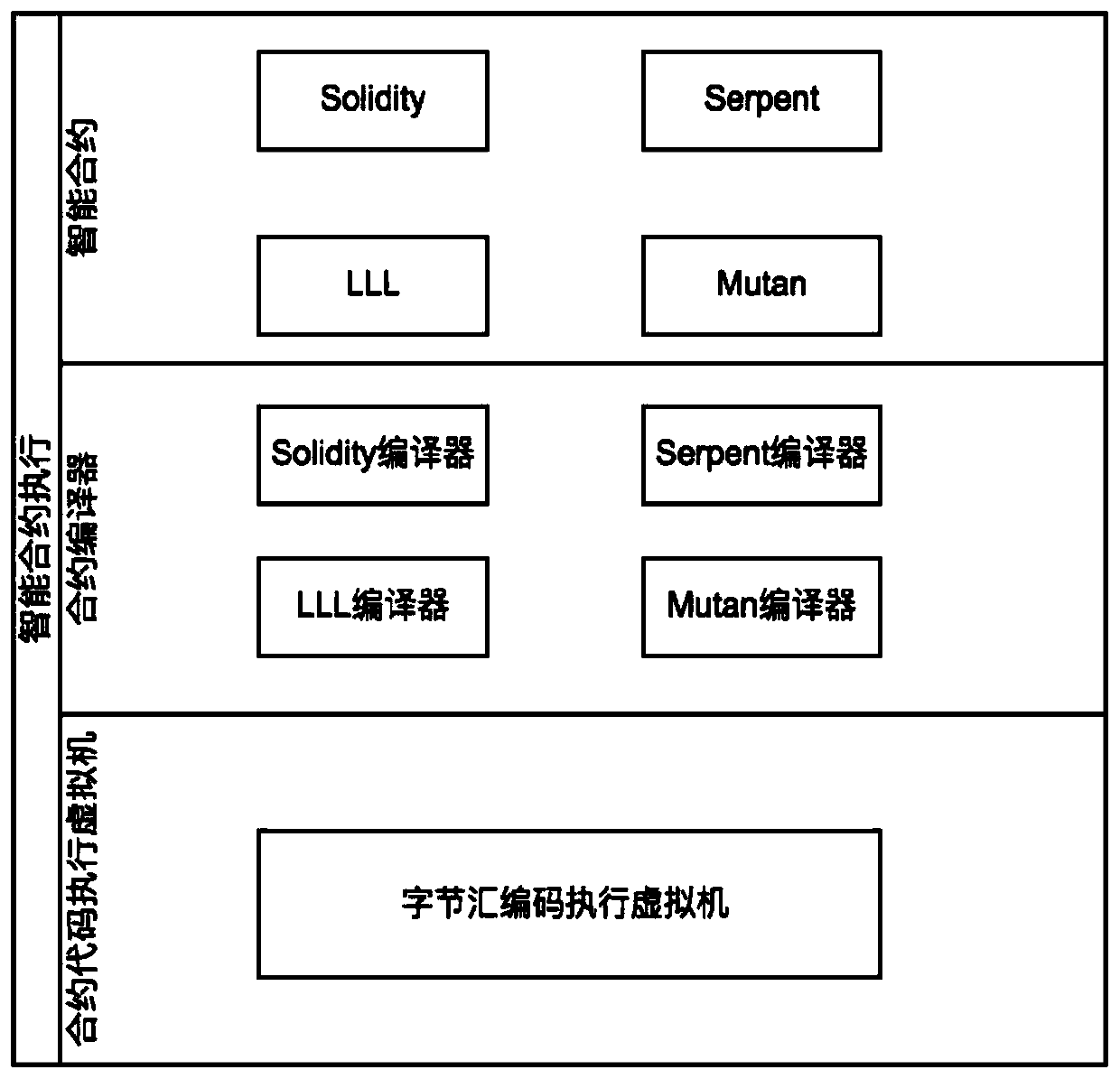
A highly available contract execution method and system
An execution method and contract technology, which is applied in the field of blockchain smart contracts and virtual machine implementations, can solve problems such as limited stack storage and inconvenient data random access, and achieve the effect of low execution cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
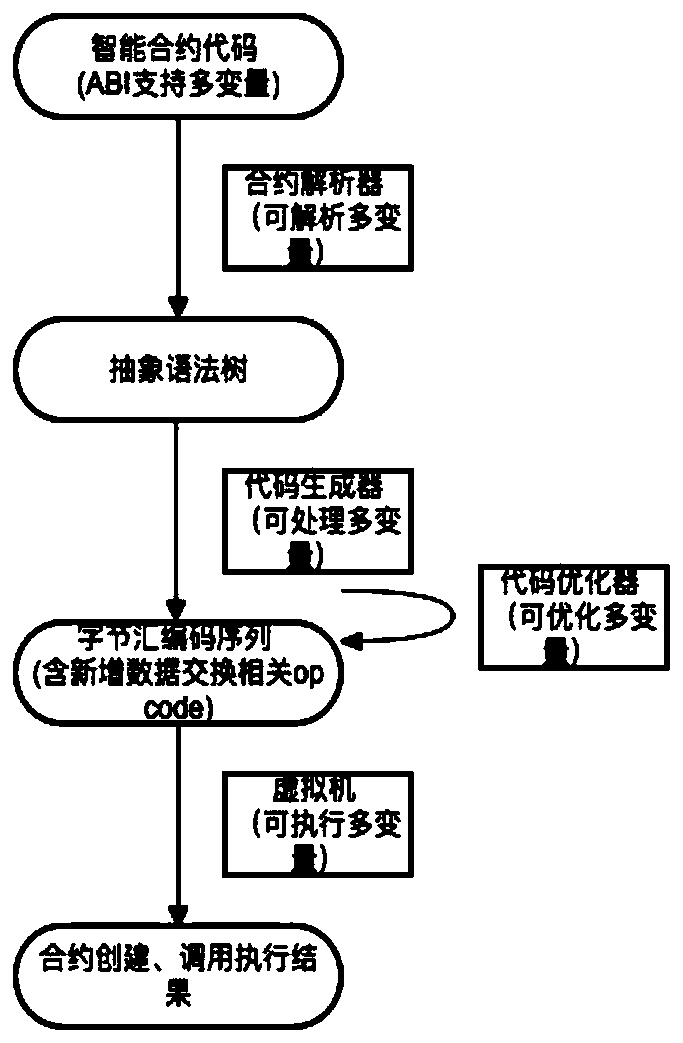
[0029] figure 2 For the ABI to support local variables or parameters that exceed the maximum stack depth (for example, a maximum of 16 is allowed when written in Solidity language), the implementation scheme of adding push offset and swapx or push offset and dupx bytecode sequence includes the following steps:
[0030] (1) Contract writers can write corresponding smart contract codes with more than 16 local variables or parameters according to the contract information, and are no longer restricted by the ABI information of the number of local variables or parameters when writing contracts.
[0031] (2) The contract language parser, after analyzing the syntax and semantics of the above-mentioned ABI-extended smart contract code, generates a corresponding abstract syntax tree. Among them, when more than 16 local variables and parameters are parsed or combined in expressions and arrays, these extended information will be generated into the corresponding abstract syntax tree acco...
Embodiment 2
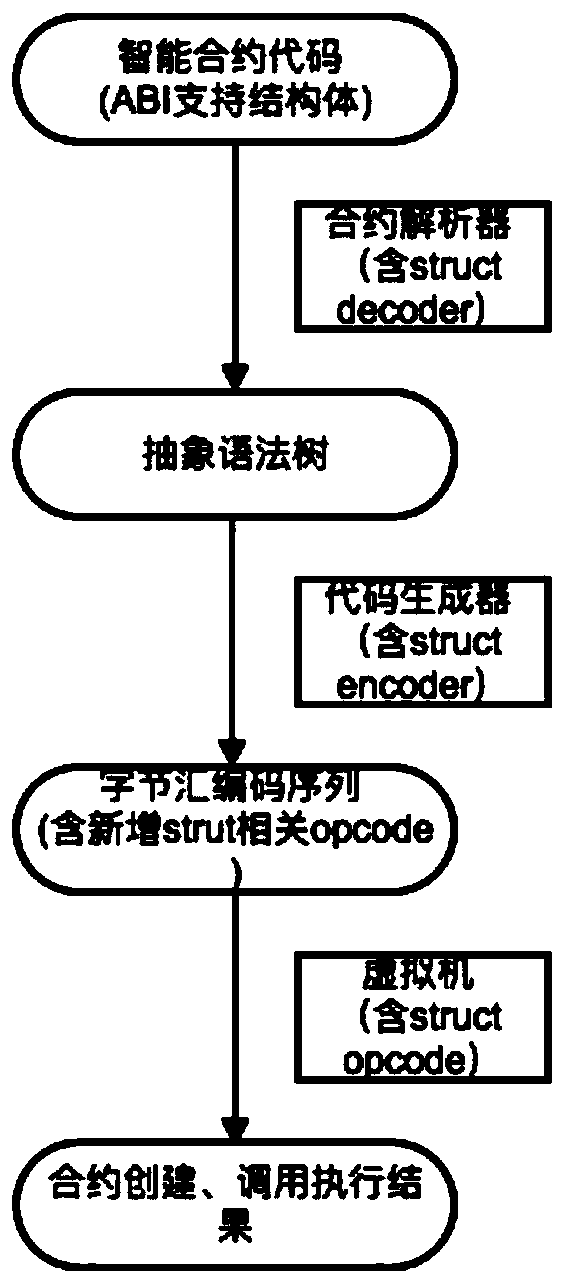
[0037] Such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0038] (1) Contract writers can write corresponding smart contract codes based on contract information. ABI supports member variable structures that exceed the maximum number of stack depth elements, which can be passed as local variables of functions (including internal or external functions) or as parameters.
[0039] (2) The contract language parser, after analyzing the syntax and semantics of the above-mentioned ABI-extended smart contract code, generates a corresponding abstract syntax tree. Among them, when the member variable structure that exceeds the maximum number of stack depth elements is parsed as a local variable of a function (including internal or external functions) or passed as a parameter, the decoding (decoder) process including the structure itself and its member variables, The structure itself and the member variable information of the member variables exceeding the maximum number of stack d...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Such as Figure 4 shown, including the following steps:
[0046] (1) Contract writers can write high-availability smart contract codes based on contract information, that is, local variables, function parameters and structures that exceed the maximum stack depth are supported in terms of ABI.
[0047] (2) The contract language parser generates the corresponding abstract syntax tree after analyzing the syntax and semantics of the above-mentioned ABI-extended smart contract code. The parser can parse the above-mentioned extended ABI information and can handle errors, and the syntax tree data structure includes the above-mentioned extended ABI information.
[0048] (3) For the part that does not exceed the depth of the stack, convert the abstract syntax tree data structure into a corresponding binary bytecode sequence, which can be interpreted and executed by the contract virtual machine. For local variables that exceed the stack depth, the stack depth is pushed to the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com