A delayed coking processing method of oil sand pitch
A technology of delayed coking and processing method, which is applied in the field of delayed coking processing of oil sand asphalt, which can solve problems such as easy abrasion, increased equipment maintenance and repair costs, and heating temperature limitations, so as to reduce maintenance and maintenance costs, slow down the tendency of coking, and improve abrasion Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
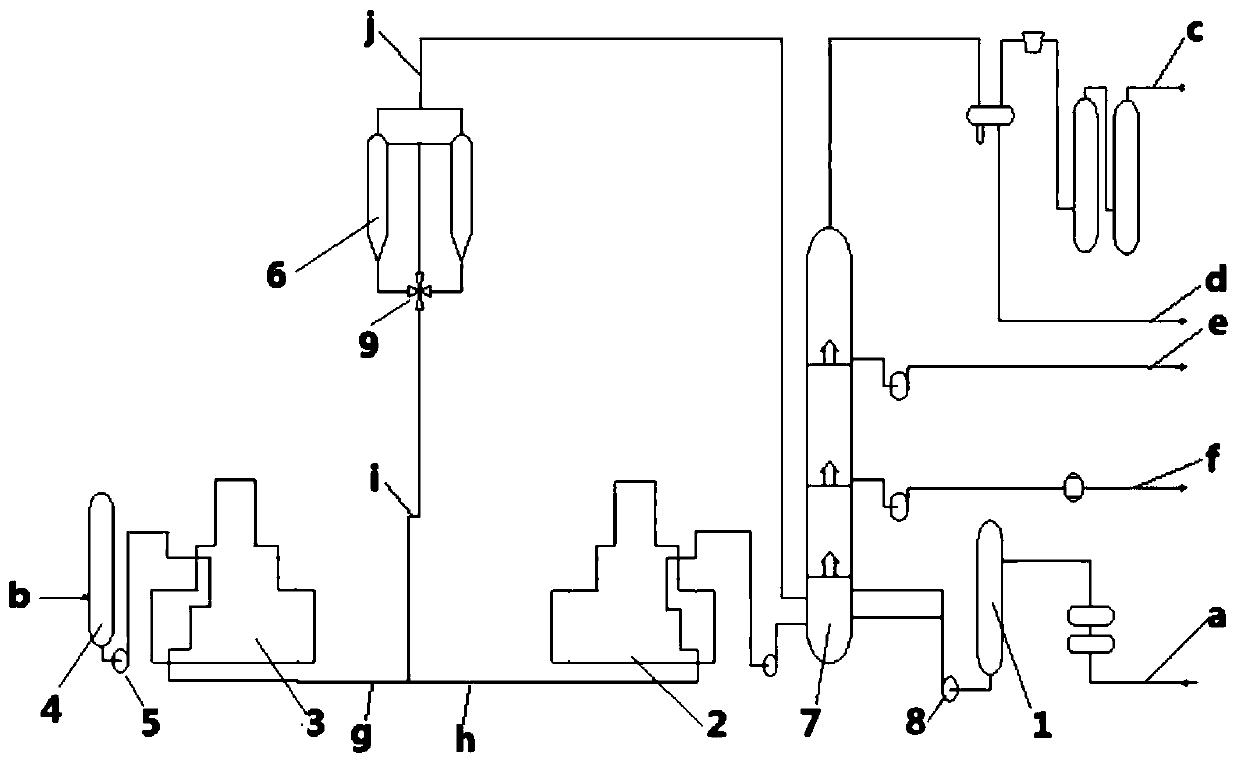
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, bituminous oil b is obtained from the mined oil sands after washing with water as the raw material, and is sent to a separately established bitumen raw material tank 4, and the bitumen oil is sent to a separately established bitumen oil heating furnace through the bitumen feed pump 5 at the bottom of the tank 3 Carry out the first coking reaction and heat it to 495-505°C to form g of high-temperature asphalt oil.
[0034] The residual oil a enters the residual oil raw material buffer tank 1, and enters the residual oil heating furnace 2 through the residual oil feed pump 8 for the second coking reaction, and is heated to 490°C to become the high-temperature residual oil h.
[0035] High-temperature bitumen oil g and high-temperature residue oil h are mixed to form a mixed feedstock oil. The blending ratio of bitumen oil is 1%, and it enters the coke tower 6 through the four-way valve 9 for the third coking reaction. The reaction temperature is 490°...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, bituminous oil b is obtained from the mined oil sands after washing with water and sent to a separately established bitumen raw material tank 4, and the bitumen oil b is sent to a separately established bitumen oil heating through the bitumen feed pump 5 at the bottom of the tank Furnace 3 undergoes the first coking reaction and is heated to 500°C to form g of high-temperature asphalt oil.
[0038] The residual oil a enters the residual oil raw material buffer tank 1, and enters the residual oil heating furnace 2 through the residual oil feed pump 8 for the second coking reaction, and is heated to 500° C. to become the high-temperature residual oil h.
[0039] The high-temperature asphalt oil g and the high-temperature residue oil h are mixed to form the mixed raw material oil i. The blending ratio of the high-temperature asphalt oil g is 10%, and enters the coke tower 10 through the four-way valve 9 for the third coking reaction. The reaction temp...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, bituminous oil b is obtained from the mined oil sands after washing with water and sent to a separately established bitumen raw material tank 4, and the bitumen oil b is sent to a separately established bitumen oil heating through the bitumen feed pump 5 at the bottom of the tank Furnace 3 performs the first coking reaction and is heated to 505°C to form g of high-temperature asphalt oil.
[0042] The residual oil enters the residual oil raw material buffer tank 1, and enters the residual oil heating furnace 2 through the residual oil feed pump 8 for the second coking reaction, and is heated to 505°C to become the high-temperature residual oil h.
[0043] The high-temperature asphalt oil g and the high-temperature residue oil h are mixed to form the mixed raw material oil i. The blending ratio of the high-temperature asphalt oil g is 20%, and enters the coke tower 6 through the four-way valve 9 for the third coking reaction. The reaction temperatur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com