High conductivity grid structure and processing method of lead-acid battery
A lead-acid battery and processing method technology, applied in the direction of electrode carrier/current collector, etc., can solve the problems of inability to be popularized, complicated process, high copper price, ensure charging acceptance and cycle life, reduce cost, and improve current distribution. The effect of uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
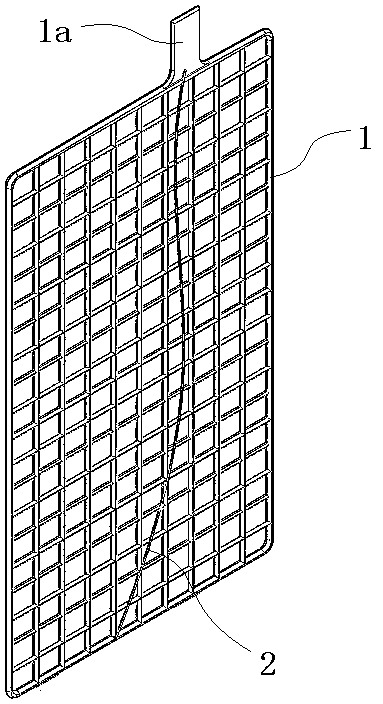
[0024] like figure 1 In the illustrated embodiment, a high-conductivity grid structure for a lead-acid battery includes a grid 1 in a grid state. One side of the grid is provided with tabs 1a, which protrude from the edge of the grid and are used to connect with external wires. At least one highly conductive rib 2 is provided on the grid, and the highly conductive rib is made of highly conductive metal or non-metal and composite materials. Highly conductive ribs are made of highly conductive metals or non-metals and composite materials. Highly conductive metals can be copper, copper alloys, aluminum, aluminum alloys and other metal materials. Non-metals include graphite, conductive polymers, etc., and composite materials include graphite. vinyl composite materials and other materials. One end of the highly conductive rib is fixedly connected to the tab, and the other end of the high conductive rib is fixedly connected to one side of the grid. Highly conductive ribs can be s...
Embodiment 2
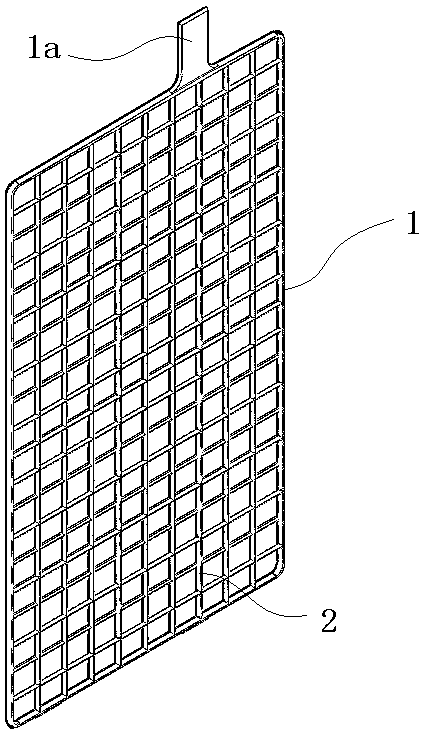
[0031] like figure 2 In the illustrated embodiment, a high-conductivity grid structure for a lead-acid battery includes a grid 1 in a grid state. One side of the grid is provided with tabs 1a, which protrude from the edge of the grid and are used to connect with external wires. At least one highly conductive rib 2 is arranged on the grid, and the highly conductive rib is made of highly conductive metal or non-metal and composite materials. Highly conductive ribs are made of highly conductive metals or non-metals and composite materials. Highly conductive metals can be copper, copper alloys, aluminum, aluminum alloys and other metal materials. Non-metals include graphite, conductive polymers, etc., and composite materials include graphite. vinyl composite materials and other materials. One end of the highly conductive rib is fixedly connected to the tab, and the other end of the high conductive rib is fixedly connected to one side of the grid. The highly conductive ribs can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com