Subsynchronous oscillation random time-varying mode identification method
A sub-synchronous oscillation and time-varying mode technology, applied in the direction of measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems affecting the EMD process, distortion of decomposition results, inaccurate local mean curves, etc., and achieve accurate mode identification results , Improvement of endpoint effect, improvement of endpoint effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
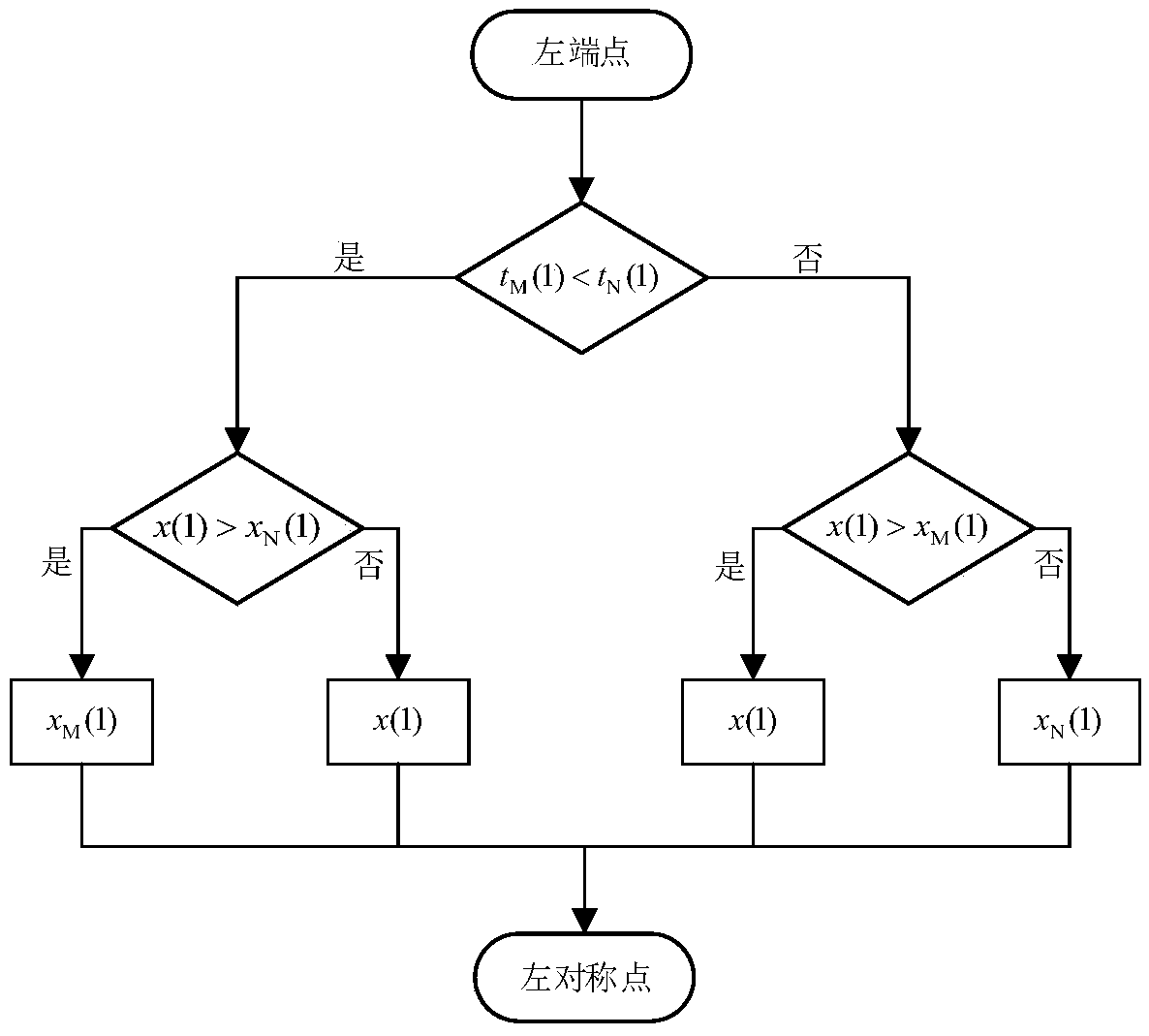
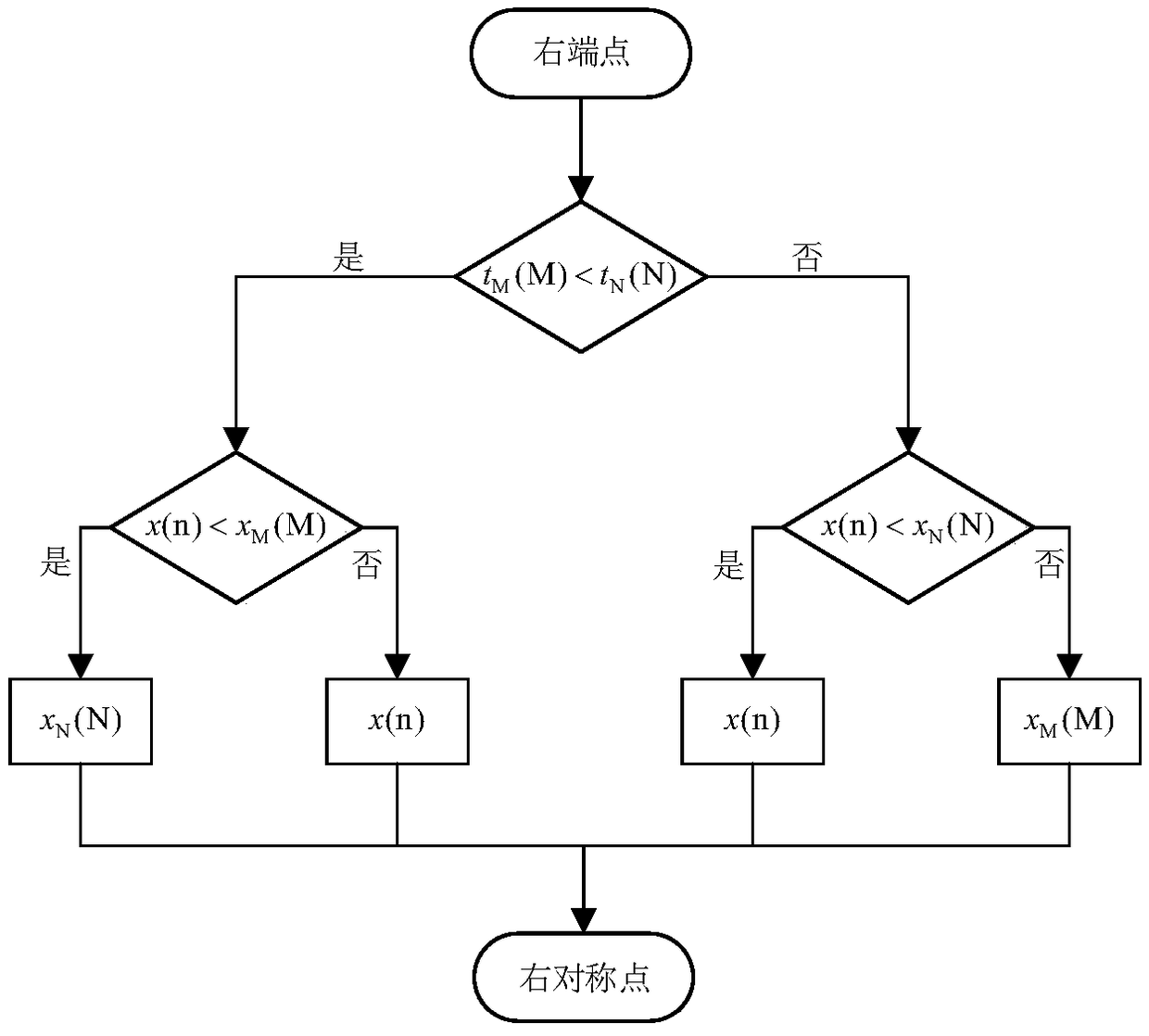
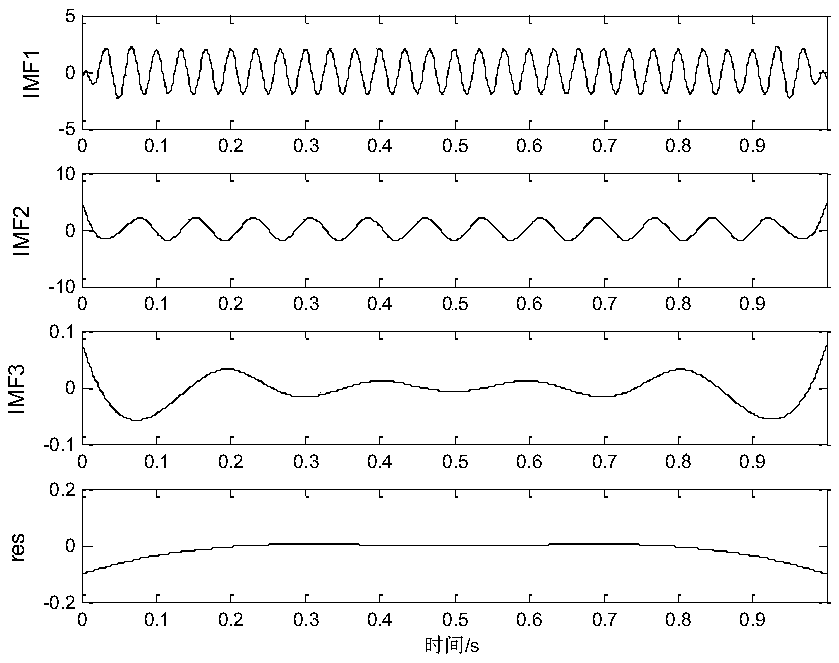
[0057] A subsynchronous oscillation stochastic time-varying mode identification method. Firstly, empirical mode decomposition is used to decompose the sampled signal x(n) into a finite number of intrinsic mode functions and a residual quantity, and then Hibert transformation is performed on each intrinsic mode component . The transformed signal is taken as the imaginary part, and the original signal is taken as the real part to form a complex signal, that is, an analytical signal. Use the analytical signal to obtain the instantaneous amplitude, instantaneous frequency and instantaneous phase information of the original signal.
[0058] The empirical mode decomposition divides the original signal into a number of IMF components (intrinsic mode functions) and a residual. The calculated IMF components need to meet the following two IMF conditions:
[0059] Conditio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com