Nut and fastening method
A nut and double nut technology, applied in the direction of nuts, threaded fasteners, screws, etc., can solve the problems of reduced occlusal force and tightening force, falling off of connecting parts of fixed parts, falling off of nuts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
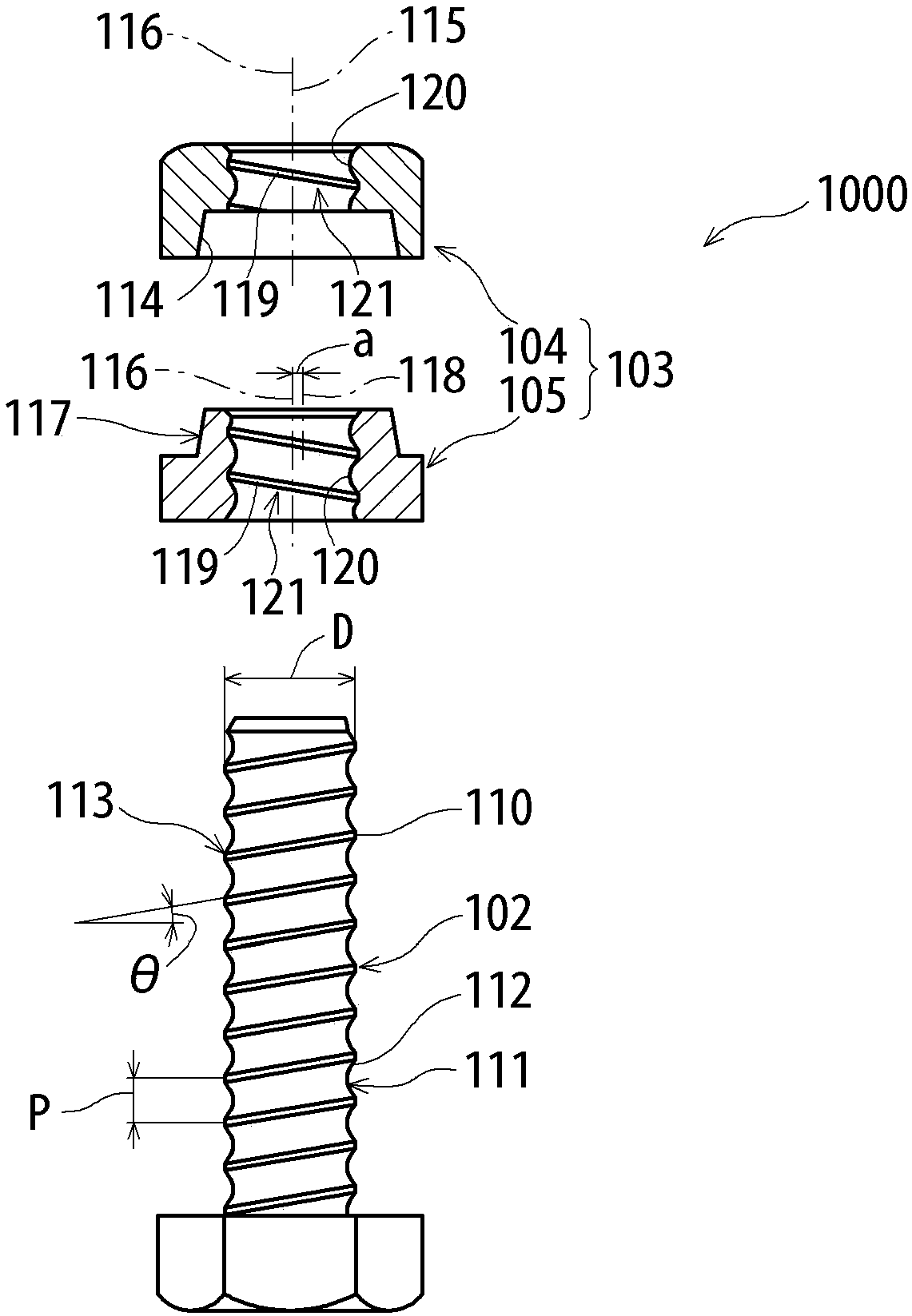
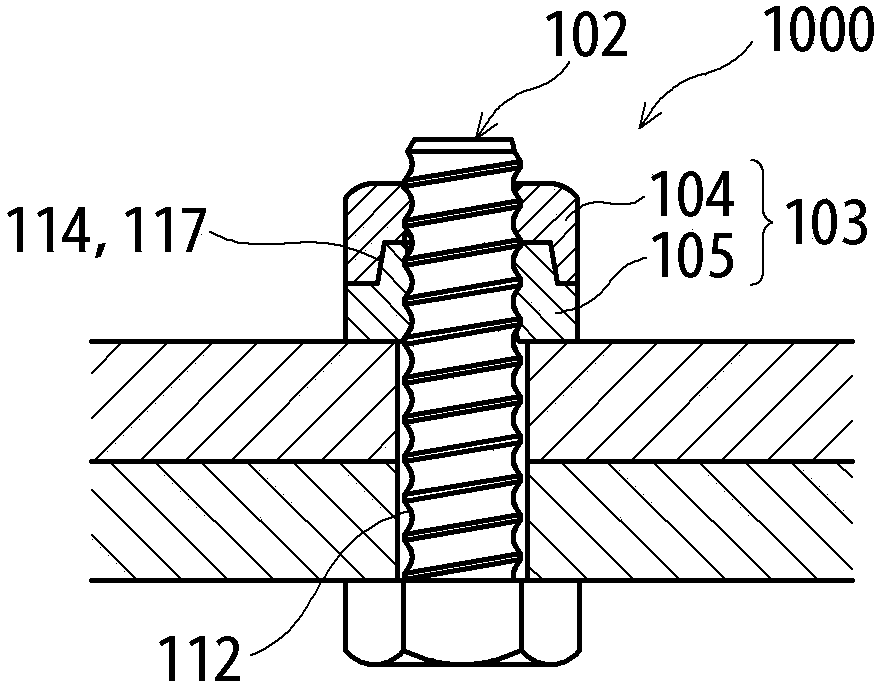
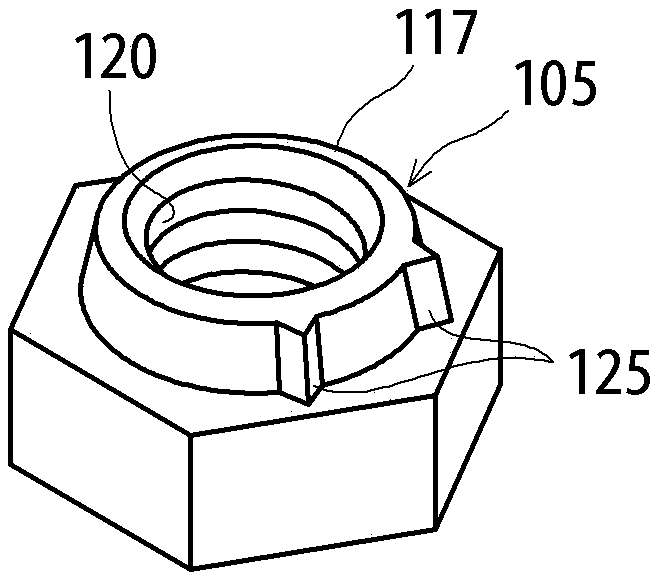
[0253] Figure 8 It is a perspective view showing the structure of the nut 100 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. in addition, Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view (front view or side view) for explaining the structure of the nut 100 according to the first embodiment. in addition, Figure 8 The upward arrow 99 in the vertical direction is shown in , and the upward side is called "upper" or "upper surface" for convenience. The direction of "upper" is a convenient term, and according to the orientation of the nut 100, the surface named "upper surface" may sometimes be horizontal or downward, and an additional explanation is hereby given.
[0254] The nut 100 of this embodiment is a polygonal nut, and the illustrated example is a hexagonal nut. The nut 100 is composed of a nut main body 10 in which a screw hole 30 is formed, and an upper surface 11 and a side surface 15 of the nut main body 10 . Threads 31 are formed on the inner surface of the screw hole...
Embodiment approach 2
[0275] Figure 16 It is a perspective view showing the structure of the nut 100 concerning Embodiment 2 of this invention. in addition, Figure 17 It is a cross-sectional view (front view or side view) for explaining the structure of the nut 100 according to the second embodiment. In the nut 100 of the above-mentioned embodiment, the slit 20 is formed obliquely, however, in the nut of the second embodiment, the slit 20 is formed to extend in the horizontal direction. By appropriately adjusting the thickness D of the slit 20 so that the slit 20 is extended horizontally (parallel to L3), the same effect as that of the nut 100 of the first embodiment described above can be obtained. In addition, compared with the case where the slit 20 is provided obliquely, there is an advantage that the forming process of the slit 20 is easier, and at the same time, there is an advantage that it is easy to predict the strength of the nut 100 (nut body 10) with the slit.
[0276] In other res...
Embodiment approach 3
[0278] Figure 21 It is a perspective view showing the nut 100 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. in addition, Figure 22 is a sectional view (front view or side view) for explaining the structure of the nut 100 according to the third embodiment. The nut 100 of the above-mentioned second embodiment has the upper surface 11 formed obliquely, but the lower surface 13 of the nut according to the third embodiment is also formed obliquely. In the inclined lower surface 13, facing downward, the high region is referred to as a high position 14a, and the low region is referred to as a low position 14b.
[0279] In addition, in the present embodiment, the slit 20 is formed to extend in the horizontal direction, but it may extend obliquely as in the first embodiment. However, when the slit 20 is formed to extend in the horizontal direction, there is an advantage that it is easy to use the upper surface 11 and the lower surface 13 together as a contact surface (fixed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com