A method for positioning the ceramic core of a single crystal turbine working blade
A positioning method and blade technology, applied in the direction of core, casting mold, casting mold components, etc., can solve the problems of unusable positioning, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing yield, high molding rate, and ensuring control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
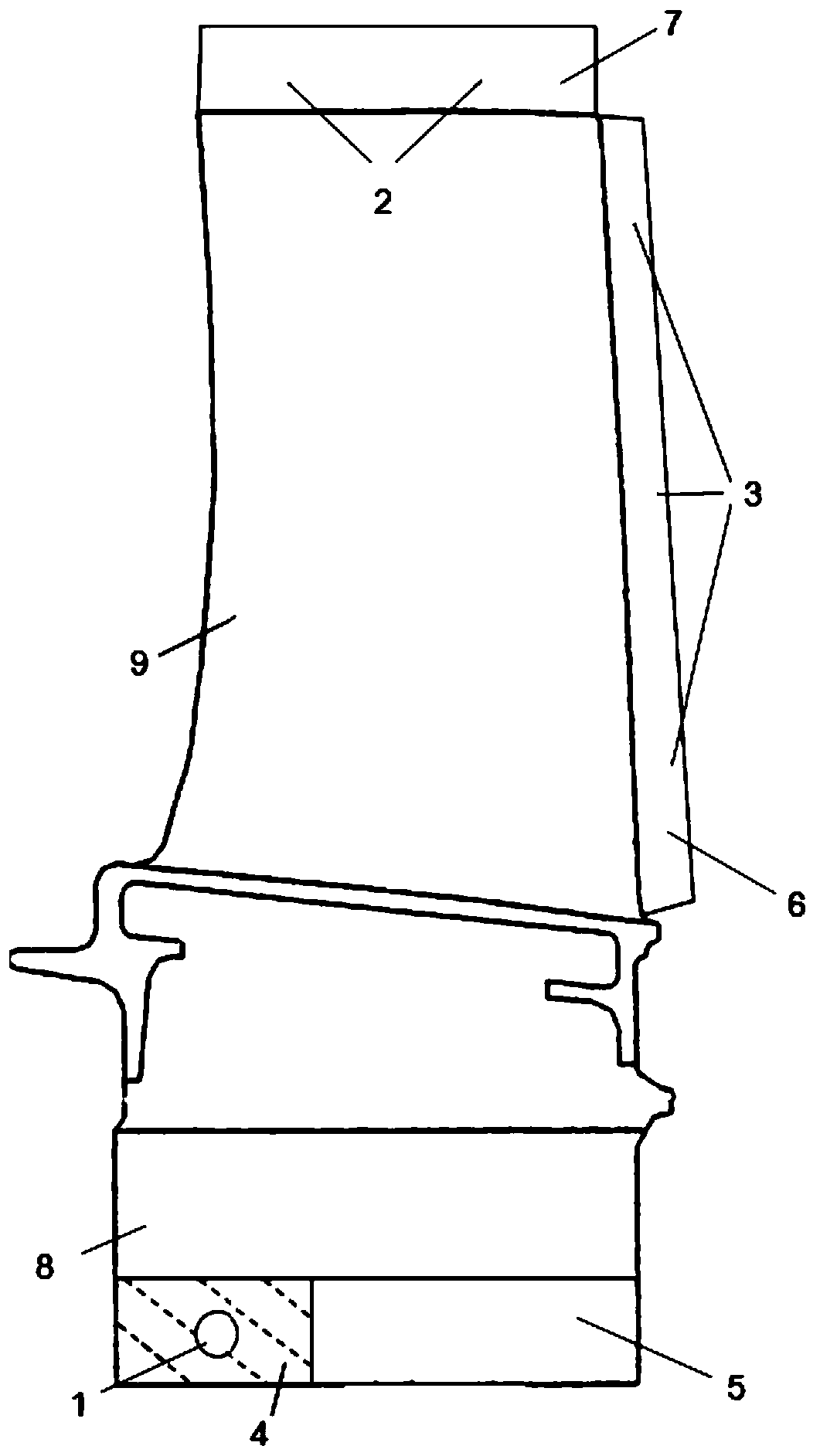
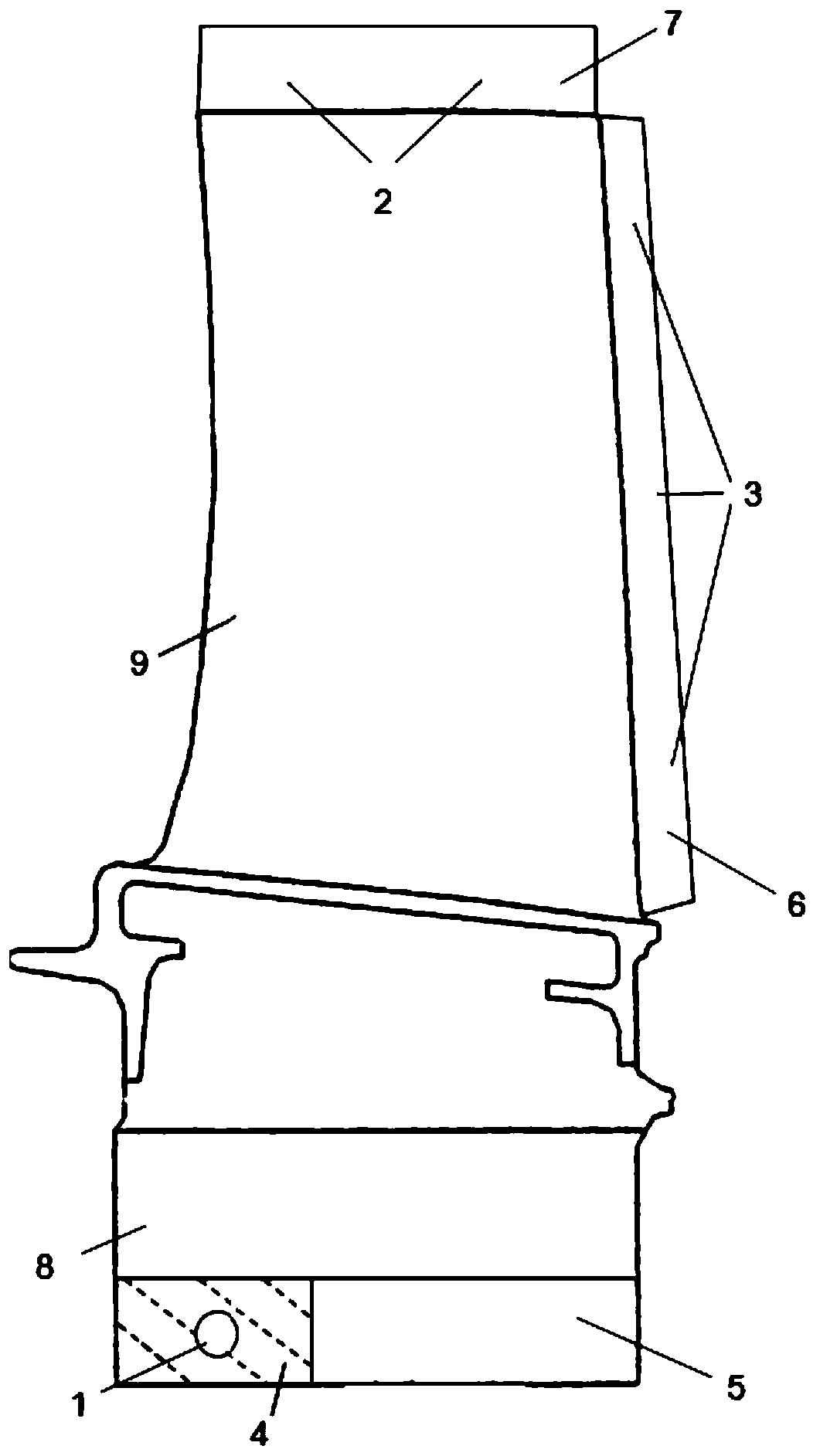
[0027] This embodiment designs a core positioning method for single-crystal high-pressure turbine working blades. In the process of making blade wax parts, the outer side of the tenon extension is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension, and the mold is set at the fixed end of the tenon extension. The positioning hole is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension to fix the axial position. In other directions, the extension of the tenon is used as the fixed end, and the exhaust edge extension and blade tip extension are used as the free end. The positioning method of the core blade pot and the blade back Again, the anchor positions are completely symmetrical.
[0028] The width of the tenon of the working blade of the single crystal turbine is 36mm, the height of the tenon is 30mm, the fixed end of the tenon extension section along the height direction is 14mm, the width is 28mm, and the diameter of the positioning hole is 5mm. The extension of the tenon and the positio...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment designs a core positioning method for single-crystal high-pressure turbine working blades. In the process of making blade wax parts, the outer side of the tenon extension is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension, and the mold is set at the fixed end of the tenon extension. The positioning hole is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension to fix the axial position. In other directions, the extension of the tenon is used as the fixed end, and the exhaust edge extension and blade tip extension are used as the free end. The positioning method of the core blade pot and the blade back Again, the anchor positions are completely symmetrical.
[0034] The width of the tenon of the working blade of the single crystal turbine is 19mm, the height of the tenon is 12mm, the fixed end of the tenon extension section is 15mm in the height direction, the width is 14mm, and the diameter of the positioning hole is 4mm. The extension of the tenon and the position o...
Embodiment 3
[0039] This embodiment designs a core positioning method for single-crystal high-pressure turbine working blades. In the process of making blade wax parts, the outer side of the tenon extension is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension, and the mold is set at the fixed end of the tenon extension. The positioning hole is used as the fixed end of the tenon extension to fix the axial position. In other directions, the extension of the tenon is used as the fixed end, and the blade tip extension is used as the free end. Symmetrical, there is no exhaust channel on the exhaust side, and it is a closed channel.
[0040] The width of the tenon of the working blade of the single crystal turbine is 70mm, the height of the tenon is 54mm, the fixed end of the tenon extension section along the height direction is 19mm, the width is 65mm, and the diameter of the positioning hole is 14mm.
[0041] The exhaust side of the working blade of the single crystal turbine is a closed channel, w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com