Fusion satellite-ground system frequency sharing method and system based on dynamic spectrum allocation
A technology of system frequency and dynamic spectrum, applied in the field of frequency sharing of fusion satellite-ground systems, can solve the problem of low density of active users, and achieve the effect of reducing effect, reducing interference and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
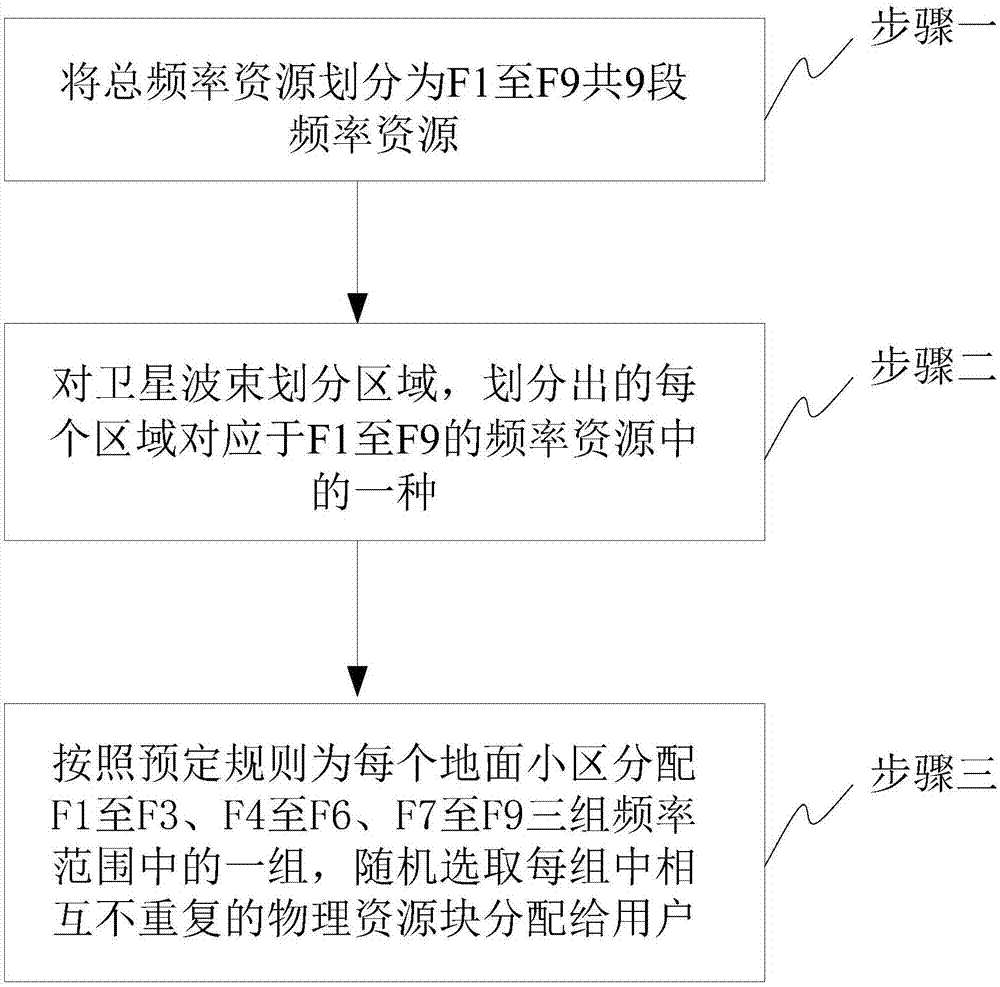
[0020] Specific implementation mode 1: The frequency sharing method of the integrated satellite-earth system based on dynamic spectrum allocation in this implementation mode, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0021] Step 1: Divide the total frequency resources into 9 segments of frequency resources from F1 to F9.
[0022] Step 2: Divide areas for the satellite beams, and each divided area corresponds to one of the frequency resources F1 to F9.
[0023] Step 3. The terrestrial cells covered by satellite beams use a 1 / 3 multiplexing scheme, specifically: allocate one of the three groups of frequency ranges F1 to F3, F4 to F6, and F7 to F9 for each terrestrial cell according to predetermined rules , randomly select non-repeating physical resource blocks in each group and assign them to users.
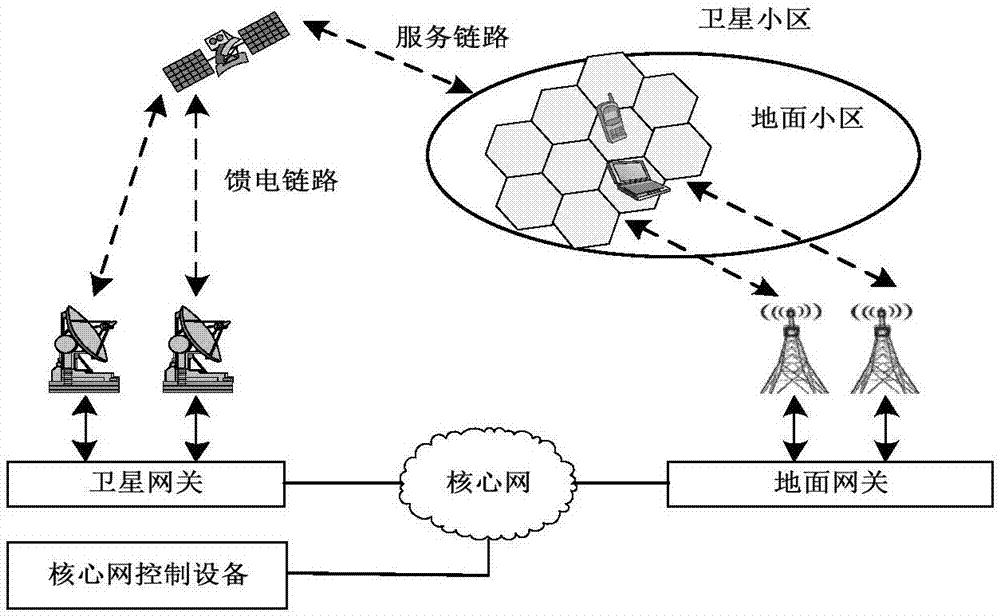
[0024] The method of the present invention is based on the fusion of the satellite network and the ground network. The fusion of the satellite network and the ground network has vario...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031]Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: in step two:
[0032] The division of satellite beams is as follows: determine the number of regions that can be divided according to the satellite parameters; allocate one of the frequency resources from F1 to F9 for each region, and ensure the sum of the distances of the regions where the same frequency resources are located during allocation higher than the preset value.
[0033] This embodiment is for Figure 7 The process of allocating F1-F9 frequencies to each satellite cell in , the principle of allocation is to make the physical distance of the same frequency as far as possible, for example Figure 7 In , all satellite cells of the same frequency are separated by at least two satellite cells. In actual operation, the sum of the distances in the same frequency area can be calculated. If the sum of the distances is the largest, the isolation ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: in step 3, the predetermined rule is a random selection rule. That is, when one of the three frequency ranges is selected for the ground cell, random selection is adopted.
[0036] In this principle, the satellite and ground parts are uncoordinated, and the resources in the ground system are allocated randomly according to the allocation pattern established in the ground system, regardless of the cell location or ground user conditions in the satellite frequency pattern. The terrestrial network cell adopts 1 / 3 color multiplexing, and randomly allocates available frequencies to users in the cell in the terrestrial network. exist Figure 9 It can be seen from the figure that the terrestrial network cell numbered 17 can use the frequency resources of F4-F6 (physical resource block numbers are 25-48). If there are 8 users in each cell, then any number 25-48 can be used without repetition The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com