A kind of preparation method of high-strength beta titanium alloy wire for spring
A technology of titanium alloy wire and wire, which is applied in the field of preparation of high-strength β titanium alloy wire for springs, to achieve high strength, good size consistency, and reduce the effect of hydrogen absorption process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
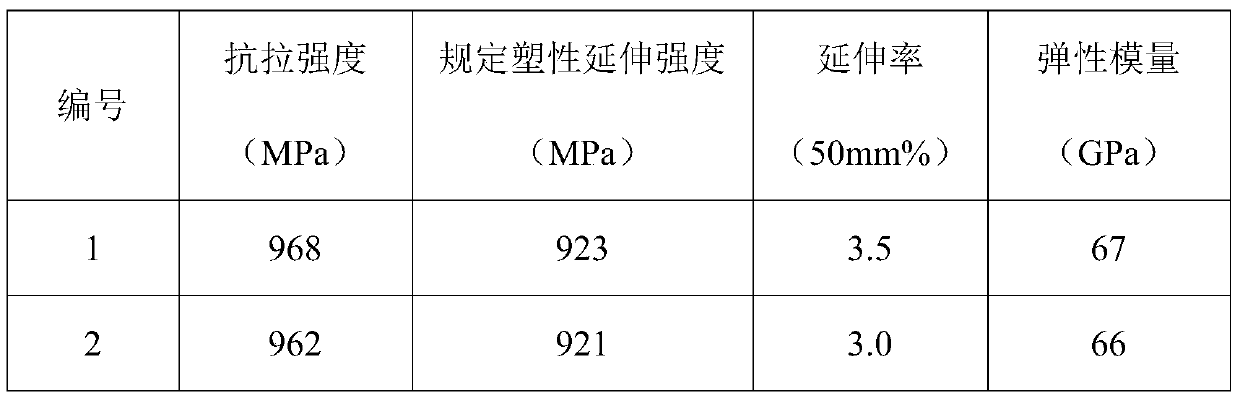
[0022] A method for preparing a β-type titanium alloy wire for springs, which uses free forging, precision forging, rolling, and hot drawing processes to prepare β-type titanium alloy wires for springs with a diameter of Ф1 mm to Ф3 mm. Specifically include the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: Using β-type titanium alloy ingot as raw material, free forging at 1100℃~1170℃ into rods of Ф120~Ф150mm, and then removing scale and forging cracks by centerless lathe;
[0024] Step 2: Precisely forge the bar prepared in step 1 into a bar of Ф40-Ф60 mm, use a centerless lathe to remove the scale on the surface, and use a grinder to grind the surface cracks;
[0025] Step 3: Roll the bar prepared in step 2 into a bar of Ф8-Ф9mm, use a centerless lathe to remove the scale on the surface, and use a grinder to grind the surface cracks;
[0026] Step 4: Continuously heat the surface-treated rod in step 3 in a tube furnace at 700°C to 720°C at a speed of 13 to 15m / min to form an oxide layer...
Embodiment 1
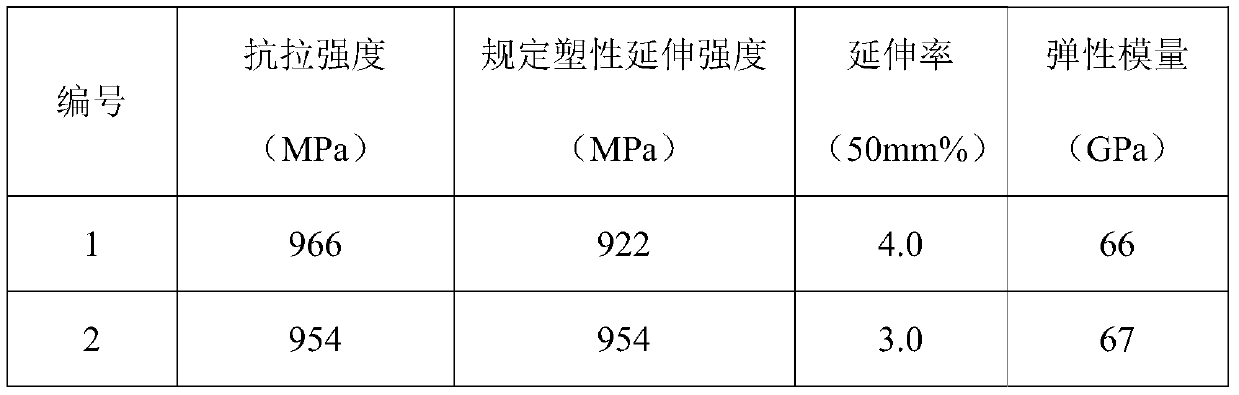
[0032] Taking the preparation of Φ3.0mmβ-type titanium alloy welding wire as an example, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0033] Step 1: A β-type titanium alloy ingot is used as a raw material, and the billet is forged at 1170°C, and the finished product is forged at 800°C to make a Ф130mm bar, and then the scale is removed by a centerless lathe to remove forging cracks.
[0034] Step 2: Precision forging the bar prepared in step 1 into a Ф50mm bar by precision forging, using a centerless lathe to remove the scale on the surface, and using a grinder to grind surface cracks.
[0035] Step 3: The bar prepared in step 2 is rolled into a Ф8.5mm bar by rolling, the scale on the surface is removed by using a centerless lathe, and the surface cracks are ground by a grinder.
[0036] Step 4: Continuously heat the surface-treated bar in step 3 in a tube furnace at 700°C and a speed of 13m / min to form an oxide layer, and when the bar comes out of the furnace, it is equipped with ...
Embodiment 2
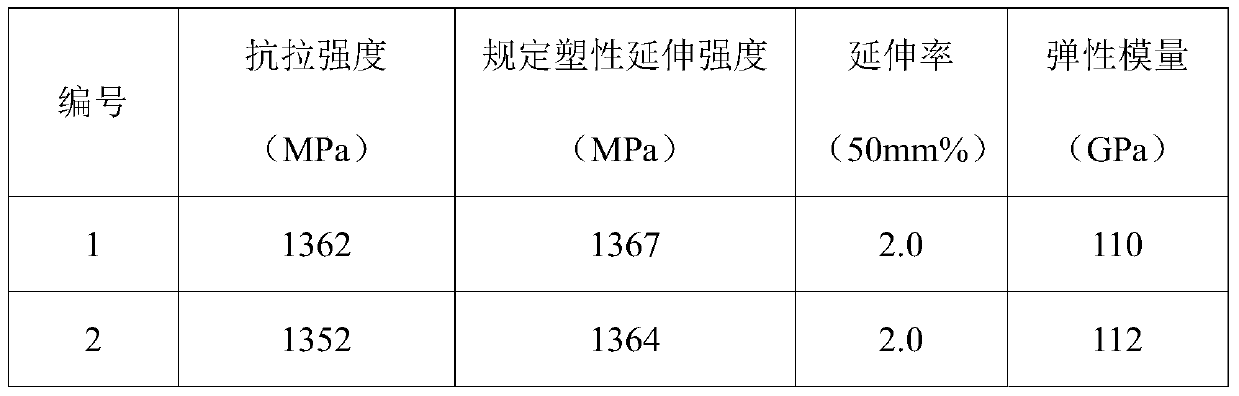
[0047] Taking the preparation of Φ2.0mmβ-type titanium alloy welding wire as an example, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0048] Step 1: A β-type titanium alloy ingot is used as a raw material, through free forging at 1150°C, and the billet is made into a Ф130mm bar at 810°C, and then the scale is removed by a centerless lathe to remove forging cracks.
[0049] Step 2: Precision forging the bar prepared in step 1 into a Ф50mm bar by precision forging, using a centerless lathe to remove the scale on the surface, and using a grinder to grind surface cracks.
[0050] Step 3: The bar prepared in step 2 is rolled into a Ф8.5mm bar by rolling, the scale on the surface is removed by using a centerless lathe, and the surface cracks are ground by a grinder.
[0051] Step 4: Continuously heat the surface-treated bar in step 3 in a tube furnace at 710°C and a speed of 14m / min to form an oxide layer, and when the bar comes out of the furnace, it is equipped with a drawing machine w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com