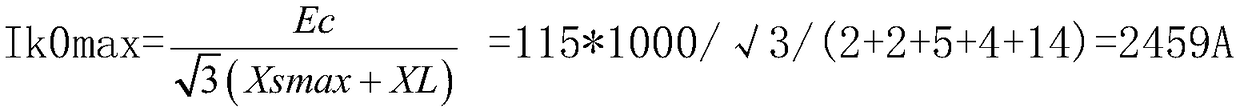Adaptive zero sequence current quick-break protection method
A technology of zero-sequence current and quick-break protection, which is applied in the direction of protection reacting to overcurrent, emergency protection device for automatic disconnection, emergency protection circuit device, etc. Quick-break protection and other issues to achieve the effect of improving protection efficiency and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0033] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but the following embodiments in no way limit the present invention.
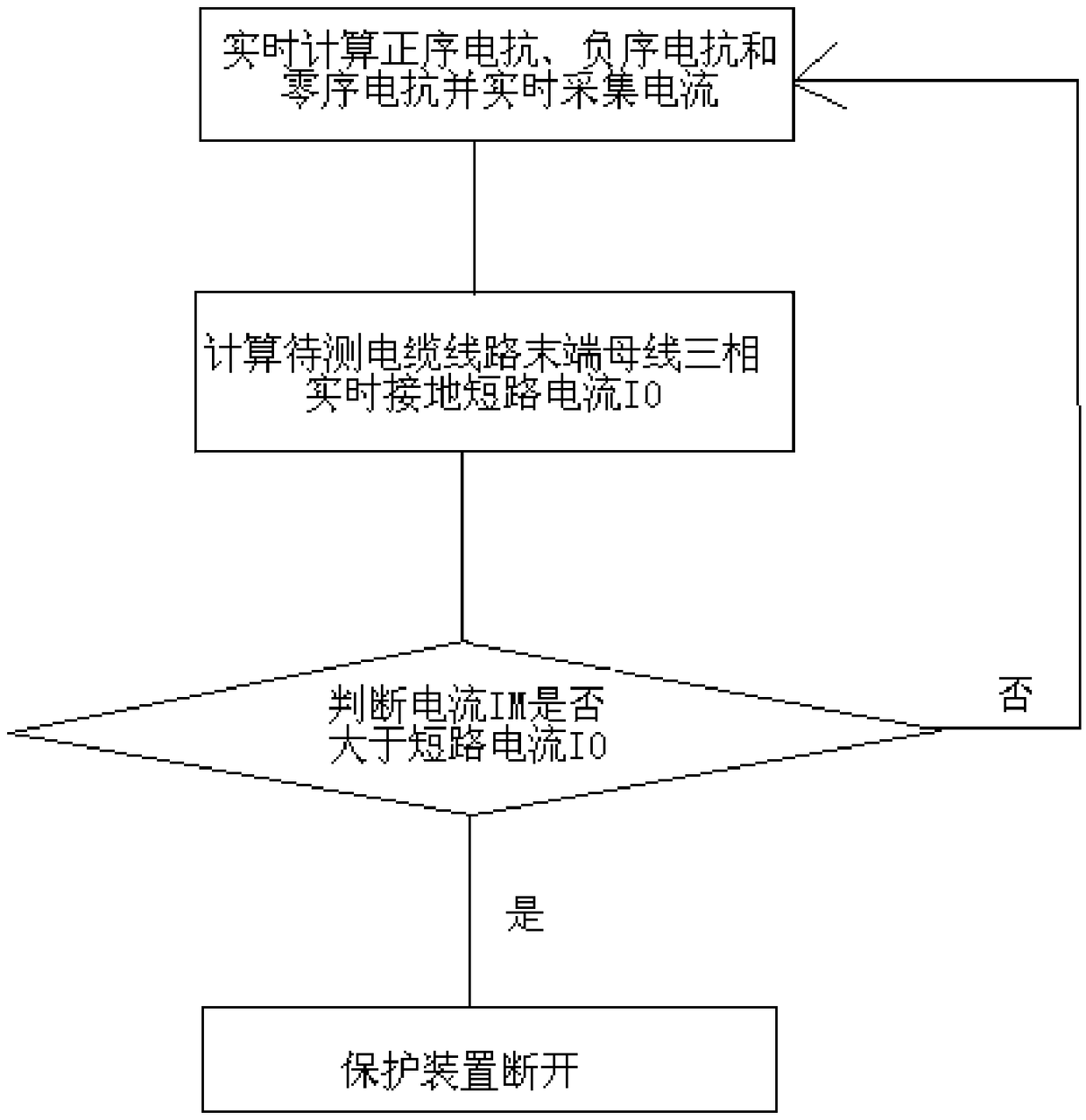
[0034] An adaptive zero-sequence current quick-break protection method includes the following steps performed in sequence:
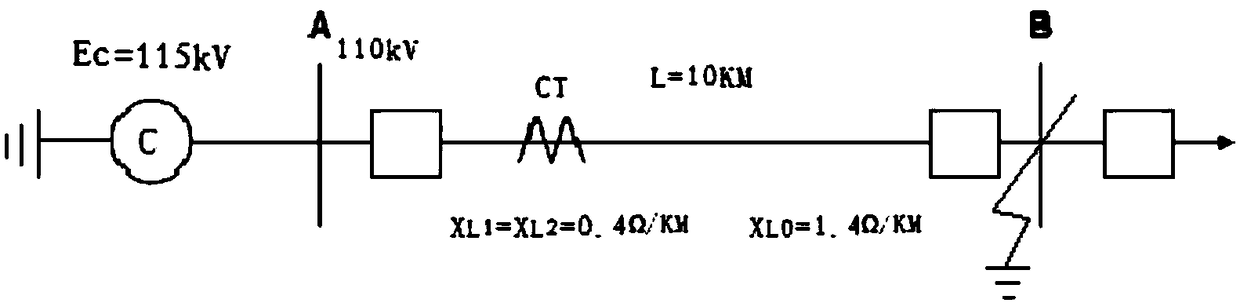
[0035] 1) The microcomputer protection calculates the positive sequence reactance X of the cable line to be tested in real time C1 , Negative sequence reactance X C2 and zero sequence reactance X C0 ;
[0036] 2) According to the positive sequence reactance X calculated in step 1) C1 , Negative sequence reactance X C2 , zero sequence reactance X C0 Calculate the real-time short-circuit current I at the end of the line 0 and the short-circuit current I 0 stored in memory RAM;
[0037] 3) Judgment step 1) The line fault current I measured by the microcomputer protection M greater than I 0 , if the judgment result is "Yes", the protective device w...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap