Optical system
An optical system and optical axis technology, applied in the field of optical systems, can solve problems such as unfavorable lens miniaturization, poor imaging quality, and inability to meet requirements, and achieve the effect of meeting the needs of depth recognition projection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
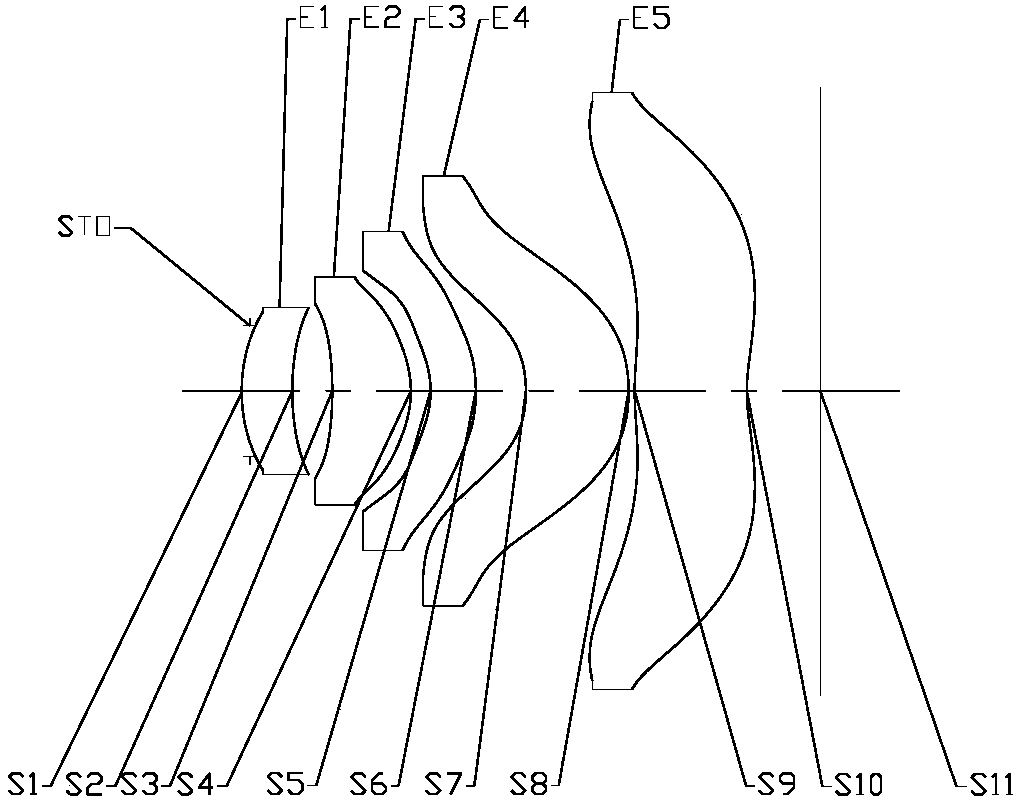
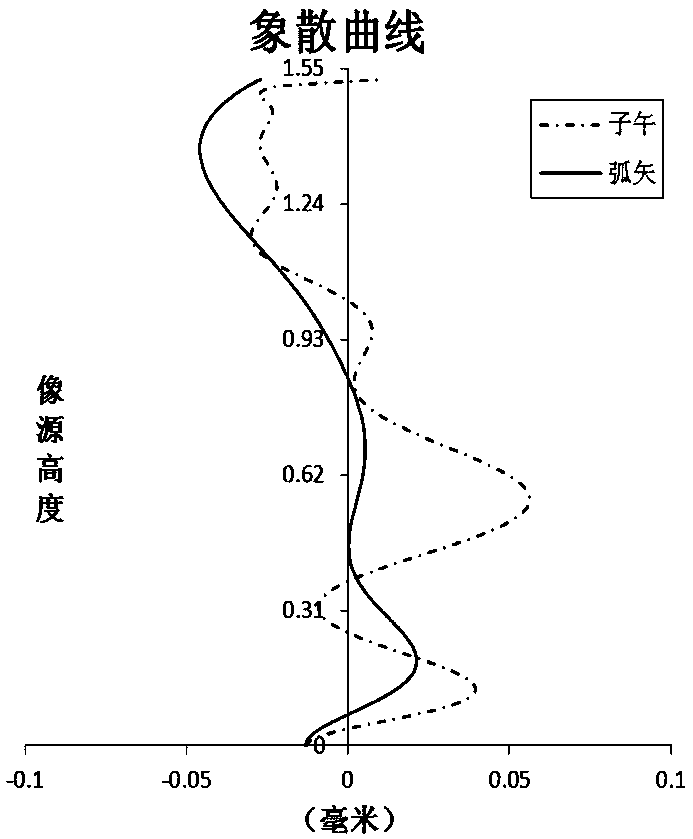
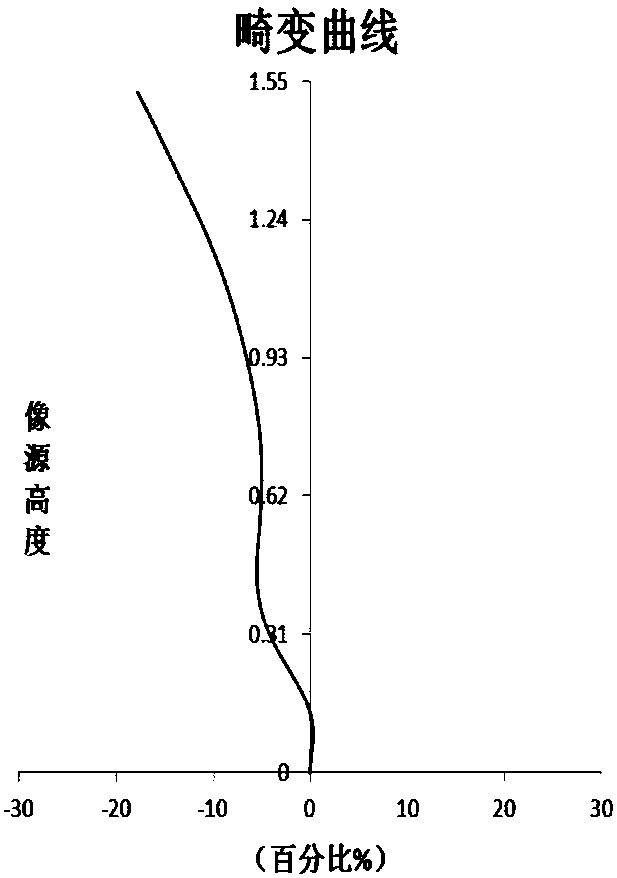
[0070] Refer to the following Figure 1 to Figure 2C An optical system according to Embodiment 1 of the present application is described. figure 1A schematic structural diagram of an optical system according to Embodiment 1 of the present application is shown.
[0071] like figure 1 As shown, the optical system according to the exemplary embodiment of the present application includes sequentially along the optical axis from the imaging side to the image source side: a diaphragm STO, a first lens E1, a second lens E2, a third lens E3, and a fourth lens E4 and fifth lens E5.
[0072] The first lens E1 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S1 is convex, and its near image source side S2 is concave; the second lens E2 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S3 is concave, and its near image source side S4 is convex; The third lens E3 has negative refractive power, its near imaging side S5 is concave, and its near image source side S6 is convex; the f...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Refer to the following Figure 3 to Figure 4C An optical system according to Embodiment 2 of the present application is described. In this embodiment and the following embodiments, for the sake of brevity, descriptions similar to those in Embodiment 1 will be omitted. image 3 A schematic structural diagram of an optical system according to Embodiment 2 of the present application is shown.
[0100] like image 3 As shown, the optical system according to the exemplary embodiment of the present application includes sequentially along the optical axis from the imaging side to the image source side: a diaphragm STO, a first lens E1, a second lens E2, a third lens E3, and a fourth lens E4 and fifth lens E5.
[0101] The first lens E1 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S1 is convex, and its near image source side S2 is concave; the second lens E2 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S3 is convex, and its near image source side S4 is convex...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Refer to the following Figure 5 to Figure 6C An optical system according to Embodiment 3 of the present application is described. Figure 5 A schematic structural diagram of an optical system according to Embodiment 3 of the present application is shown.
[0115] like Figure 5 As shown, the optical system according to the exemplary embodiment of the present application includes sequentially along the optical axis from the imaging side to the image source side: a diaphragm STO, a first lens E1, a second lens E2, a third lens E3, and a fourth lens E4 and fifth lens E5.
[0116]The first lens E1 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S1 is convex, and its near image source side S2 is concave; the second lens E2 has positive refractive power, its near imaging side S3 is concave, and its near image source side S4 is convex; The third lens E3 has negative refractive power, its near imaging side S5 is concave, and its near image source side S6 is convex; the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com