PINK1 C-terminal domain polypeptide and methods using the same in cancer treatment
A domain, cancer technology, applied to the C-terminal domain of PINK1 in cancer, in the field of cancer treatment, can solve problems such as drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
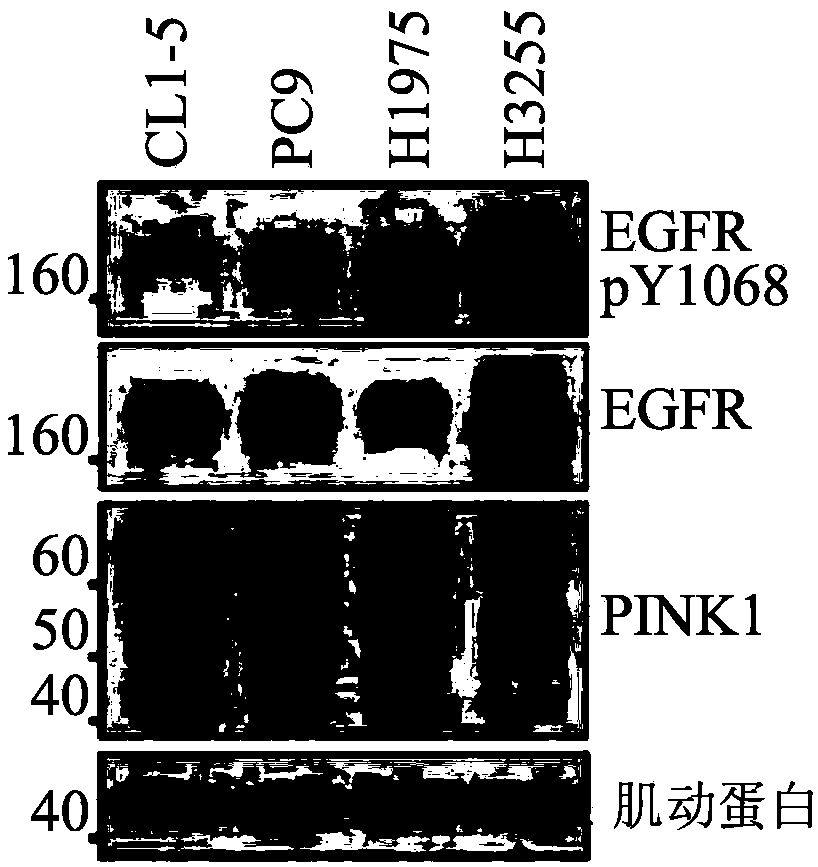
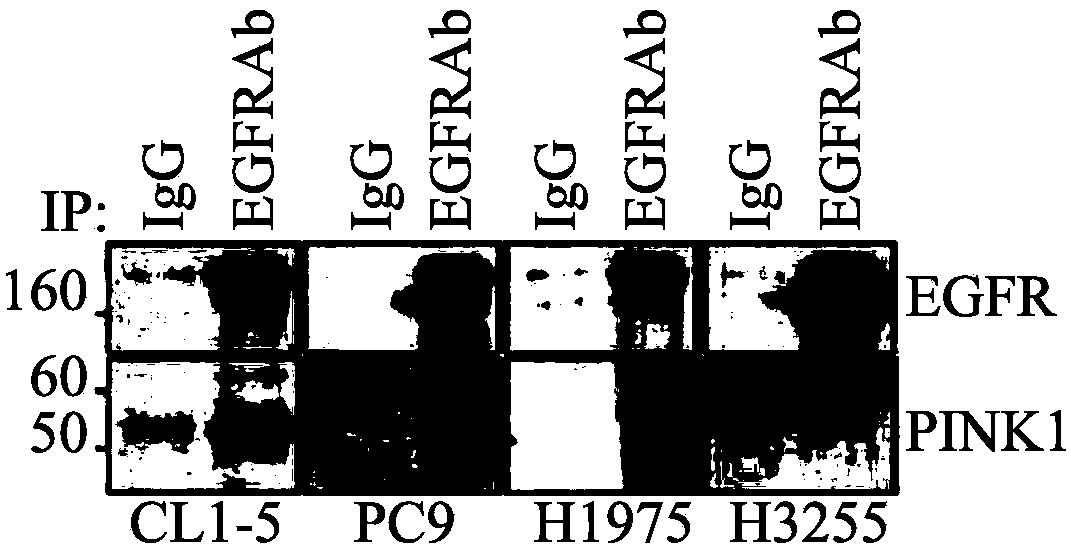
[0070] Example 1: Interaction of PINK1 and EGFR in lung adenocarcinoma
[0071] To determine whether PINK1 interacts with EGFR in lung adenocarcinoma, endogenous PINK1 and EGFR were first examined by immunoblot analysis in four lung adenocarcinoma cell lines bearing different types of EGFR: CL1-5 (wild type), PC9(Ex19Del), H1975(L858R+T790M) and H3255(L858R)( Figure 1A ). Subsequently, total cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation analysis with EGFR monoclonal antibody and immunoblot analysis with PINK1 antibody. The results showed that PINK1 was detected in all four immunoprecipitates, indicating the formation of endogenous protein complexes ( Figure 1B ). To visualize the interaction of PINK1 with EGFR proteins, wild-type EGFR-GFP was co-overexpressed with PINK1-myc in CL1-5 cells. The results showed that these two proteins were co-localized in CL1-5 cells, and most of the co-localization occurred just below the plasma membrane ( Figure 1C ). These data s...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2. Inhibition of EGFR dimerization and internalization by PINK1
[0073] Since there may be an interaction between PINK1 and EGFR, the potential role of PINK1 in EGFR was next investigated. When PINK1 was knocked out in CL1-5, PC9, H1975 and H3255 cells, the total EGFR protein was found to decrease, while the expression of EGFR mRNA was not synchronously down-regulated ( Figure 2A , 2B and 2C). A decrease in protein levels without a concomitant decrease in mRNA expression suggests an increase in protein turnover. Based on current knowledge, EGFR turnover is mediated by receptor dimerization and internalization (A.V.Vieira, C.Lamaze, S.L.Schmid.Science.274, 2086-2089 (1996); R.Heukers et al.J. Cell . Sci. 126, 4900-4912 (2013); and A. Tomas, C.E. Futter, E.R. Trends. Cell. Biol. 24, 26-34 (2014)). Therefore, it was investigated whether PINK1 plays a role in these processes. To assess changes in EGFR dimerization under PINK1 manipulation, a lysosomal inhibit...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3. Direct interaction of PINK1-CTD with EGFR-TKD
[0076] To dissect the interaction of PINK1 with EGFR, it was subsequently investigated whether these two protein kinases interact directly and via their interacting domains. Construction of marker-fused full-length EGFR based on different functional EGFR domains (amino acids 1 to 378, 1 to 621, 1 to 644, 1 to 690, 1 to 954, 645 to 1210, 645 to 954, 955 to 1210) Construct, EGFR-marker (amino acids 1 to 1210) and 8 progressively truncated EGFR-marker constructs ( Figure 3A ). Each of these nine constructs was co-overexpressed with full-length PINK1 in HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot with PINK1 antibody. The data showed that only the full-length EGFR-tagged construct and constructs containing amino acids 1 to 954, 645 to 1210, and 655 to 954 interacted with PINK1, suggesting that EGFR-TKD is a region impor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com