Uplink data sending method and device
A data transmission method and a technology for transmitting data, which are applied in the field of uplink data transmission methods and devices, and can solve problems such as high transmission failure rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
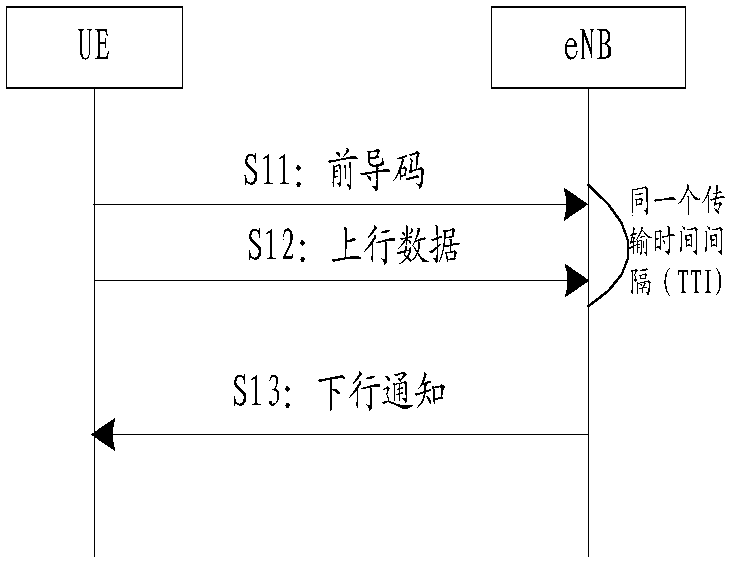
[0207] When the UE sends uplink data using unlicensed resources, it adopts the power control method of increasing power.
[0208] When the UE uses unlicensed resources to send uplink data for the first time, it sends uplink data according to the initial target received power (corresponding to the initial target received power). If it is unsuccessful for the first time, when the UE sends uplink data using the unlicensed resource again, it needs to increase the transmit power again. and so on. Every time the transmission is unsuccessful, the transmission power is increased.
[0209] For example, the initial target received power is InitialReceivedTargetPower, and the received power compensation for each increment is powerRampingStep, then, when sending TRANSMISSION_COUNTER times of unlicensed uplink data, the target received power ReceivedTargetPower is: ReceivedTargetPower=InitialReceivedTargetPower+(TRANSMISSION_COUNTER–1)*powerRampingStep.
[0210] Among them, the initial t...
example 2
[0212] If the UE uses unlicensed resources to send uplink data, the transmission power is not enough, which will cause the base station to fail to monitor the unlicensed uplink data. In this case, the base station may successfully monitor the preamble sequence, but cannot monitor the uplink data. However, the base station can reply a random access response to the preamble sequence, and then the unlicensed uplink sending process can be transformed into a traditional random access process.
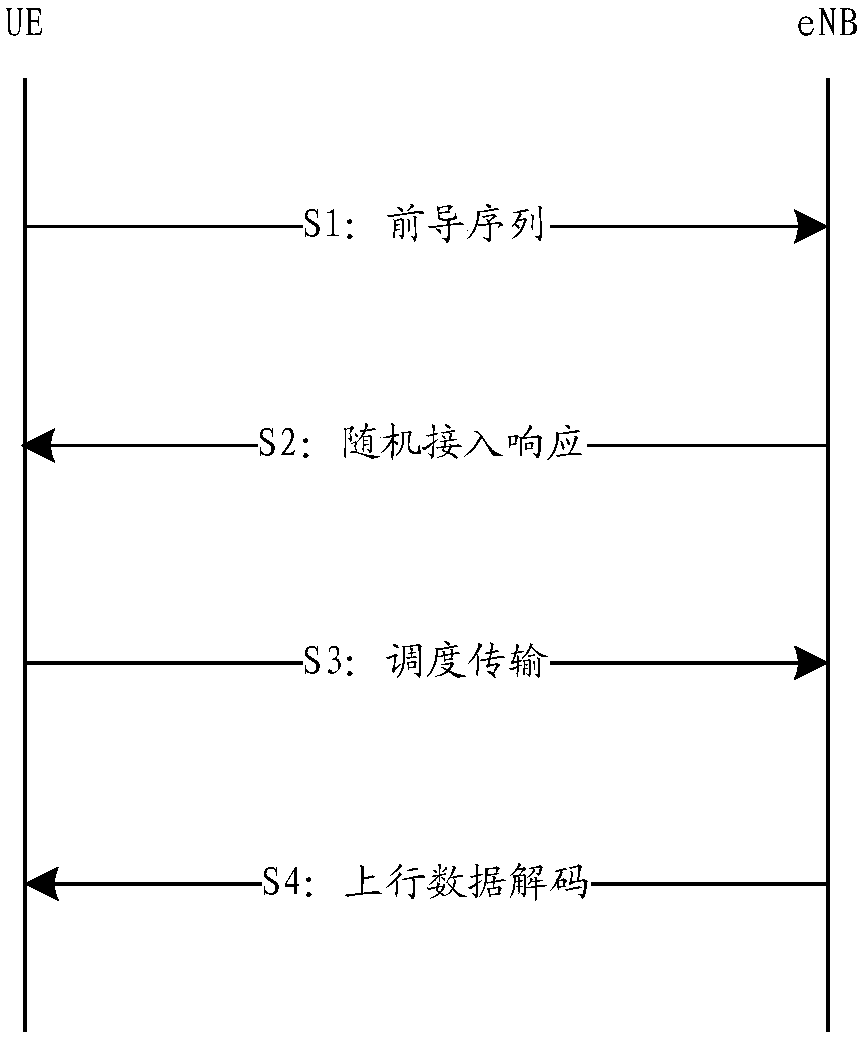
[0213] When the UE fails to send unlicensed uplink data, the UE then initiates a traditional random access procedure. Such as Figure 11 shown, including:
[0214] Step S21: UE sends a preamble sequence, and selects resources in unlicensed resources, and sends uplink data;
[0215] Step S22: The eNB parses the preamble sequence, but no unauthorized uplink data is detected, and replies with a random access response carrying an uplink authorization;
[0216] Step S23: The UE retransmits th...
example 3
[0220] If the UE uses unlicensed resources to send uplink data, the transmission power is not enough, which will cause the base station to fail to monitor the unlicensed uplink data. In this case, the base station may not successfully monitor the preamble sequence, and the base station cannot reply a random access response, so the unlicensed uplink transmission process can be converted to a traditional random access process.
[0221] When the UE fails to send unauthorized uplink data for n times, where n times are configured by system information broadcast or RRC signaling, the UE then initiates a traditional random access procedure.
[0222] Or the UE still fails to send unlicensed uplink data up to the maximum transmission power, and then the UE initiates a traditional random access procedure.
[0223] Flowchart such as Figure 12 shown, including:
[0224] Step S31: The UE sends the preamble sequence, selects resources in the unlicensed resources, and sends uplink data; t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com