An optimization method for blockchain anti-tampering technology
An optimization method and blockchain technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems such as application impact, destruction of ledger original data, and acquisition of historical transaction data by smart contracts, achieving high verification efficiency and fewer verification times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
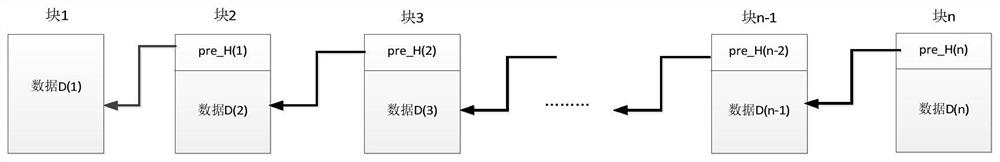
[0036] Suppose node A maintains a image 3 In the blockchain shown, each block is interconnected through the hash value of the previous block according to the timestamp T. There are currently n blocks, and the content of each block includes: the data D of the block and the previous block Hash pointer pre_H of the block.
[0037] The hash pointer on the blockchain can be simplified as:
[0038] pre_H(1)=hash(D(1))
[0039] pre_H(2)=hash(pre_H(1)||D(1))
[0040] ...
[0041] pre_H(n-2)=hash(pre_H(n-3)||D(n-2))
[0042] pre_H(n-1)=hash(pre_H(n-2)||D(n-1))
[0043] pre_H(n)=hash(pre_H(n-1)||D(n))
[0044] The anti-tampering detection mechanism is as follows:
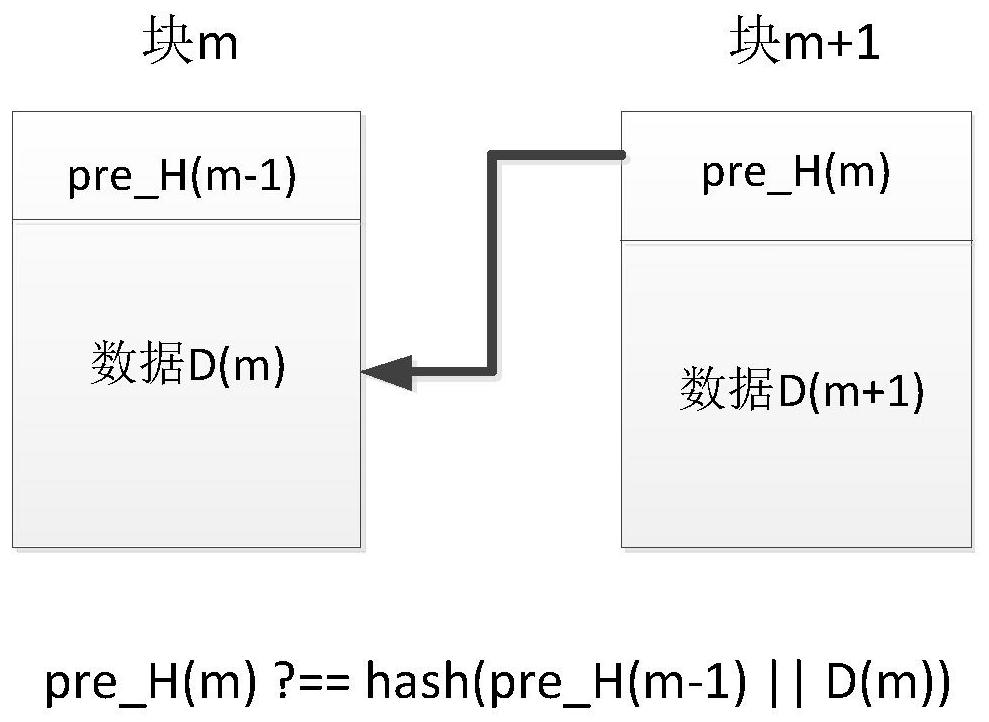
[0045] 1. Start the first detection, mainly to perform inter-block pre_H comparison detection on the entire blockchain, such as figure 1 As shown, if pre_H(m)=hash(pre_H(m-1)||D(m)), the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com