A point cloud splicing method for flat parts based on invariant features in multi-dimensional space
A multi-dimensional space, point cloud stitching technology, applied in image data processing, instruments, computing and other directions, can solve the problems of poor operational flexibility, less point cloud surface information, large equipment volume, etc., to achieve the effect of good robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
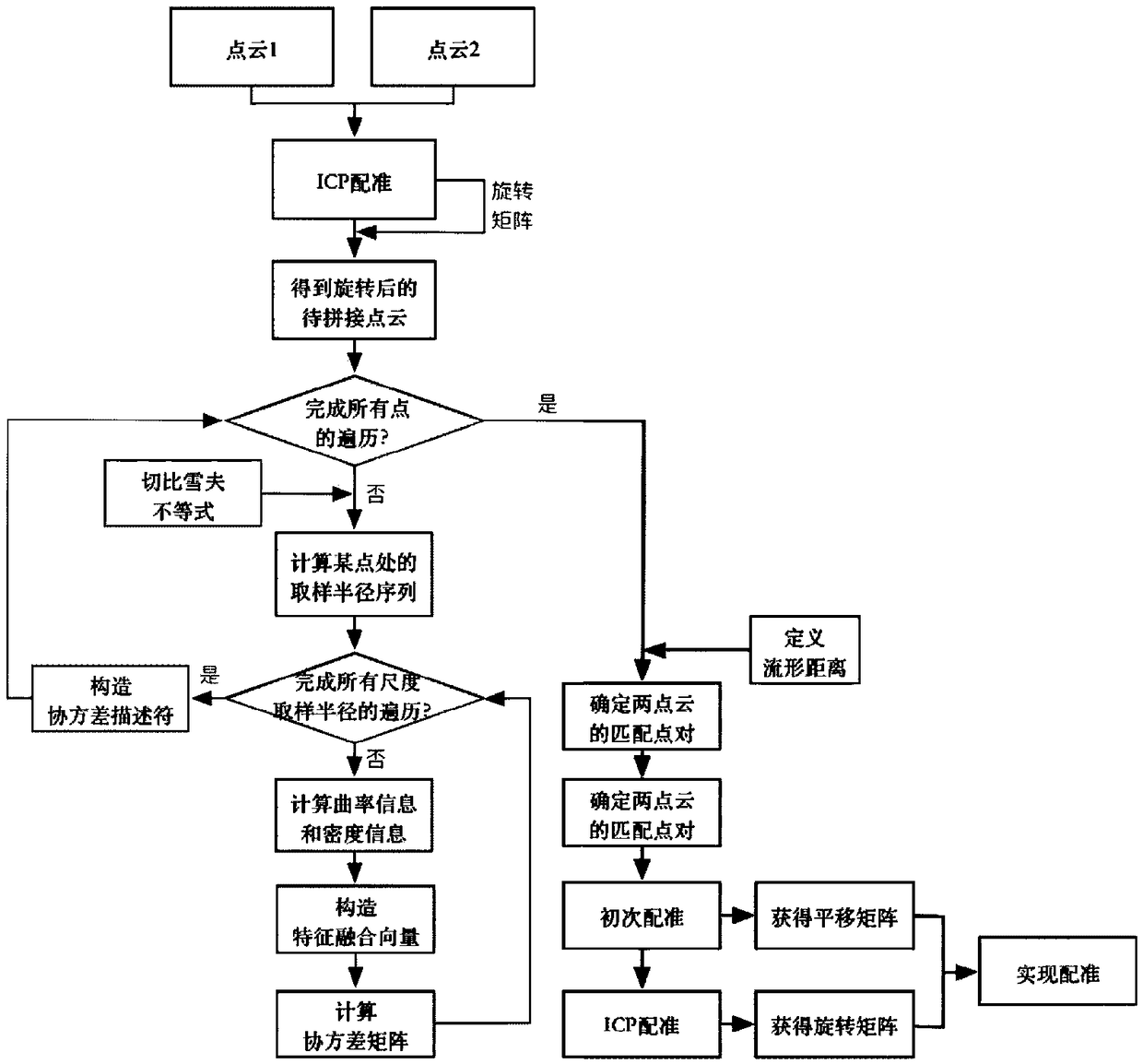
[0072] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with figures and examples.
[0073] For the point clouds to be spliced of two plate-shaped mechanical parts with hole features, the embodiment implemented according to the complete method of the present invention adopts the following steps to splice:
[0074] Step 1: Use the nearest neighbor iterative algorithm to calculate the point cloud rotation matrix, and use the rotation matrix to transform the spatial position of the point cloud to be stitched, and use the transformed point cloud to provide an initial value for subsequent stitching. Thus, two initial point clouds are obtained, one of which is the point cloud to be stitched after space transformation, and the other initial point cloud is another point cloud to be stitched without space transformation.
[0075] The rotation matrix R obtained in step 1 1 for:
[0076]
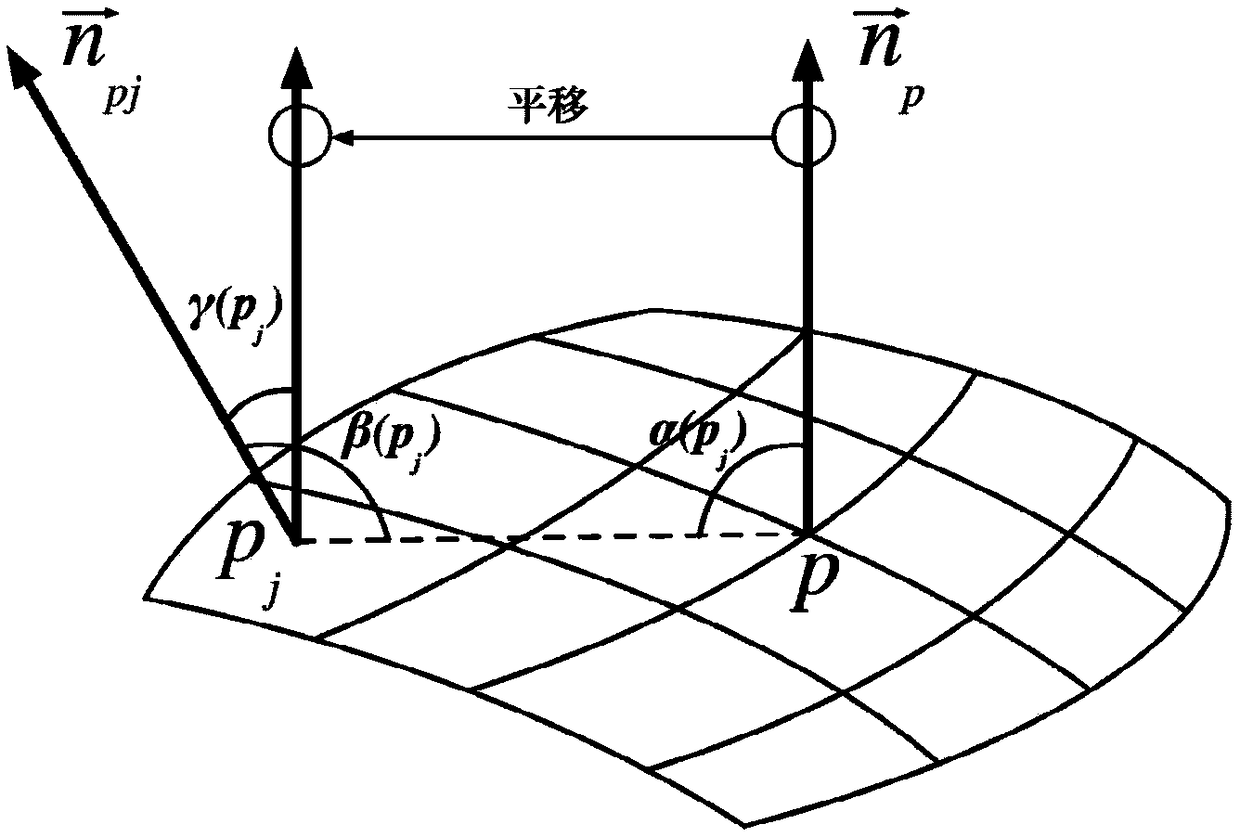
[0077] Step 2: According to Chebyshev's inequality, under the premise of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com