A block chain-based key management method, device and storage medium in CCN
A key management and blockchain technology, applied in the field of blockchain-based key management and computer-readable storage media, can solve problems such as excessive overhead, potential security risks, and malicious users, to ensure authenticity and integrity The effect of avoiding single point of failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
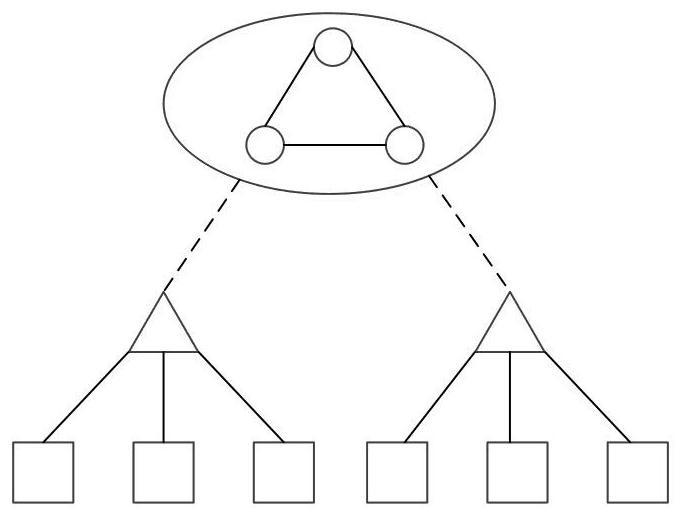
[0089] figure 1 The basic architecture of the blockchain-based key management system in the present invention is shown. refer to figure 1 , the system is divided into three layers from top to bottom, among which, the top layer (marked by the area surrounded by an oval) is the blockchain layer, which is composed of each independent trust domain administrator as a consensus node, which is used to store user A hash of the public key to guarantee the authenticity of the user's public key. The middle layer (marked by a triangle) is the user public key layer, which is used to verify the public key of the next layer; the bottom layer (marked by a square) is the device and application key layer.
[0090] In order to avoid a single point of failure, the present invention uses the blockchain composed of trust domain administrators as the starting point of trust, and each trust domain administrator serves as a consensus node. The blockchain is used to store the public key hashes of us...
Embodiment 2
[0152] refer to Figure 5 , which shows a flow chart of the steps of a blockchain-based key management method in a CCN of the present invention, which may specifically include:
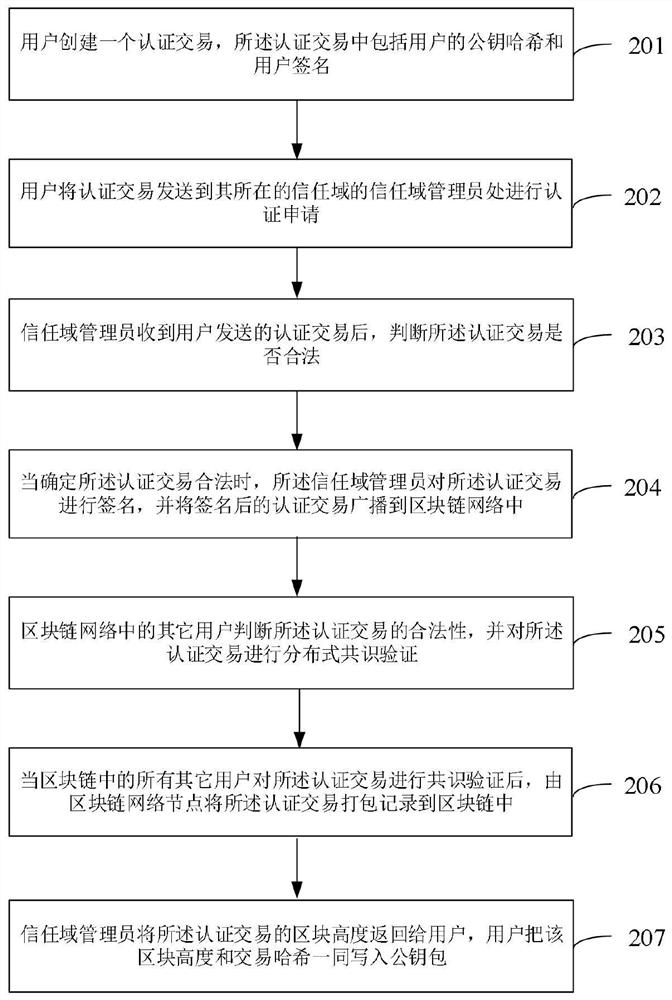
[0153] Step 501, the user creates an authentication transaction, which includes the user's public key hash and user signature;
[0154] Step 502, the user sends the authentication transaction to the trust domain administrator of the trust domain where the user is located to apply for authentication, wherein the user refers to an ordinary node in the trust domain;
[0155] Step 503, the user receives the block height of the authentication transaction sent by the trust domain administrator, and writes the block height and transaction hash together into a public key bag;
[0156] In an alternative embodiment of the present invention, refer to Figure 6 , the above method also includes the following steps:
[0157] Step 504, the user creates a revocation transaction, the revocation transa...
Embodiment 3
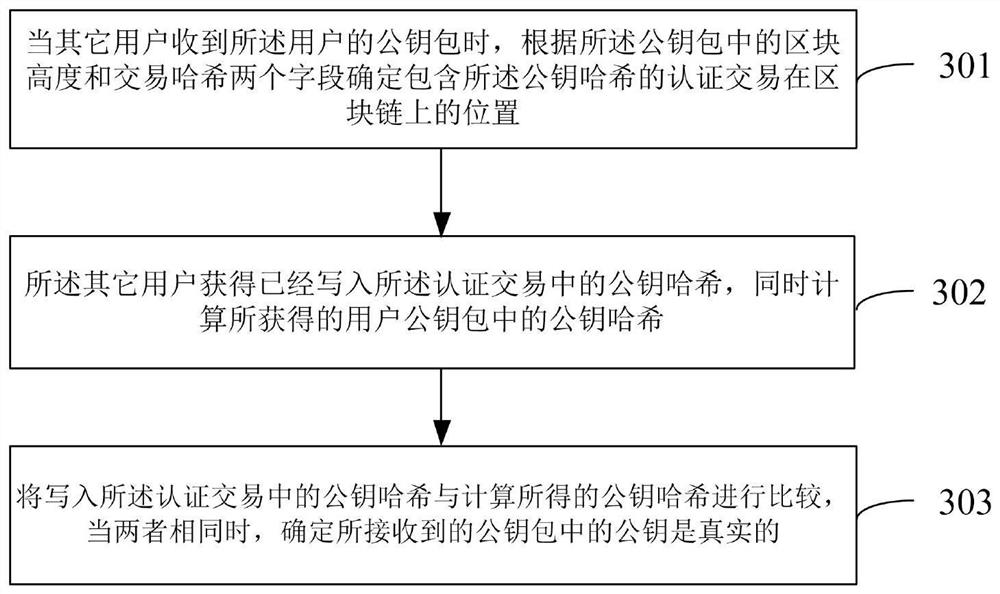
[0161] refer to Figure 7 , which shows a flow chart of the steps of a blockchain-based key management method in a CCN of the present invention, which may specifically include:
[0162] Step 701, the trust domain administrator receives the authentication transaction sent by the user;
[0163] Step 702, judging whether the authentication transaction is legal;
[0164] Specifically, the judging whether the authentication transaction is legal includes:
[0165] The trust domain administrator verifies the user signature in the authentication transaction, and judges whether the user is a legal user in the trust domain, and if so, determines that the authentication transaction is legal; if not, confirms that the authentication transaction is illegal.
[0166] Step 703, when it is determined that the authentication transaction is legal, the trust domain administrator signs the authentication transaction, and broadcasts the signed authentication transaction to the block...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com