A value-at-risk simulation dynamic task scheduling method based on collaborative computing
A technology of dynamic tasks and scheduling methods, applied in the field of high-performance computing, can solve problems such as low utilization of computing resources and uneven task distribution, and achieve the effect of maximizing computing efficiency and realizing dynamic load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
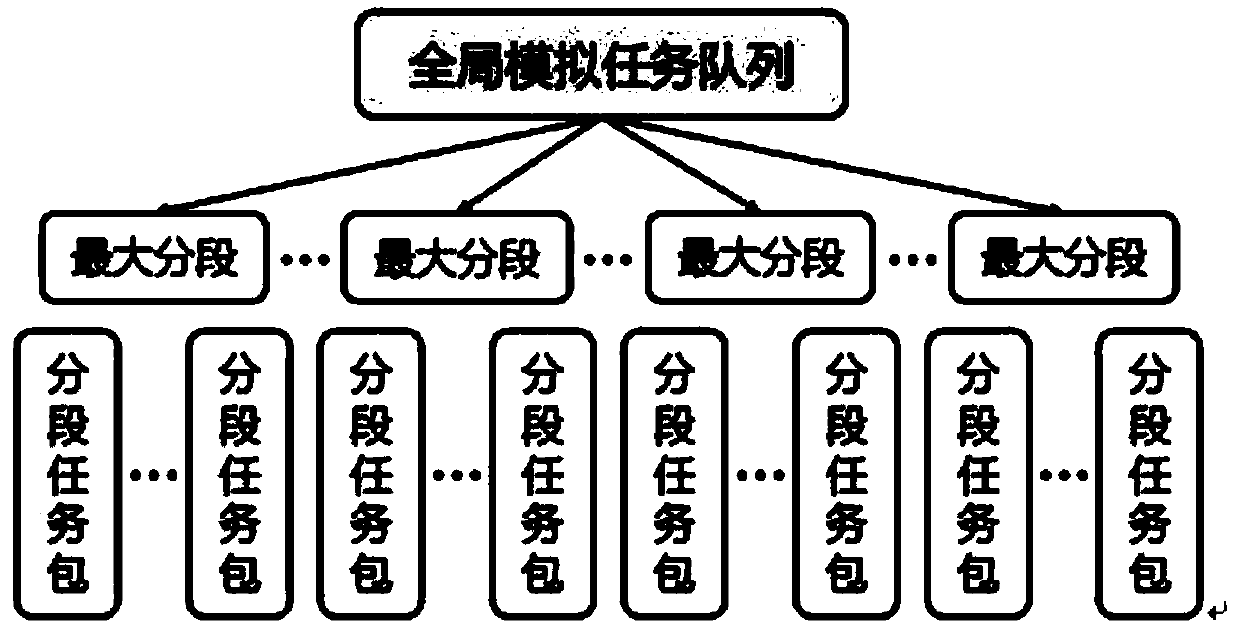
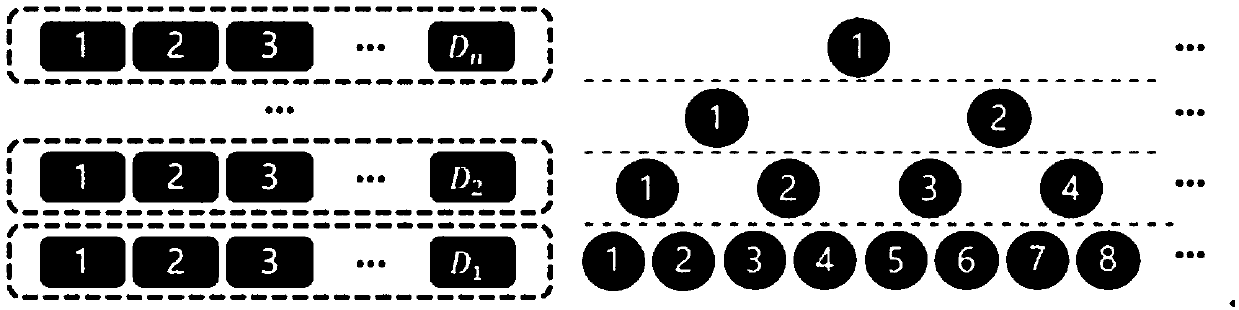
[0053] Now it is set that a value-at-risk Monte Carlo simulation is expected to produce 1 million simulation results, and the median value is taken as the simulation result. One computing unit of the computing platform used contains 1 CPU and 3 MICs, and the number of MIC cores is 61. At this point, the estimated total number of simulations N 0 =1000000, the value order α=0.5, the standard size P of the segmented task package D =2×61=122, the maximum number of segments
[0054]
[0055] When the task starts, the computing node generates a global simulation task queue, which contains 1024 maximum segments, and the number of segment task packets for each segment is
[0056]
[0057] then the actual number of simulations
[0058] N=N P ×N D ×P D =999424
[0059] loss rate
[0060]
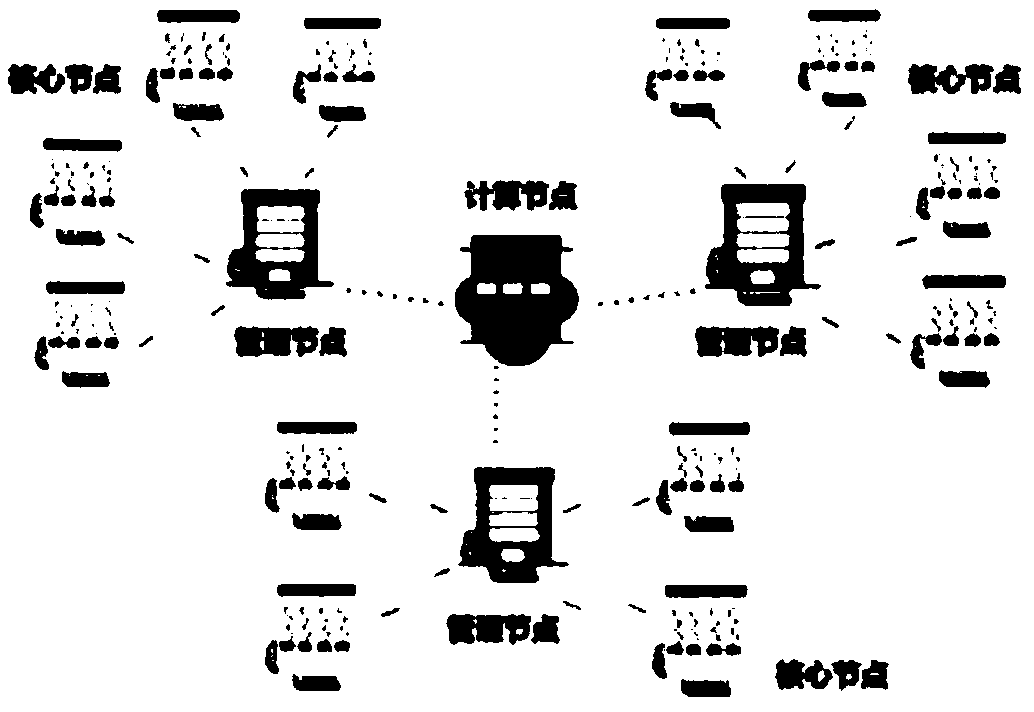
[0061] Assume that the computing framework is actually composed of 1 computing node, each computing node has 8 management nodes, and each management node has 8 core nodes. The specif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com