Peacock Breeding Method for High Yield Peacock Eggs
A peacock, high-yield technology, applied in animal husbandry and other directions, can solve the problem of difficulty in realizing the demand for peacock eggs, and achieve the effect of meeting the demand and increasing egg production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
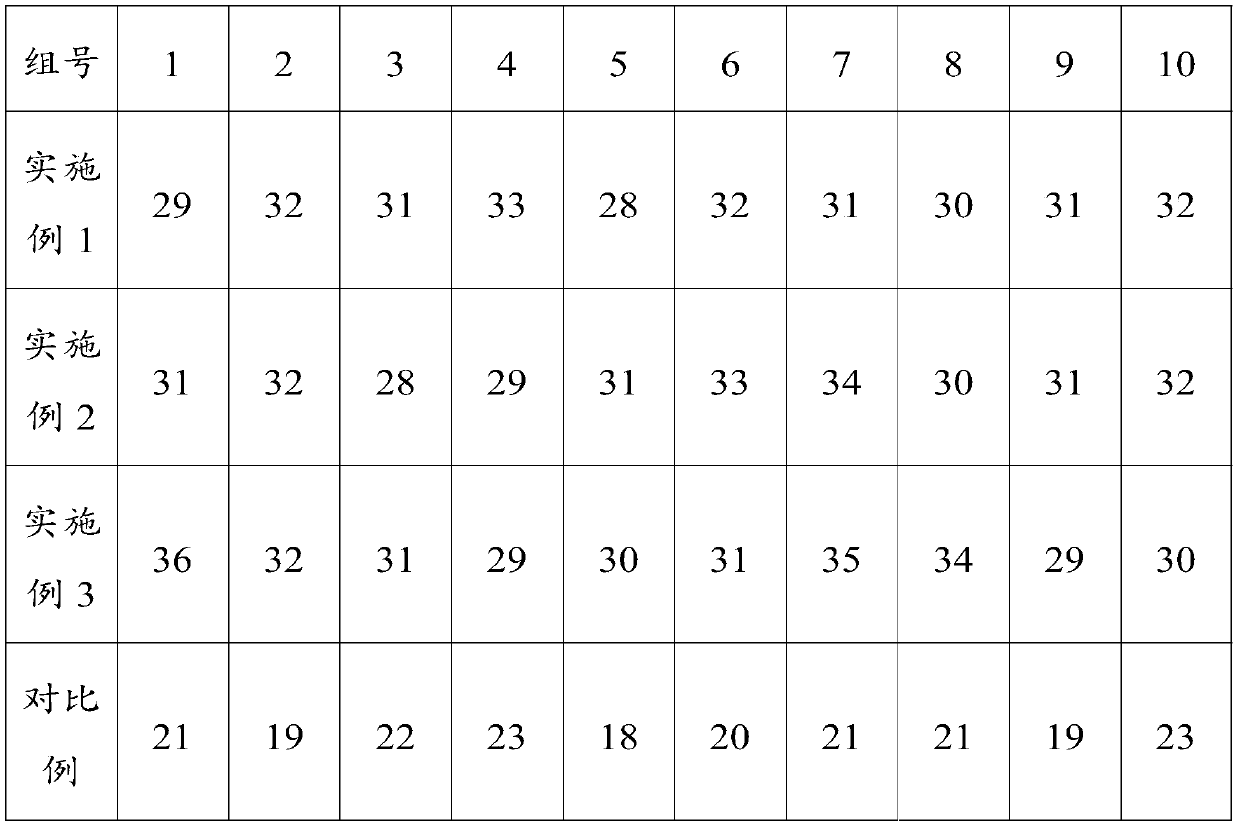
[0033] Select 100 female peacocks (blue peacocks) hatched in the same month, raise all the selected peacocks in the same feeding environment, feed each of the above-mentioned female peacocks for two years, and count the annual output of each female peacock in the third year Egg volume, count as A1, and calculate the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks fed, and calculate the ratio P1 of the annual egg production of each female peacock with A1 greater than A2 to the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks , the formula is: P1=A1 / A2×100%, wherein, A2 is 24.6, and there are 72 female peacocks with P1 greater than 110%, and the above-mentioned 72 female peacocks are used as the original mothers.
[0034] In the fourth year, count the annual egg production B1 of each of the above-mentioned former female generation peacocks, and calculate the average annual egg production B2 of all the original female generation, B2 is 28.1, and calculate the annual...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Select 120 female peacocks (blue peacocks) hatched in the same month, place all the selected peacocks in captivity in the same feeding environment, feed each of the above-mentioned female peacocks for two years, and count the annual output of each female peacock in the third year Egg volume, count as A1, and calculate the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks fed, and calculate the ratio P1 of the annual egg production of each female peacock with A1 greater than A2 to the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks , the formula is: P1=A1 / A2×100%, wherein, A2 is 23.1, and there are 81 female peacocks with P1 greater than 115%, and the above-mentioned 81 female peacocks are used as the original mothers.
[0040] In the fourth year, count the annual egg production B1 of each of the above-mentioned former female generation peacocks, and calculate the average annual egg production B2 of all the original female generation, B2 is 26.8, and calcula...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Select 150 female peacocks (blue peacocks) hatched in the same month, and place all the selected peacocks in captivity in the same feeding environment, feed each of the above-mentioned female peacocks for two years, and count the annual output of each female peacock in the third year. Egg volume, count as A1, and calculate the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks fed, and calculate the ratio P1 of the annual egg production of each female peacock with A1 greater than A2 to the average annual egg production A2 of all female peacocks , the formula is: P1=A1 / A2×100%, wherein, A2 is 25.5, and there are 101 female peacocks with P1 greater than 120%, and the above-mentioned 101 female peacocks are used as the original mothers.
[0046] In the fourth year, count the annual egg production B1 of each of the above-mentioned former female generation peacocks, and calculate the average annual egg production B2 of all the original female generation, B2 is 31.7, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com