Learned profiles for malicious encrypted network traffic identification
A network traffic, malicious technology, applied in the field of improved malicious network traffic detection, can solve the problem of automatic malicious program detection system not working correctly, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
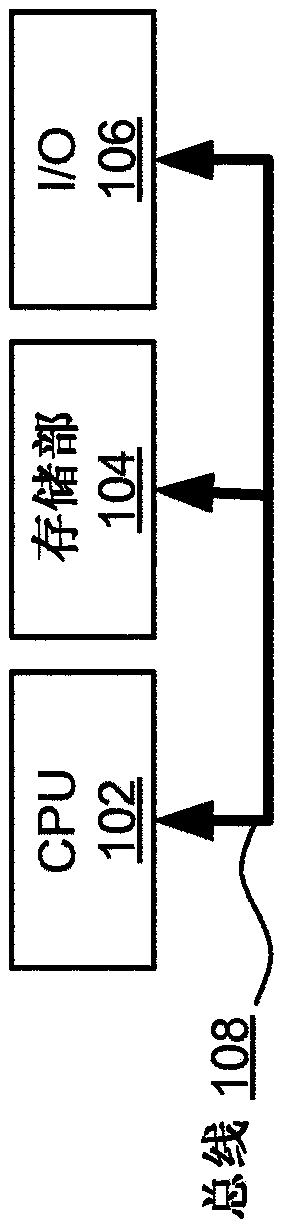
[0048] figure 1 It is a block diagram of a computer system suitable for the operation of the embodiment of the present invention. The central processing unit (CPU) 102 is communicably connected to the storage 104 and an input / output (I / O) interface 106 via a data bus 108. The storage section 104 may be any read / write storage device (such as a random access memory (RAM) or a non-volatile storage device). Examples of non-volatile storage devices include disk or tape storage devices. The I / O interface 106 is an interface for devices used for data input or data output, or both for data input and data output. Examples of I / O devices connectable to the I / O interface 106 include a keyboard, a mouse, a display (such as a monitor), and a network connection.
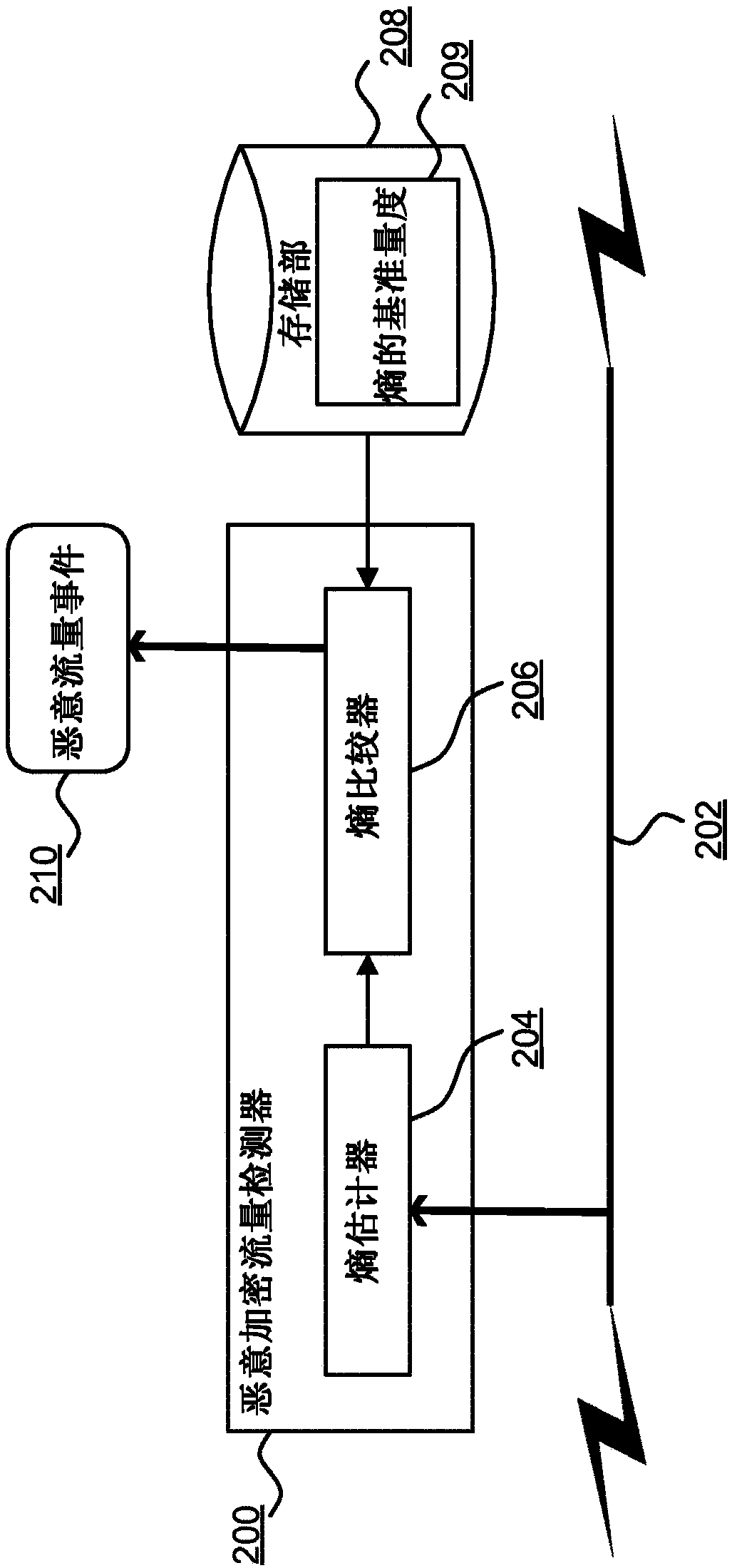
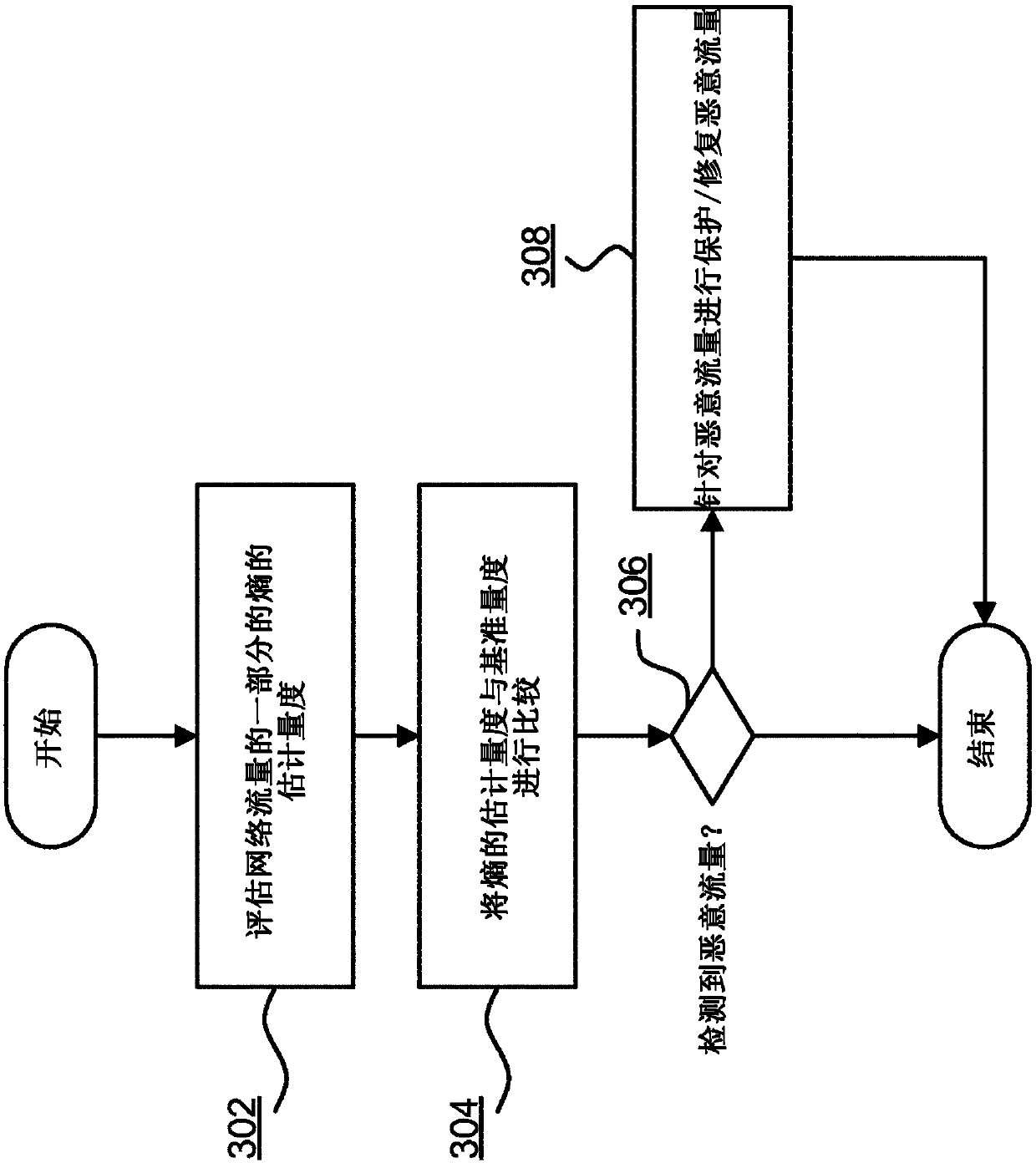
[0049] figure 2 It is a component diagram of the malicious encrypted traffic detector 200 according to the embodiment of the present invention. The detector 200 is a software, hardware, or firmware component for monitoring networ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com