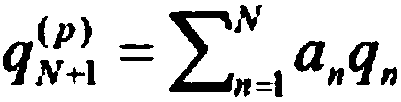Method for compressing genomic data
A genome and data technology, applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of IT cost and obstacles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
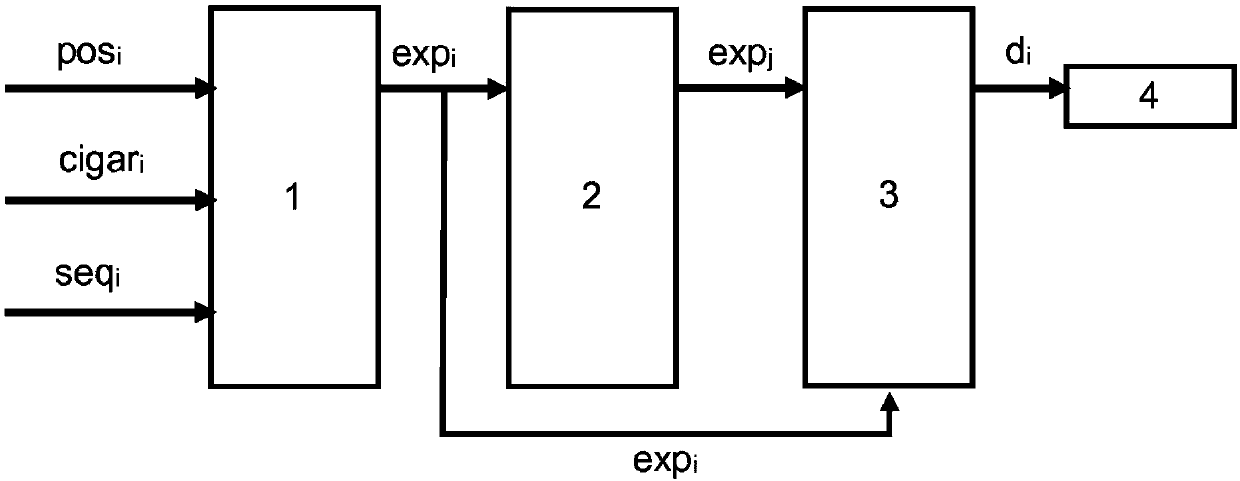
[0048] figure 1 A possible encoder structure for the proposed sequence compression algorithm is shown. Current reads i > 1 should be compressed. Read segment i With CIGAR i string, pos i and seq as a nucleotide sequence i . Read segment i These three data parameters are passed to extension module 1.
[0049] The extension module maps the position pos by using i and CIGAR string CIGAR i Expand current read i Nucleotide sequence seq i . The result of the extension module is the union sequence exp i .
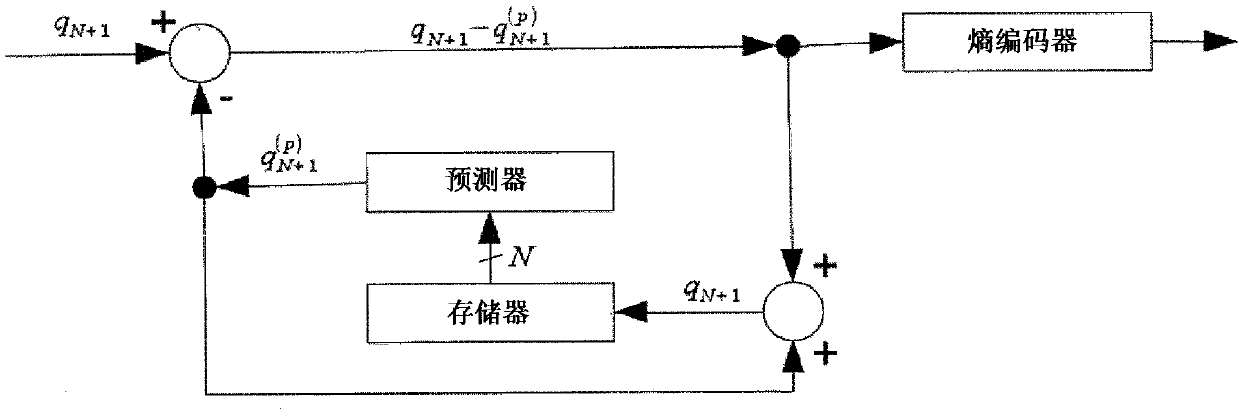
[0050] exp i The codewords are passed to ring buffer 2. Ring buffer 2 is a last-in, last-out container, particularly a modifiable and variable size container, thus remembering the N previous extended reads. exp j , 1≤ji Compare to calculate the expanded nucleotide sequence exp for the current read using difference module 3 i Expanded nucleotide sequence exp with previous reads j the difference between. The calculated difference, along with the minimum differenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com