A plant Medicago truncatula flower organ stigma exposure gene and its encoded protein and application
A technology with exposed stigma and gene encoding, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty and cost of crop hybrid breeding, low outcrossing rate of sterile lines, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1. Obtaining and phenotypic analysis of cabl2 mutants
[0030] By screening the Tnt1 insertion mutant library of Medicago truncatula, a mutant NF19675 with exposed stigma, folded and fused petals, and stamens wrapped inside the petals was obtained, named cabl2( cab bag- l ike).
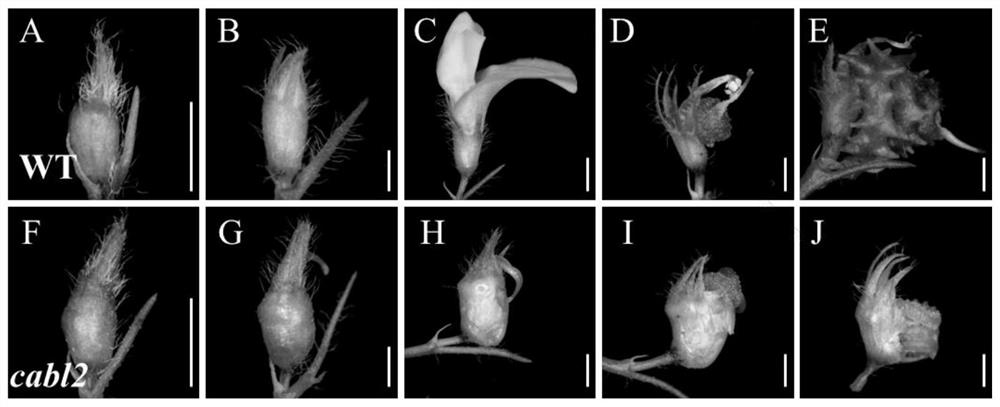
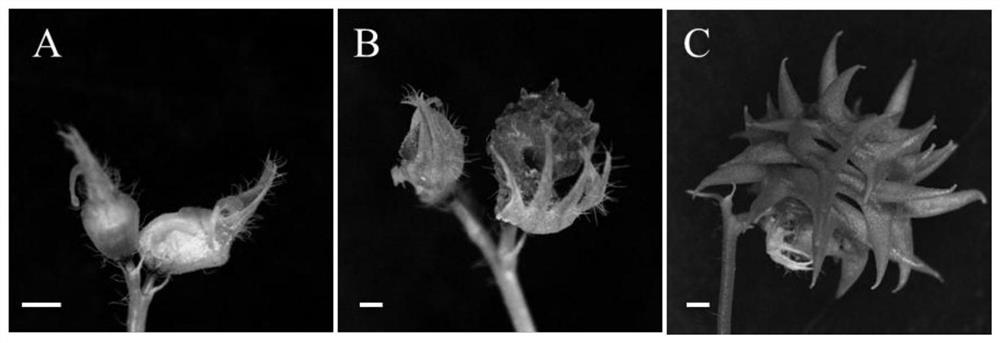
[0031] The flower phenotype observation results of cabl2 mutant and Medicago truncatula R108 (wild type) are shown in figure 1 . figure 1 Among them, A-D are the phenotype diagrams of wild-type flowers at different stages of flower development; F-H are flower phenotype diagrams of cabl2 mutants at different stages of flower development; D-E wild-type flowers form normal fruit pods after pollination; I-J cabl2 mutants, due to petal fusion, As a result, the stamens are wrapped, and normal pollination cannot be completed, and finally normal fruit pods cannot be formed.
[0032] Second, mutation analysis
[0033] Because the mutant stigma is exposed, in order to study the fertility of the mut...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Cloning of embodiment 2CABL2 gene
[0035] According to the flanking sequence of NF19675 published on the Tnt1 website (https: / / medicago-mutant.noble.org / mutant / ), corresponding primers were designed to detect the linkage between the mutant and the gene. Finally, a gene CABL2 linked to the mutant was found;
[0036] NF19675-F TCATGGACGTTAGTTGGAAA;
[0037] NF19675-R AAGCACATTACCAGACATGA;
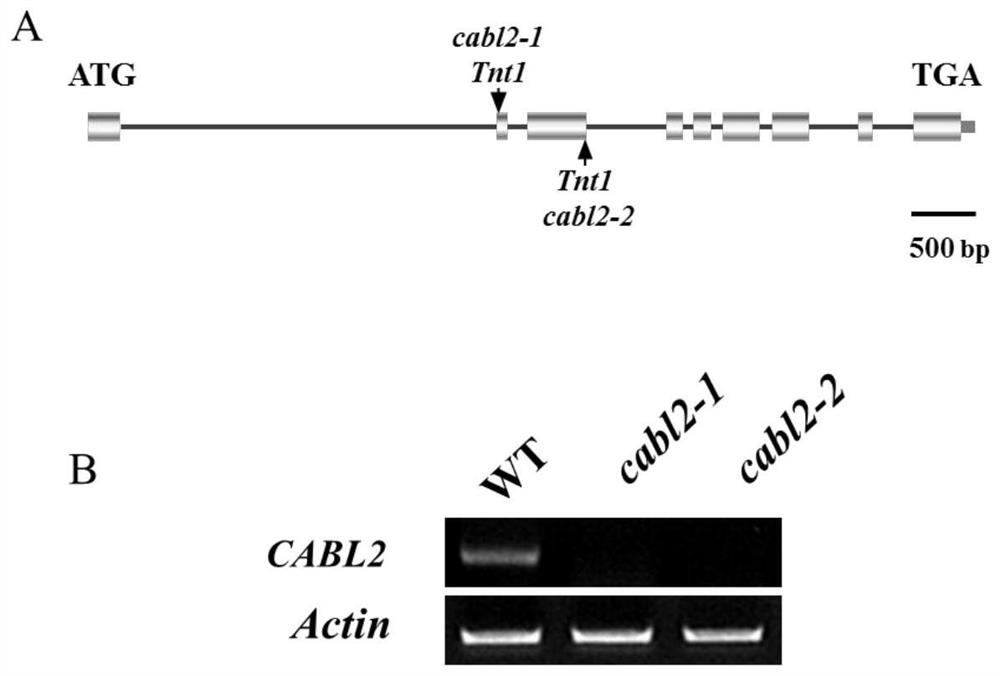
[0038] In the NF19675 mutant, Tnt1 was inserted in the second exon of the gene. In order to prove that the CABL2 gene is the control gene of the mutant, we ordered another mutant of this gene: NF14424, inserted in the third exon. And named the previous NF19675 as cabl2-1 (see figure 2 A). Observing the phenotype of the homozygous mutant of cabl2-2, it was found that the phenotype of cabl2-1 was exactly the same. In cabl2-1, cabl2-2 homozygous mutant species, the full-length expression of CABL2 gene was completely lost ( figure 2 B). It proved that the CABL2 gene is the contr...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 The acquisition of CABL2 gene and its encoded protein CABL2
[0040] 1. Extract the RNA of the blooming flower of Medicago truncatula R108 (wild type), and reverse transcribe it into cDNA.
[0041] 2. Using the cDNA obtained in step 1 as a template, amplify using a primer pair composed of primer CABL2-F and primer CABL2-R to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0042] CABL2-F: 5'-caccATGGAGATAGAGCAAGACAATGCC-3';
[0043] CABL2-R: 5'-ATGAAATGGAGAGTTGAGACCCTCC-3'.
[0044] 3. Sequence the PCR amplification product obtained in step 2 to obtain the coding region sequence of the target gene, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence listing, and encode the protein shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence listing. It consists of 689 amino acid residues. The CDS of the gene was compared on the Medicago truncatula website (http: / / blast.jcvi.org / Medicago-Blast / ), and the genome sequence of the CABL2 gene was obtained, as shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The protein shown in SEQ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com