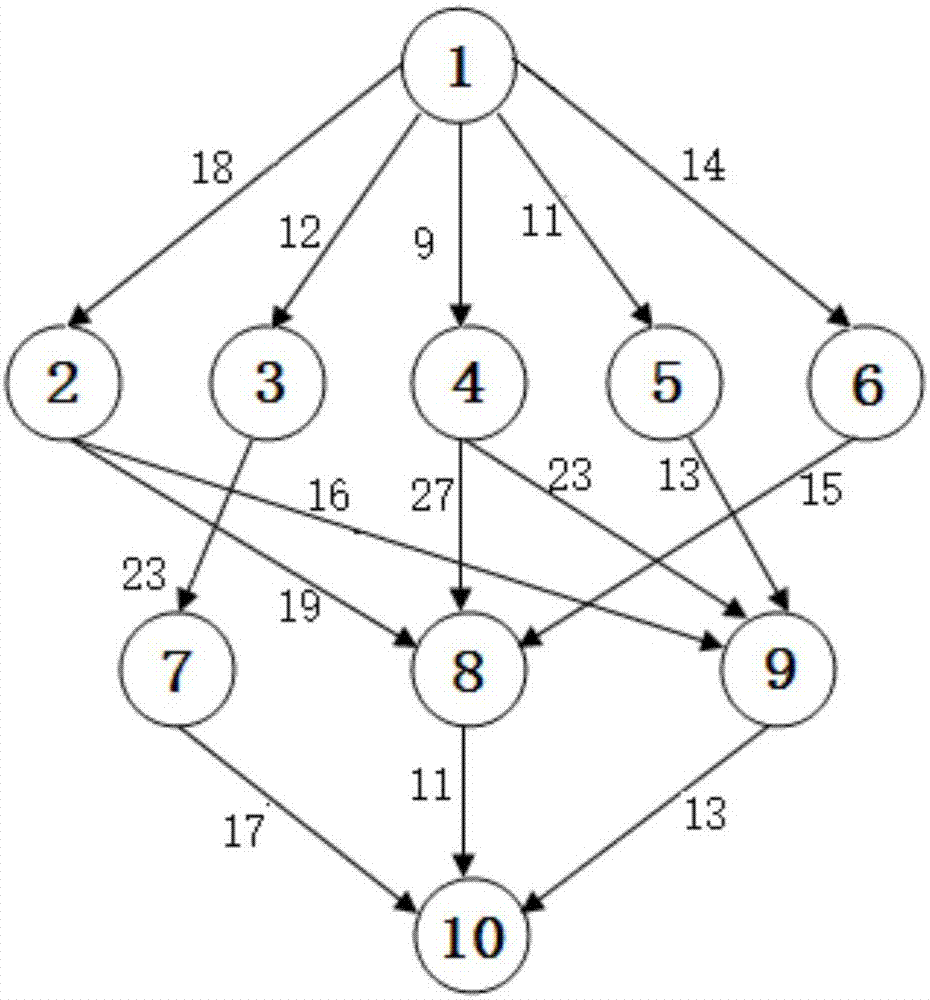
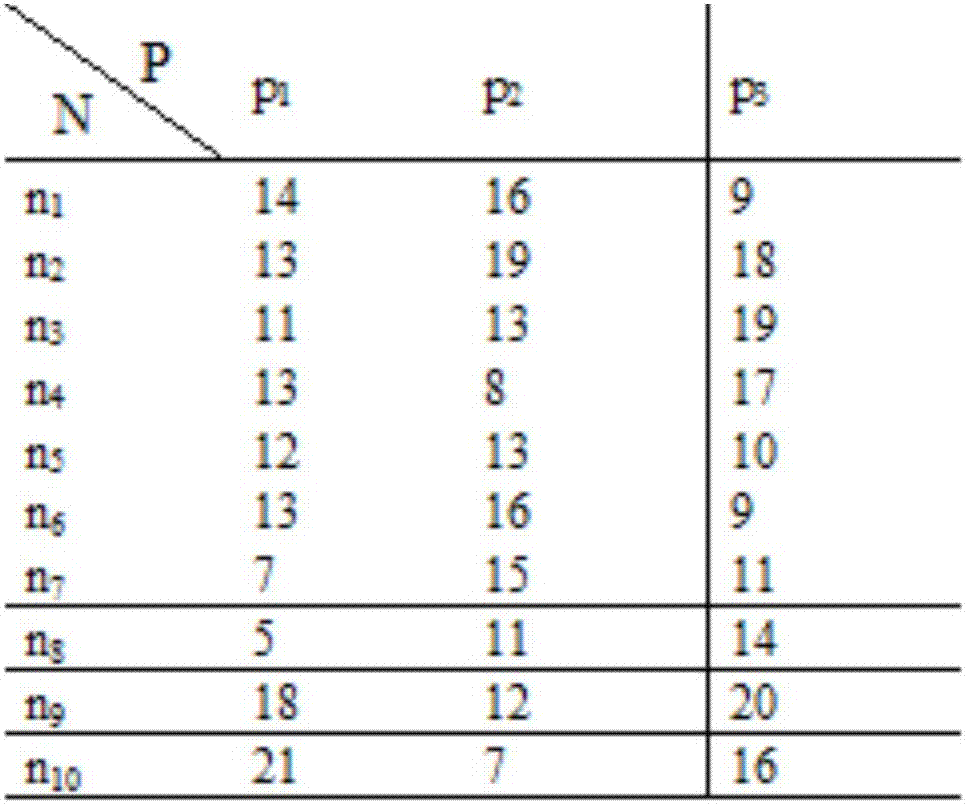
[0067] Step 1, convert the workflow into a DAG task scheduling model, the DAG graph structure is as follows figure 1 As shown, the weight of each directed edge is equal to the average communication time between tasks, such as figure 1 The average communication time between task 5 and task 9 is 13 time units. The computing time of each task node in the DAG graph on each processor can be found in figure 2 , each row in the table represents the task number in the DAG graph, and each column refers to the processor number. For example, the calculation time of the task numbered 4 in Table 1 on the processor numbered 3 is 17 time units.
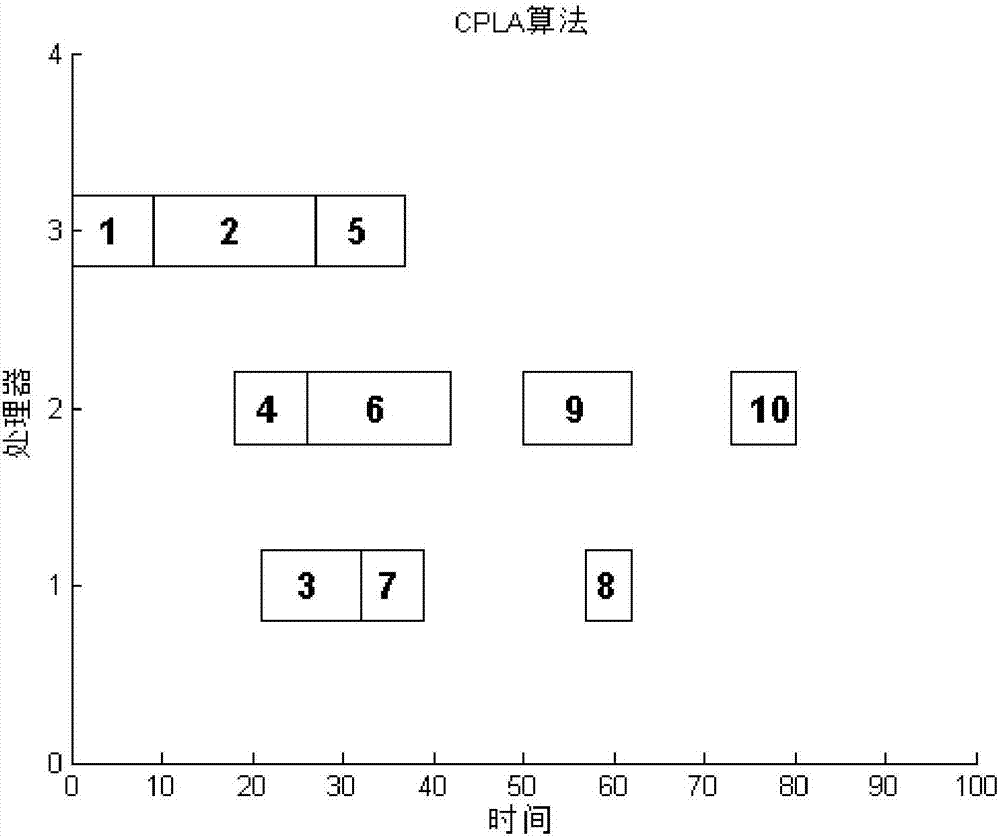
[0068] Step 2, according to the formula (3), calculate the upward sorting value of each task node in the DAG graph, and the results are shown in the second column of Table 1.
[0069] Step 3, calculate the downward sorting value of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com