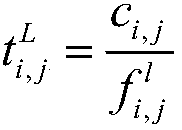MEC (Mobile Edge Computing)-based energy-sensing unloading energy delay compromise proposal under Internet of vehicles
An energy-sensing, car networking technology, applied in the field of computing offloading and resource allocation solutions based on mobile edge computing, which can solve the problems of limited computing resources of MEC servers, inability to offload tasks, and network interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
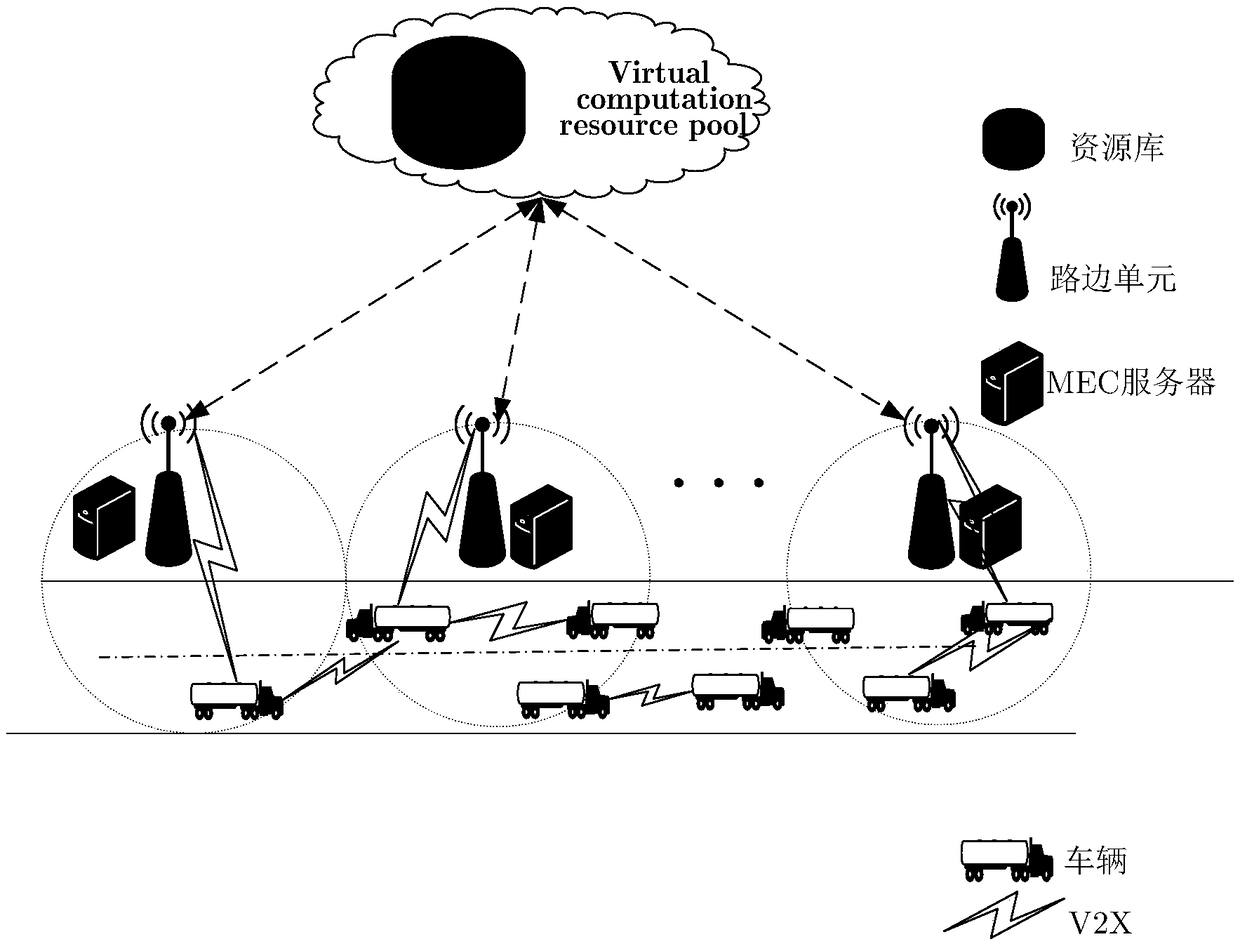
[0014] The task can be executed locally by the vehicle using its own resources, or it can be offloaded to the MEC server through the RSU in the form of V2I, or it can be offloaded to the surrounding vehicles in the form of V2V. the s i,j Denotes the unloading decision of vehicle i in cell j. If the vehicle offloads the task to the MEC server, s i,j = 1, otherwise, s i,j =0.
[0015] computing power per vehicle different, when the task τ i,j The computation execution time when computed locally is expressed as:
[0016]
[0017] The energy consumption performed locally by the vehicle can also be expressed as: where k=10 -26 is a coefficient that depends on the chip architecture, considering the Simultaneously affects computing time and energy consumption, and schedules CPU cycle frequency through dynamic voltage and power scaling techniques.
[0018] When the input data is transmitted to the MEC server through the base station, the transmission expenditure between...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com