RNA polymerase ii33 nucleic acid molecules to control insect pests
A molecular and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of plant protection effects, can solve problems such as inability to accurately identify effective targets a priori
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0365] Example 1: Materials and methods
[0366] Sample Preparation and Bioassays
[0367] use A number of dsRNA molecules (including those corresponding to the following: rpII33-1 reg1 (SEQ ID NO:5), rpII33-2reg1 (SEQ ID NO:6), rpII33-2 v1 (SEQ ID NO:7) and rpII33-2 v2 (SEQ ID NO:8)). Purified dsRNA molecules were prepared in TE buffer, which consisted of a control treatment for all bioassays, which served as a background check for mortality or growth inhibition of WCR (Maize root beetle). use NANODROP TM An 8000 Spectrophotometer (THERMOSCIENTIFIC, Wilmington, DE) measured the concentration of dsRNA molecules in the bioassay buffer.
[0368] Samples were tested for insect activity in a bioassay using neonatal insect larvae fed an artificial insect diet. WCR eggs were obtained from CROP CHARACTERISTICS, INC. (Farmington, MN).
[0369] Bioassays were performed in 128-well plastic trays (C-D INTERNATIONAL, Pitman, NJ) specially designed for insect bioassays. Each well c...
Embodiment 2
[0379] Example 2: Identification of Candidate Target Genes
[0380] Insects from multiple WCR (corn root firefly beetle) developmental stages were selected for pooled transcriptome analysis to provide candidate target gene sequences controlled by RNAi technology for transgenic plant insect protection.
[0381] In one example, total RNA was isolated from approximately 0.9 g of intact first instar WCR larvae (4 to 5 days after hatch; maintained at 16°C) and analyzed using the following phenol / TRI-based The method (MOLECULAR RESEARCH CENTER, Cincinnati, OH) purification:
[0382] Place the larvae in a container containing 10 mL TRI at room temperature Homogenize in a 15 mL homogenizer until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. After 5 minutes of incubation at room temperature, the homogenate was dispensed into 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (1 mL per tube), and the mixture was vigorously shaken for 15 seconds after the addition of 200 μL of chloroform. After allowing the extr...
Embodiment 3
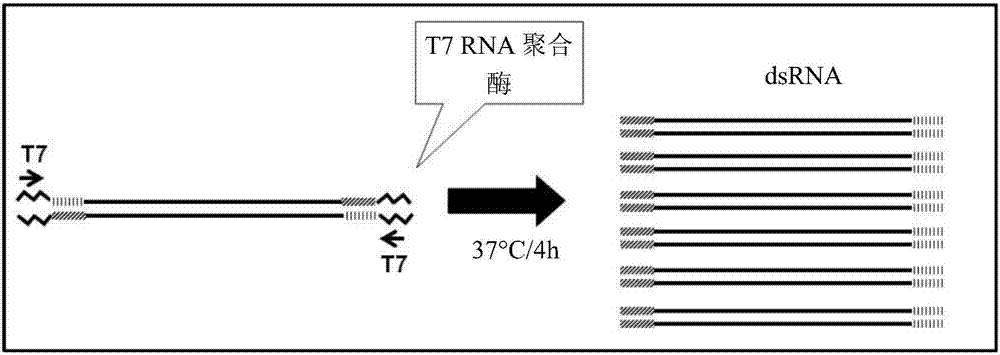
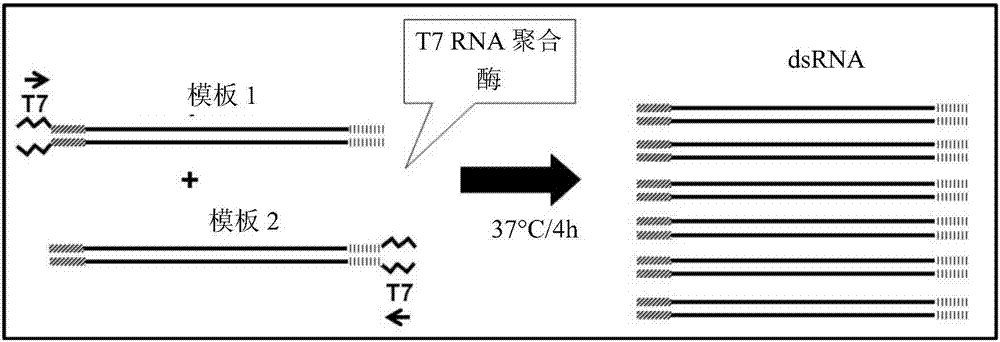
[0392] Example 3: Amplification of target genes to generate dsRNA
[0393] Full-length or partial clones of the sequence of the rpII33 candidate gene were used to generate PCR amplicons for dsRNA synthesis. Primers were designed to amplify the portion of the coding region of each target gene by PCR. See Table 1. The T7 bacteriophage promoter sequence (TTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA; SEQ ID NO:9) was incorporated into the 5' end of the amplified sense or antisense strand, as appropriate. See Table 1. use (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) extracted total DNA from WCR, then used the total DNA, using The first-strand synthesis system and the manufacturer's oligo-dT priming instructions (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) were used to make first-strand cDNA. The first-strand cDNA is used as a template for a PCR reaction employing reverse-positioned primers to amplify all or part of the native target gene sequence. dsRNA was also amplified from a DNA clone containing the cod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap